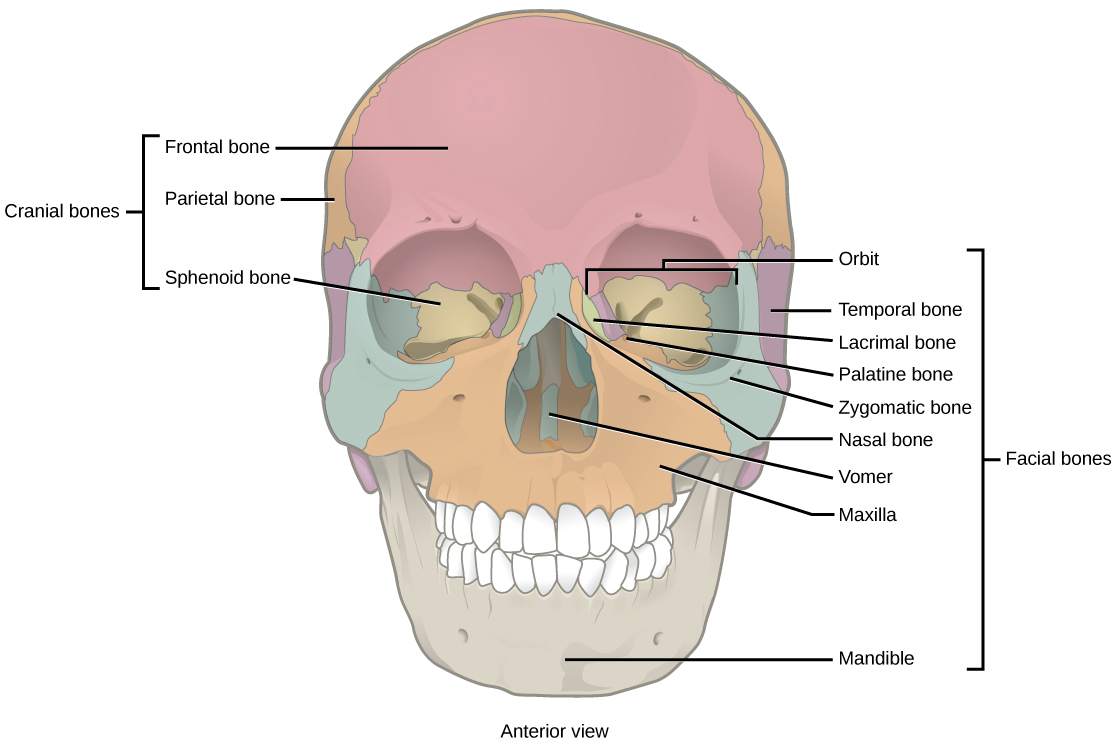
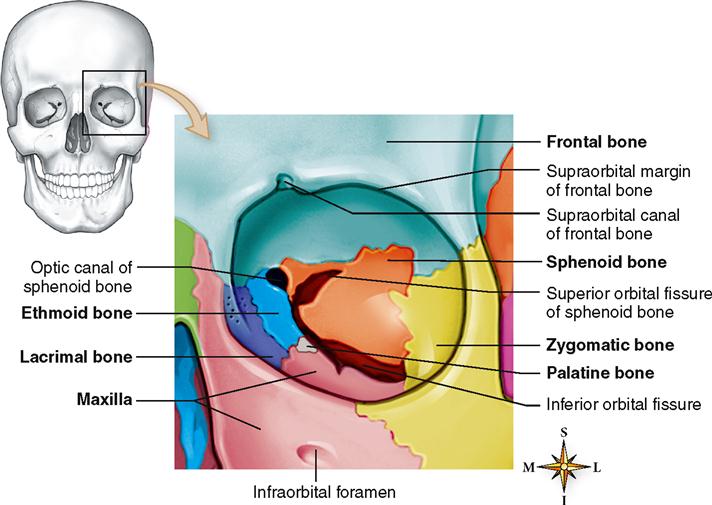
Bones That Form The Orbit
Bones That Form The Orbit - The entrance to the globe anteriorly is approximately 35 mm high and 45 mm wide. The lateral wall comprises the greater wing of the sphenoid bone and zygomatic bone. Formed by the greater wing of the sphenoid bone and the zygomatic bone. Web the following seven bones form the orbit: What is the function of the orbit? Zygomatic process of the maxilla and the zygomatic bone zygomatic process of the. Yellow = frontal bone green = lacrimal bone brown = ethmoid bone blue = zygomatic bone purple = maxillary bone aqua = palatine bone red = sphenoid bone teal = nasal bone (illustrated but not part of the orbit) Web bones of the orbit and some of the major landmarks. Formed by the lesser wing of the sphenoid and the frontal bone. Though small, the orbital bones are quite strong to protect the eye inside the head.
Seven bones conjoin to form the. Web the orbit is the bony cavity in the skull that houses the globe of the eye (eyeball), the muscles that move the eye (the extraocular muscles), the lacrimal gland, and the blood vessels and nerves required to supply these structures. Pars orbitalis of the frontal bone lacrimal bone lamina papyracea of the ethmoid bone orbital process of the zygomatic bone orbital surface of the maxillary bone orbital process of the palatine bone greater and lesser wings and body of the sphenoid bone The orbit is made up of portions of both the cranial and the facial skeletal systems. Web seven bones form each orbit: Though small, the orbital bones are quite strong to protect the eye inside the head. The paired bones are the maxilla, palatine, zygomatic, nasal, lacrimal, and inferior nasal conchae bones. Optic foramen orbital margin (rim): Frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid four facial bones: Formed by the greater wing of the sphenoid bone and the zygomatic bone.
The orbital roof is formed by the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. Web the orbit is the bony cavity in the skull that houses the globe of the eye (eyeball), the muscles that move the eye (the extraocular muscles), the lacrimal gland, and the blood vessels and nerves required to supply these structures. Web there are seven orbital bones that make up this structure: The facial bones include 14 bones, with six paired bones and two unpaired bones. The orbit is made up of portions of both the cranial and the facial skeletal systems. The path of a celestial body or an artificial satellite as it revolves around another body due to their mutual gravitational attraction. Yellow = frontal bone green = lacrimal bone brown = ethmoid bone blue = zygomatic bone purple = maxillary bone aqua = palatine bone red = sphenoid bone teal = nasal bone (illustrated but not part of the orbit) Frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid four facial bones: Web the seven bones that form the orbit: Optic foramen orbital margin (rim):
Orbital Bone Anatomy Human Anatomy Diagram Medical anatomy, Human
Web start studying bones that form the orbit part 1. Formed by the lesser wing of the sphenoid and the frontal bone. Though small, the orbital bones are quite strong to protect the eye inside the head. It is our job as ophthalmologists to be able to readily identify these bones and know pretty much every bump, notch, hole, and.
Bones That Form The Orbit / Orbital Bones Ophthalmology Review
Web seven bones form each orbit: Frontal, sphenoid, maxillary, zygomatic, palatine, ethmoid, and lacrimal. It is our job as ophthalmologists to be able to readily identify these bones and know pretty much every bump, notch, hole, and contour of these bones and what structures pass through, travel along, and attach to these bones. Lesser wing of the sphenoid bone. They.
Bones of orbit lateral wall Human anatomy and physiology, Human
Bones, muscles, arteries, veins and nerves. It is our job as ophthalmologists to be able to readily identify these bones and know pretty much every bump, notch, hole, and contour of these bones and what structures pass through, travel along, and attach to these bones. Web seven bones form each orbit: Frontal, ethmoid, palatine, lacrimal, maxilla, zygomatic, and sphenoid. Web.
20 best Ophtho images on Pinterest Anatomy, Anatomy reference and
Web there are 7 bones that comprise the orbit. Pars orbitalis of the frontal bone lacrimal bone lamina papyracea of the ethmoid bone orbital process of the zygomatic bone orbital surface of the maxillary bone orbital process of the palatine bone greater and lesser wings and body of the sphenoid bone What is the function of the orbit? Web the.
19.1 Types of Skeletal Systems Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Web seven bones form each orbit: What is the function of the orbit? There are 7 bones that form the orbit: Bones of the orbit synonyms, bones of the orbit pronunciation, bones of the orbit translation, english dictionary definition of bones of the orbit. Seven bones conjoin to form the.
Skeletal System Basicmedical Key
It is our job as ophthalmologists to be able to readily identify these bones and know pretty much every bump, notch, hole, and contour of these bones and what structures pass through, travel along, and attach to these bones. The orbit is made up of portions of both the cranial and the facial skeletal systems. Web names of the bones.
Bones of the orbit Human anatomy and physiology, Anatomy, Orbit anatomy
Web names of the bones of the orbit with basic anatomy 7 of the cranial and facial bones contribute to the formation of the orbital cavities, with 3 being cranial bones and the other 4 being facial bones: Web the bony orbits (or eye sockets) are bilateral and symmetrical cavities in the head. The paired bones are the maxilla, palatine,.
Anatomy bones, Orbit anatomy, Anatomy
The orbital roof is formed by the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone and the frontal bone. Yellow = frontal bone green = lacrimal bone brown = ethmoid bone blue = zygomatic bone purple = maxillary bone aqua = palatine bone red = sphenoid bone teal = nasal bone (illustrated but not part of the orbit) The sphenoid and ethmoid.
The Bony Orbit Borders Contents Fractures TeachMeAnatomy
In this article, we shall look at the borders, contents and clinical correlations of. Yellow = frontal bone green = lacrimal bone brown = ethmoid bone blue = zygomatic bone purple = maxillary bone aqua = palatine bone red = sphenoid bone teal = nasal bone (illustrated but not part of the orbit) Zygomatic process of the maxilla and the.
bones that form the orbit Diagram Quizlet
Web the orbit is the bony cavity in the skull that houses the globe of the eye (eyeball), the muscles that move the eye (the extraocular muscles), the lacrimal gland, and the blood vessels and nerves required to supply these structures. The path of a celestial body or an artificial satellite as it revolves around another body due to their.
Zygomatic Process Of The Maxilla And The Zygomatic Bone Zygomatic Process Of The.
It is our job as ophthalmologists to be able to readily identify these bones and know pretty much every bump, notch, hole, and contour of these bones and what structures pass through, travel along, and attach to these bones. Web the facial bones of the skull form the upper and lower jaws, the nose, nasal cavity and nasal septum, and the orbit. Yellow = frontal bone green = lacrimal bone brown = ethmoid bone blue = zygomatic bone purple = maxillary bone aqua = palatine bone red = sphenoid bone teal = nasal bone (illustrated but not part of the orbit) What is the function of the orbit?
Though Small, The Orbital Bones Are Quite Strong To Protect The Eye Inside The Head.
Web there are 7 bones that comprise the orbit. The orbit is made up of portions of both the cranial and the facial skeletal systems. Web seven bones form each orbit: Frontal, ethmoid, palatine, lacrimal, maxilla, zygomatic, and sphenoid.
Maxilla, Frontal Bone, Zygomatic Bone, Ethmoid Bone, Lacrimal Bone, Sphenoid Bone, And Palatine Bone.
Web the following seven bones form the orbit: Orbital plate of the frontal bone. Seven bones conjoin to form the. Web seven bones form each orbit:
Web The Orbit Is The Bony Cavity In The Skull That Houses The Globe Of The Eye (Eyeball), The Muscles That Move The Eye (The Extraocular Muscles), The Lacrimal Gland, And The Blood Vessels And Nerves Required To Supply These Structures.
Each of these plays a role in keeping the eyeball protected. There are 7 bones that form the orbit: They enclose the eyeball and its associated structures. The entrance to the globe anteriorly is approximately 35 mm high and 45 mm wide.