Cartilage Drawing
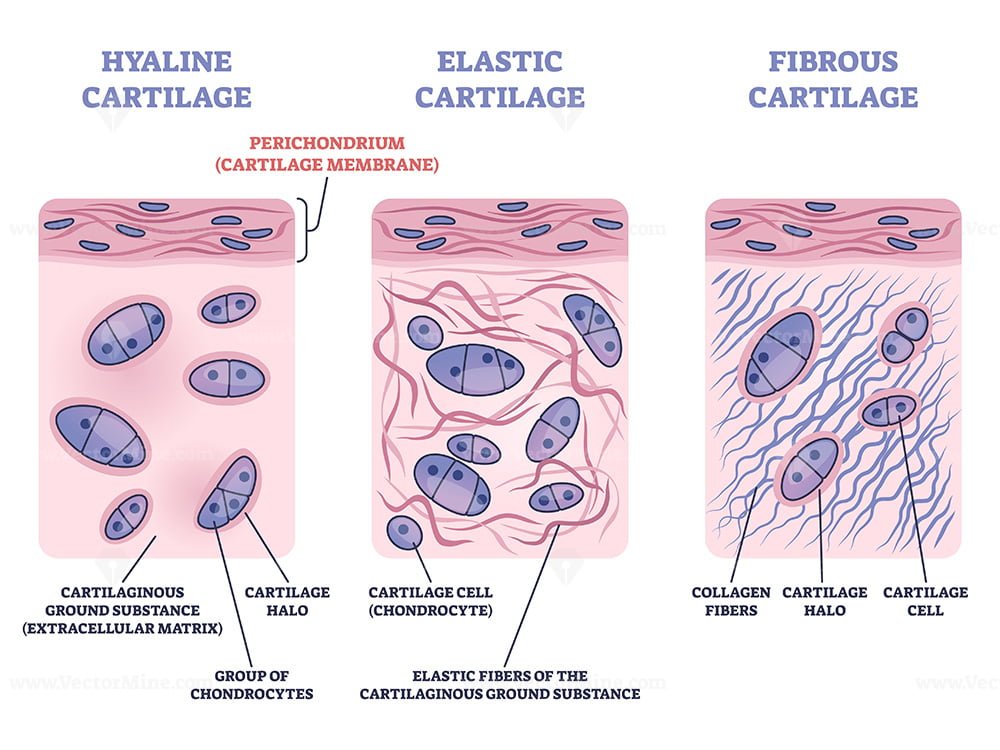
Cartilage Drawing - Web matrix of hyaline structure. Cartilage tissue is avascular and therefore relies on obtaining its nutrients via diffusion, sometimes even over large distances. Web elastic cartilage, sometimes referred to as yellow fibrocartilage, is a type of cartilage that provides both strength and elasticity to certain parts of the body, such as the ears. Loss of cartilage function may lead to a painful joint with a decreased mobility. Web cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in multiple areas of the body, including joints, the ear and nose, and intervertebral discs. Ear pinna, aldehyde fuchsin and masson, 20x (elastic cartilage). Web chapter 1 cartilage morphology. Step by step drawing of elastic cartilage how to draw elastic cartilage, histology journal.more. A type of cartilage that is characteristically glossy and smooth in appearance, and with interstitial substance containing fine type ii collagen fibres obscured by the ground substance. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright.
Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage serves as temporary cartilage models that are essential precursors to the formation of most of the axial and appendicular skeleton. Decreases friction and distributes loads. Its principal function is to provide a smooth, lubricated surface for articulation and to facilitate the transmission of loads with a low frictional coefficient ( figure 1 ). Step by step drawing of elastic cartilage how to draw elastic cartilage, histology journal.more. This article will focus on important features of hyaline cartilage, namely its matrix, chondrocytes, and perichondrium. Intervertebral disc, h&e, 40x (fibrocartilage and dense irregular connective tissue, nucleus pulposus). During pregnancy and early childhood, much of the skeleton ossifies, or is Web elastic cartilage, sometimes referred to as yellow fibrocartilage, is a type of cartilage that provides both strength and elasticity to certain parts of the body, such as the ears. Web chapter 1 cartilage morphology. Web matrix of hyaline structure.
Cartilage is a dense structure, that resembles a firm gel, made up of collagen and elastic fibres. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each isogenous group and is high in glycosaminoglycans. Ac is a dense connective tissue mainly comprised of collagen, proteoglycans, organized in special zones containing special types of cells called articular chondrocytes [ 1, 2 ]. Cartilage is a connective tissue composed of chondrocytes (cells) that produce long proteins called fibers, and smaller molecules such as glycoproteins that are collectively referred to as ground substance. Web hyaline cartilage is the most abundant type of cartilage in the body. The four groups were evaluated by assessing tissue regeneration within the defect. 2.9k views 4 years ago vadnagar. A type of cartilage that is characteristically glossy and smooth in appearance, and with interstitial substance containing fine type ii collagen fibres obscured by the ground substance. Web elastic cartilage histology labeled diagram and drawing. Cartilage occurs where flexibility is required, while bone resists deformation.
Perichondrium as hyaline and elastic cartilage membrane outline diagram
First, i would like to point out the essential histological features from the hyaline cartilage histology slide under the light microscope. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each isogenous group and is high in glycosaminoglycans. First, you should know the important structures of elastic cartilage that you might identify under the light compound microscope. Intervertebral disc, h&e, 40x (fibrocartilage and dense.
Cartilage and Bone Elastic Cartilage A hand drawn sketch … Flickr
Cartilage tissue is avascular and therefore relies on obtaining its nutrients via diffusion, sometimes even over large distances. This article will focus on important features of hyaline cartilage, namely its matrix, chondrocytes, and perichondrium. The fibers provide tensile strength. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each isogenous group and is high in glycosaminoglycans. Web cartilage, bone and bone development.
Schematic drawing of the locations of measurement of cartilage
2.9k views 4 years ago vadnagar. Hyaline cartilage provides support and flexibility to different parts of the body. Therefore, this matrix stains more intensely than matrix farther from an isogenous group, the interterritorial matrix. Hyaline cartilage, the most abundant type of cartilage, plays a supportive role and assists in movement. Decreases friction and distributes loads.
Cartilage Definition, Function and Types Biology Dictionary
Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage serves as temporary cartilage models that are essential precursors to the formation of most of the axial and appendicular skeleton. A type of cartilage that is characteristically glossy and smooth in appearance, and with interstitial substance containing fine type ii collagen fibres obscured by the ground substance. The four groups were evaluated by assessing.
How to Draw Hyaline Cartilage Simple and easy steps Biology Exam
There are 3 types of cartilage: Cartilage and bone are specialized connective tissues that provide support to other tissues and organs. Therefore, this matrix stains more intensely than matrix farther from an isogenous group, the interterritorial matrix. Cartilage occurs where flexibility is required, while bone resists deformation. Epiglottis, h&e, 20x (elastic cartilage).
Cartilage My Family Physio
Cartilage is a dense structure, that resembles a firm gel, made up of collagen and elastic fibres. Ac is a dense connective tissue mainly comprised of collagen, proteoglycans, organized in special zones containing special types of cells called articular chondrocytes [ 1, 2 ]. It contains polysacchride derivaites called chondroitin sulfates which complex with protein in the ground substance forming.
Cartilage Basic Science Orthobullets
Step by step drawing of histology of hyaline cartilage There are 3 types of cartilage: Within the outer ear , it provides the skeletal basis of the pinna, as well as the lateral region of the external auditory meatus. This article will focus on important features of hyaline cartilage, namely its matrix, chondrocytes, and perichondrium. Cartilage is a dense structure,.
types of cartilage front view skeleton Cartilage, Hyaline cartilage, Body
Loss of cartilage function may lead to a painful joint with a decreased mobility. Cartilage tissue is avascular and therefore relies on obtaining its nutrients via diffusion, sometimes even over large distances. During pregnancy and early childhood, much of the skeleton ossifies, or is A fetal skeleton begins entirely as cartilage. Isogenous groups and interstitial growth results when chondrocytes divide.
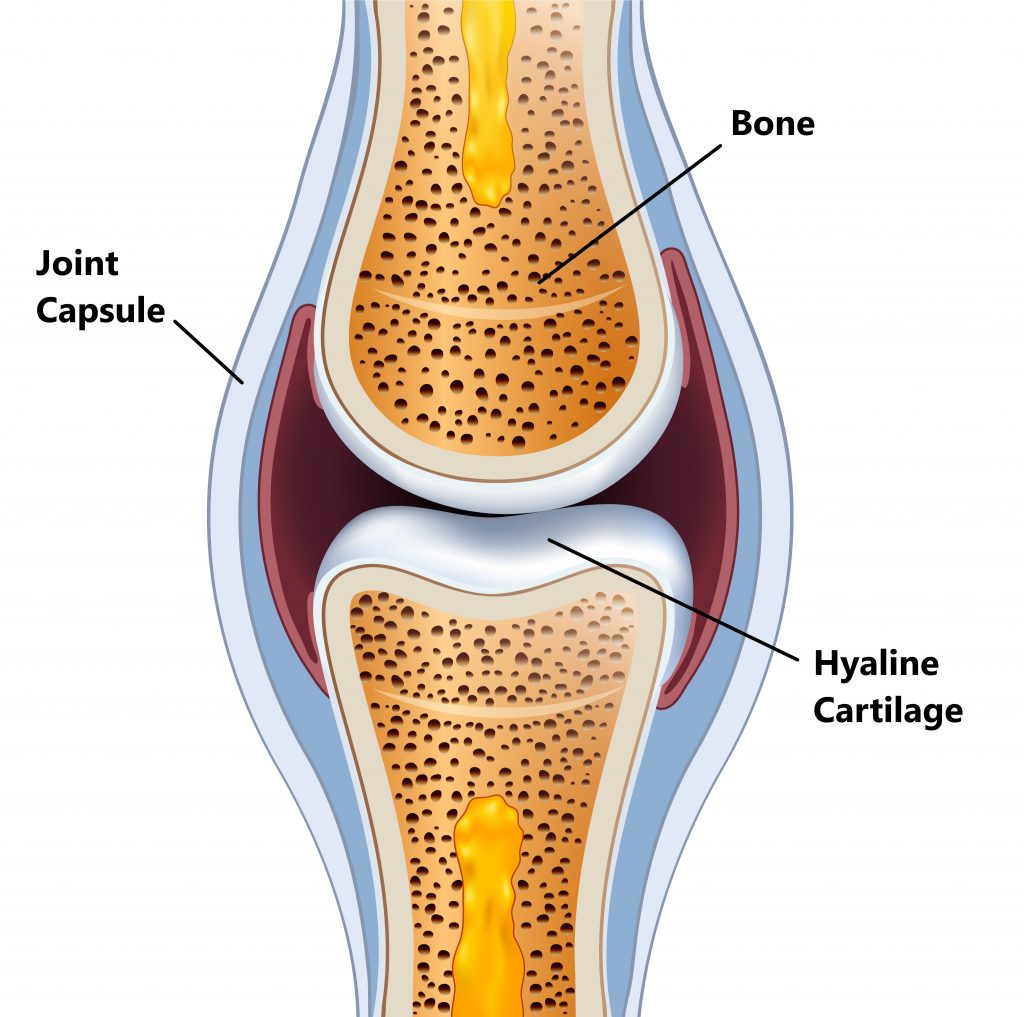
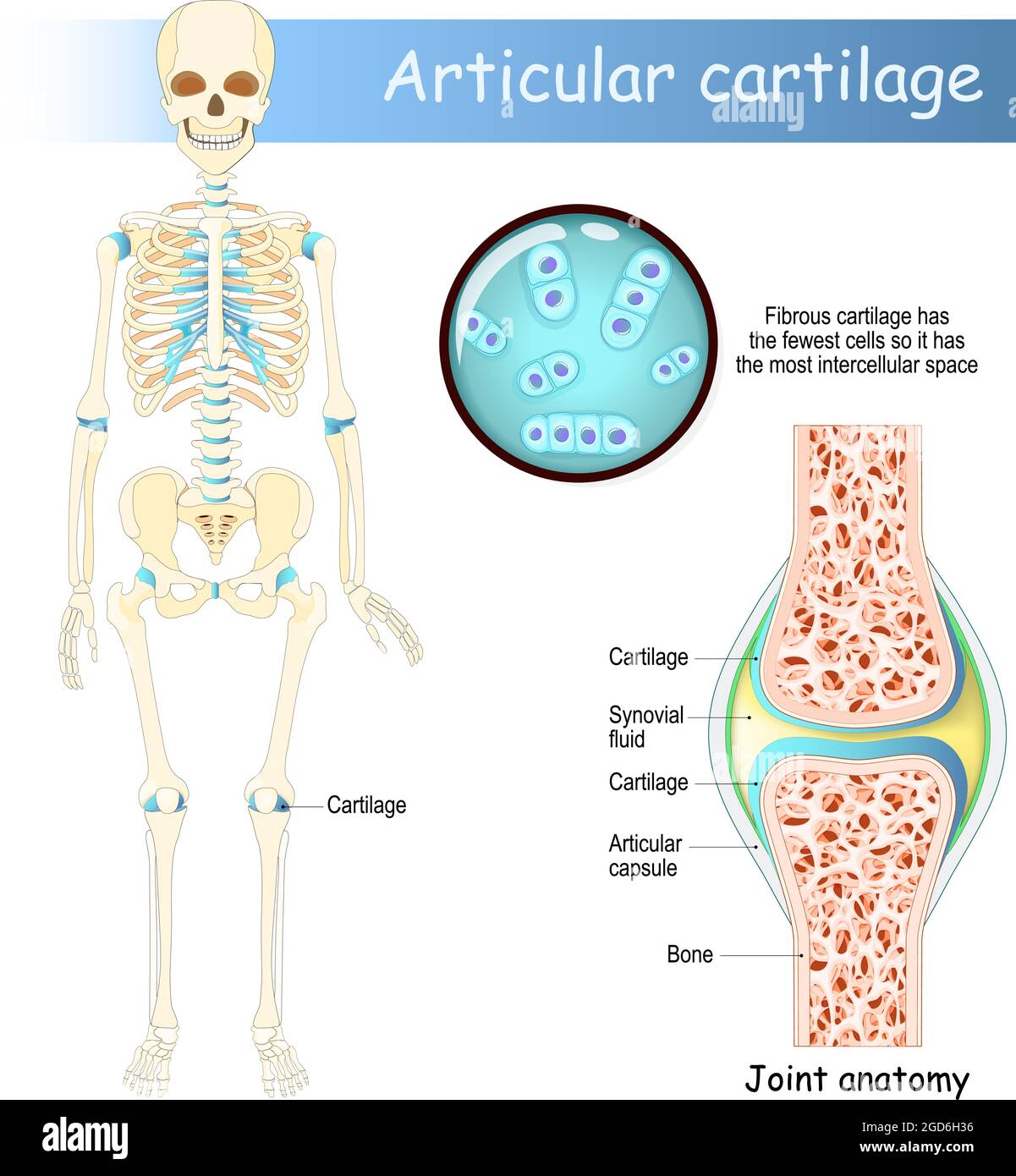
Cartilage. Human skeleton with articular cartilage. Joint anatomy
The fibers provide tensile strength. Web matrix of hyaline structure. Hyaline cartilage provides support and flexibility to different parts of the body. Hyaline cartilage, the most abundant type of cartilage, plays a supportive role and assists in movement. Hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage.
Pictures Of Cartilage
Step by step drawing of histology of hyaline cartilage Ear pinna, aldehyde fuchsin and masson, 20x (elastic cartilage). Hyaline cartilage is high in collagen, a protein that is found not only in connective tissue but also in skin and bones, and helps hold the body together. Web elastic cartilage, sometimes referred to as yellow fibrocartilage, is a type of cartilage.
Cartilage Repair Was Evaluated At Different Time Points Using Mri (Fig.
Web elastic cartilage, sometimes referred to as yellow fibrocartilage, is a type of cartilage that provides both strength and elasticity to certain parts of the body, such as the ears. Ear pinna, aldehyde fuchsin and masson, 20x (elastic cartilage). Web articular cartilage is the highly specialized connective tissue of diarthrodial joints. 2.9k views 4 years ago vadnagar.
Its Principal Function Is To Provide A Smooth, Lubricated Surface For Articulation And To Facilitate The Transmission Of Loads With A Low Frictional Coefficient ( Figure 1 ).
Ac is a dense connective tissue mainly comprised of collagen, proteoglycans, organized in special zones containing special types of cells called articular chondrocytes [ 1, 2 ]. Step by step drawing of histology of hyaline cartilage The fibers provide tensile strength. Web elastic cartilage histology labeled diagram and drawing.
Web Chapter 1 Cartilage Morphology.
Epiglottis, h&e, 20x (elastic cartilage). Loss of cartilage function may lead to a painful joint with a decreased mobility. There are 3 types of cartilage: Territorial matrix lies immediately around each isogenous group and is high in glycosaminoglycans.
Therefore, This Matrix Stains More Intensely Than Matrix Farther From An Isogenous Group, The Interterritorial Matrix.
Web hyaline cartilage is the most abundant type of cartilage in the body. A fetal skeleton begins entirely as cartilage. Hyaline cartilage is high in collagen, a protein that is found not only in connective tissue but also in skin and bones, and helps hold the body together. Cartilage occurs where flexibility is required, while bone resists deformation.