Cell Membrane Drawing Labeled
Cell Membrane Drawing Labeled - A sugar or choline, meaning that the head end of the phospholipid is. As a comparison, human red blood cells, visible via light microscopy, are approximately 8 μm thick, or approximately 1,000 times thicker than a plasma membrane. It is a selectively permeable cell organelle,allowing certain substances inside the cell while preventing others to pass through and thus is analogous to a barrier or gatekeeper. Points to the interior or inside. Controls movement of substances into/out of cell. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. I n the early stages of human embryonic development, a zygote divides into two identical totipotent. It's a complex, highly organized unit, the basic building block of all living things. Web essential biological functionsimmune response, cell metabolism, neurotransmission, photosynthesis, cell adherence, cell growth and differentiationpotential commercial applicationsdrug response monitoring, chemical manufacturing, biosensing, energy conversion, tissue engineering. A plasma membrane encloses the cell contents of both plant and animal cells, but it is the outer coating of an animal cell.
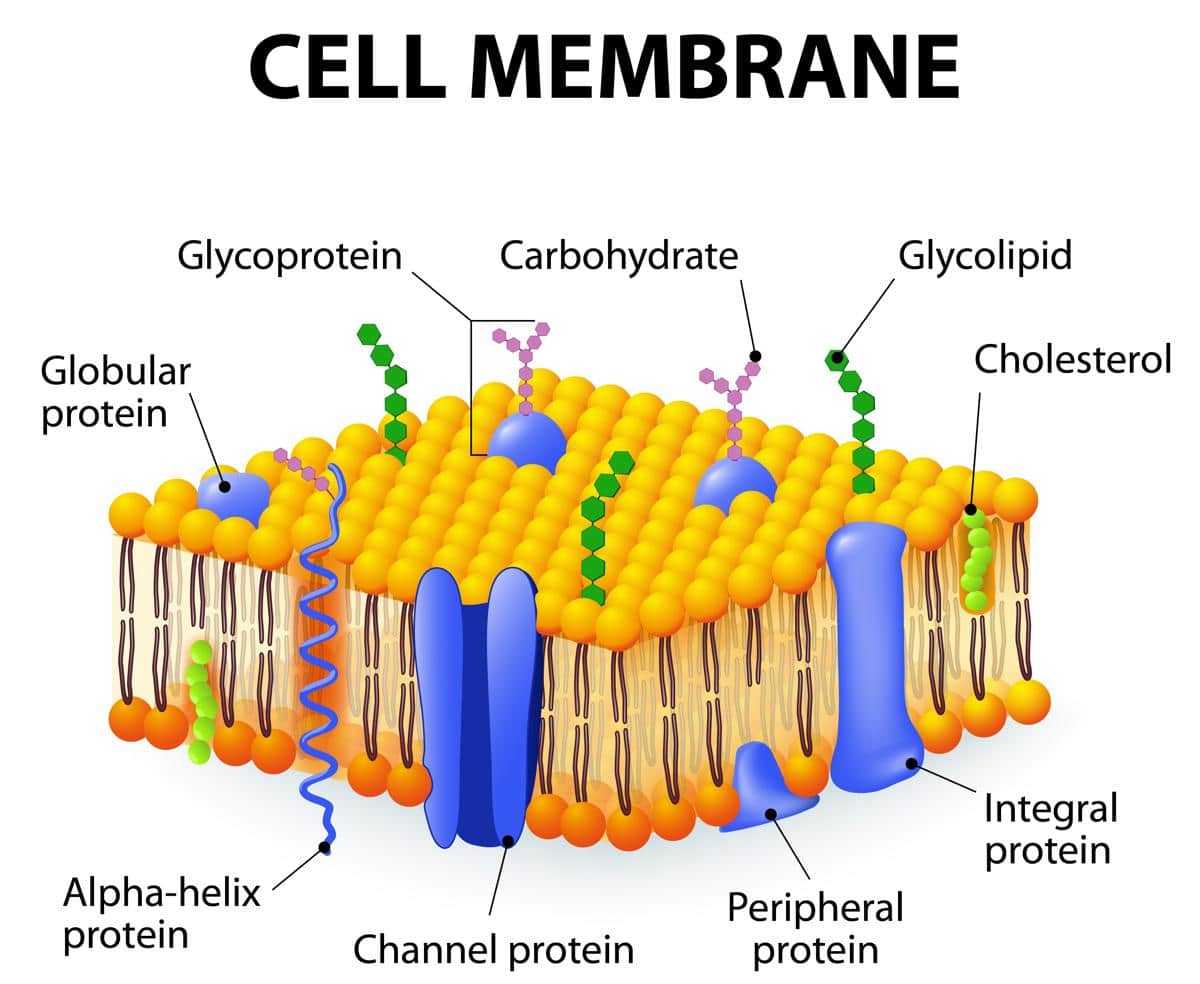
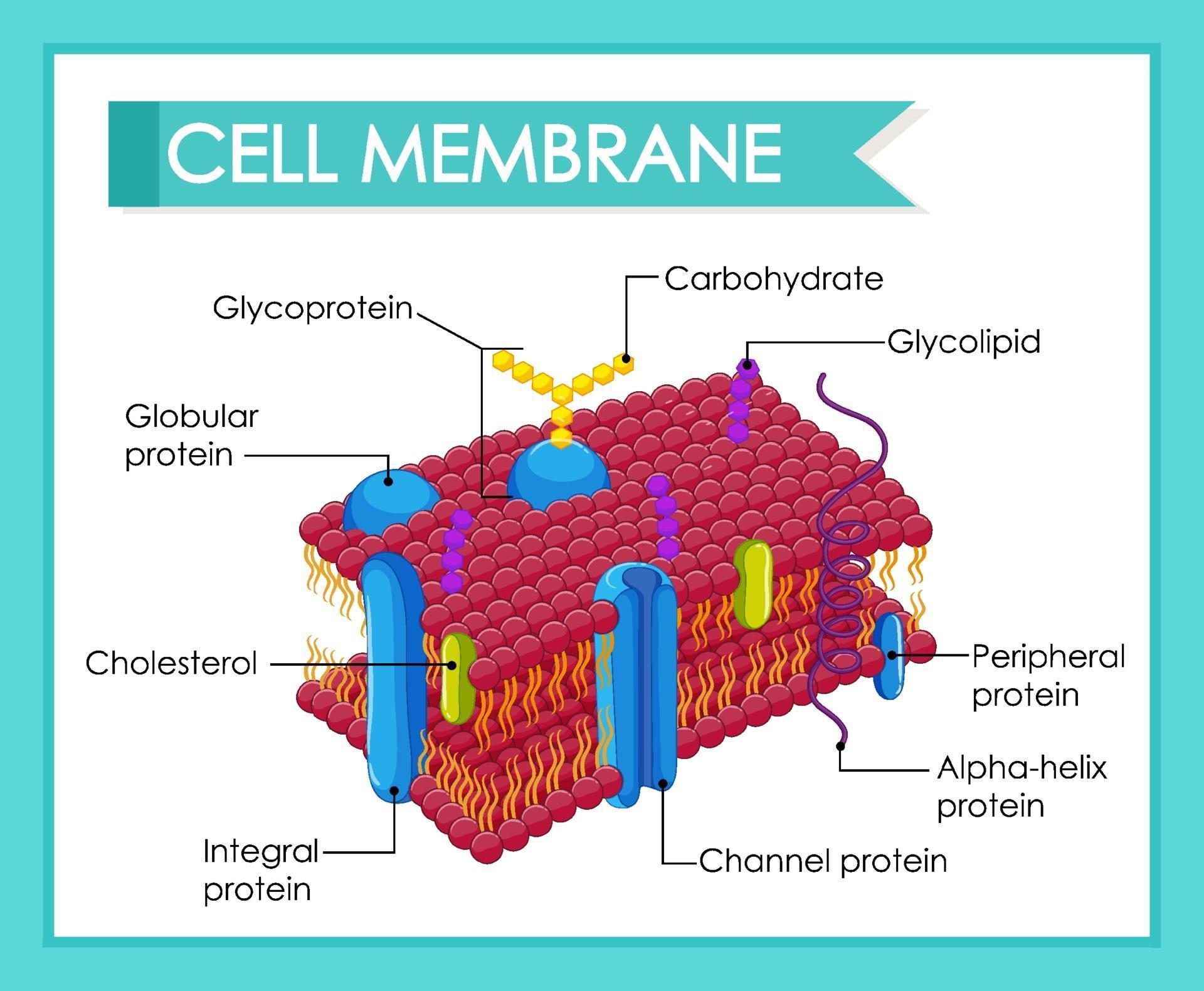
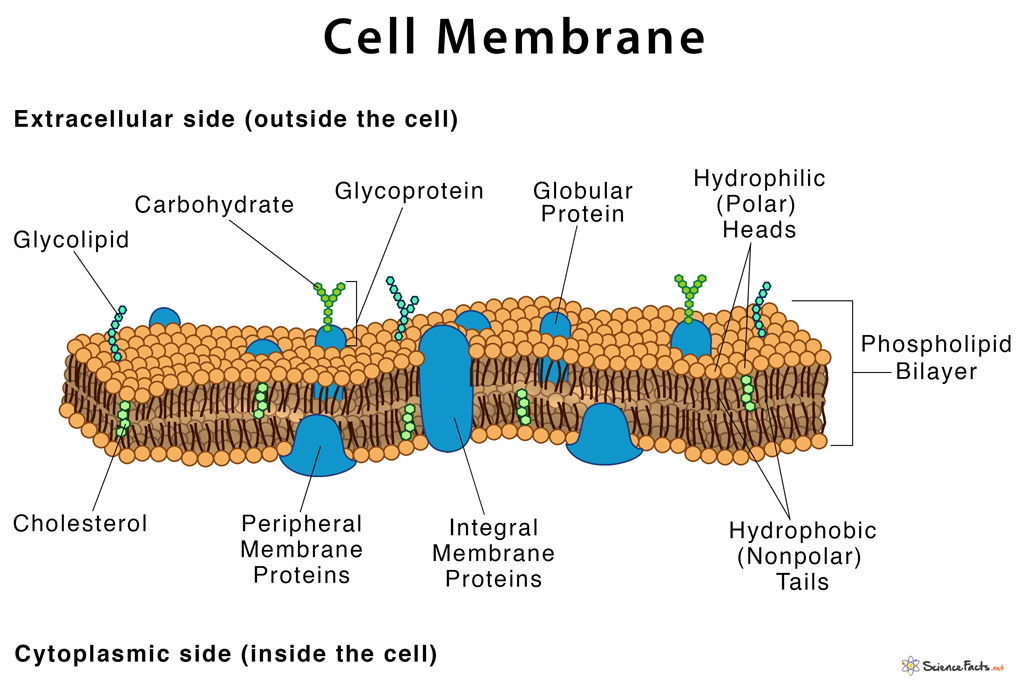
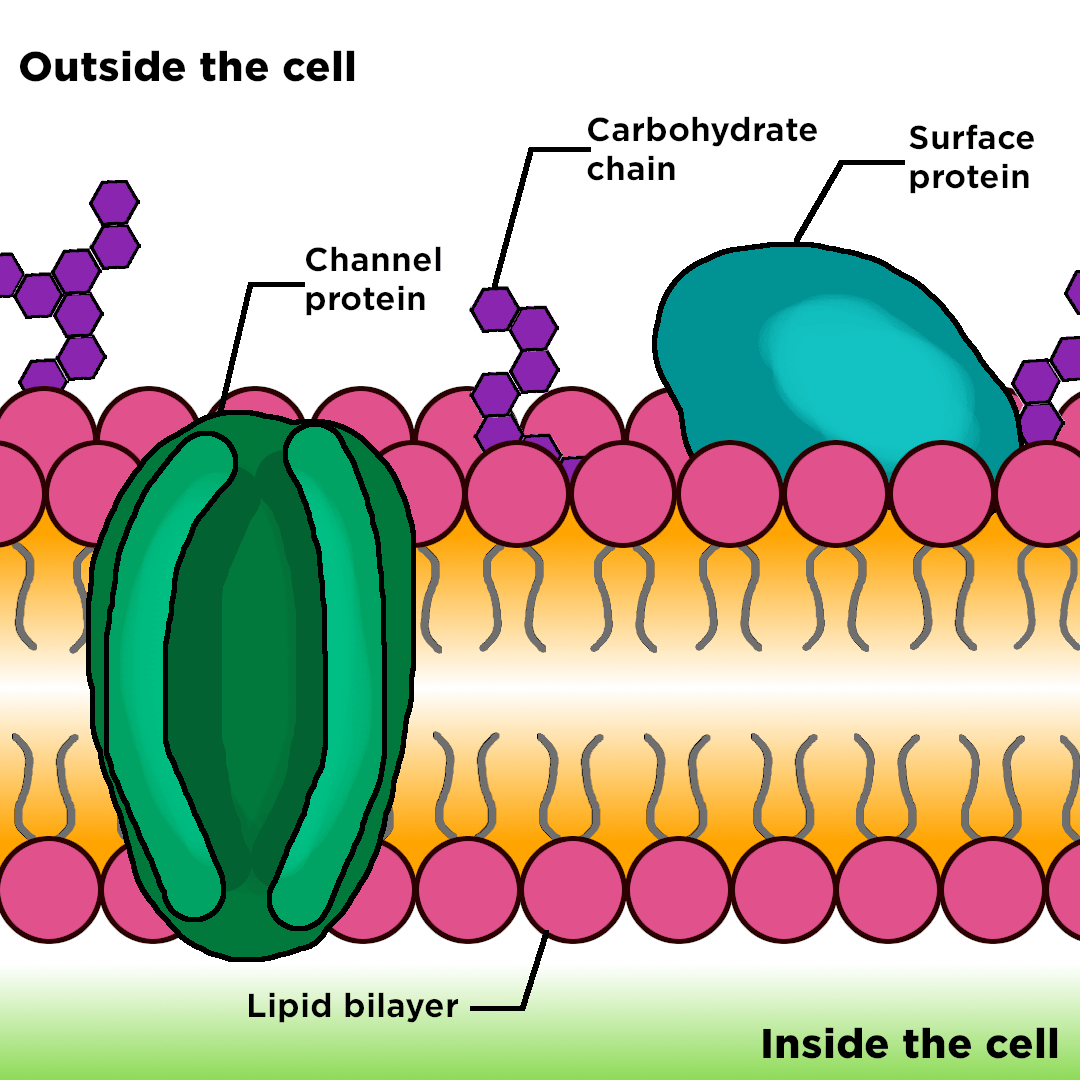
Web the cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Web like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. One of the proteins is shown with a channel in it. It was based on the plasma membrane’s “railroad track” appearance in early electron micrographs. It's a complex, highly organized unit, the basic building block of all living things. Structure, parts, functions, labeled diagram. First, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and, second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products. It is also simply called the cell membrane. The outermost part of the cell, which is shown as an outline of the cell, is labeled cell membrane.
It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. Points to the interior or inside. It was based on the plasma membrane’s “railroad track” appearance in early electron micrographs. Web like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. It is a selectively permeable cell organelle,allowing certain substances inside the cell while preventing others to pass through and thus is analogous to a barrier or gatekeeper. Specialized structure that surrounds the cell and its internal environment; Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have cell walls, allowing for more flexibility in shape and movement. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some. The cell wall is a rigid layer that provides support, protection, and shape to the cell. The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus.
Cell Membrane Function and Structure
June 6, 2023 by faith mokobi. Web the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane is how scientists describe what the cell membrane looks and functions like, because it is made up of a bunch of different molecules that are distributed across the membrane. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. Unsaturated fatty acids result in.
Cell Organelles BIOLOGY JUNCTION
Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have cell walls, allowing for more flexibility in shape and movement. Cholesterol is also present, which contributes to the fluidity of the membrane, and there are various proteins embedded within the membrane that have a variety of functions. I n the early stages of human embryonic development, a zygote divides into two identical.
Cell Membrane Diagram Labeled Functions and Diagram
Practice labeling the parts of the cell membrane learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Web fluid mosaic model. Controls movement of substances into/out of cell. Web the cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a.
Cell Membrane Diagram Labeled
A team of researchers labeled one of two cells in a developing embryo with gfp and used dna (blue) and actin (pink) labeling to track cell progeny to determine the contribution of each to developing structures. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and.
Cell membrane definition, structure, function, and biology
In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell. Web essential biological functionsimmune response, cell metabolism, neurotransmission, photosynthesis, cell adherence, cell growth and differentiationpotential commercial applicationsdrug response monitoring, chemical manufacturing, biosensing, energy conversion, tissue engineering. Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have cell walls, allowing for more flexibility in shape.
Cell membrane with labeled educational structure scheme vector
Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities. It was based on the plasma membrane’s “railroad track” appearance in early electron micrographs. An animal cell is a eukaryotic cell that lacks a cell wall, and it is enclosed by the plasma membrane. Unlike the animal cell lacking the cell wall. First, to be.
Human cell membrane structure 2053132 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Web the cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. Points to the interior or inside. Diagram of a cell membrane with labels. First, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and, second, to be a gate allowing transport into.
Cell Membrane Diagram Easy to draw cell membrane YouTube
Web the cell contains many cell parts with different shapes. Web essential biological functionsimmune response, cell metabolism, neurotransmission, photosynthesis, cell adherence, cell growth and differentiationpotential commercial applicationsdrug response monitoring, chemical manufacturing, biosensing, energy conversion, tissue engineering. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some. It was based on the plasma membrane’s “railroad track” appearance in.
Cell Membrane Definition, Structure, & Functions with Diagram
The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. It is a selectively permeable cell organelle,allowing certain substances inside the cell while preventing others to pass through and thus is analogous to a barrier or gatekeeper. The outermost part of the cell, which is shown as an outline of the.
Cell Membrane Layers Simple Functions and Diagram
It was based on the plasma membrane’s “railroad track” appearance in early electron micrographs. A team of researchers labeled one of two cells in a developing embryo with gfp and used dna (blue) and actin (pink) labeling to track cell progeny to determine the contribution of each to developing structures. Cholesterol is also present, which contributes to the fluidity of.
Web Essential Biological Functionsimmune Response, Cell Metabolism, Neurotransmission, Photosynthesis, Cell Adherence, Cell Growth And Differentiationpotential Commercial Applicationsdrug Response Monitoring, Chemical Manufacturing, Biosensing, Energy Conversion, Tissue Engineering.
It's a complex, highly organized unit, the basic building block of all living things. First, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and, second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products. The cell wall is a rigid layer that provides support, protection, and shape to the cell. June 6, 2023 by faith mokobi.
Of Course, A Cell Is Ever So Much More Than Just A Bag Of Goo.
Web plant cells comprise several organelles, each with unique functions vital to the cell’s operation: It was based on the plasma membrane’s “railroad track” appearance in early electron micrographs. Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It is also simply called the cell membrane.
Web The Cell Membrane, Also Known As The Plasma Membrane, Is A Double Layer Of Lipids And Proteins That Surrounds A Cell.
Part of phospholipid that hates water (hydrophobic); The cell organelles are enclosed by the plasma membrane including the cell nucleus. Davson and danielli theorized that the plasma membrane’s structure. The phospholipid bilayer consists of two adjacent sheets of phospholipids, arranged tail to tail.
It Is A Selectively Permeable Cell Organelle,Allowing Certain Substances Inside The Cell While Preventing Others To Pass Through And Thus Is Analogous To A Barrier Or Gatekeeper.
The outermost part of the cell, which is shown as an outline of the cell, is labeled cell membrane. Two different types of proteins that are commonly associated with the cell membrane are the integral proteins and peripheral protein ().as its name suggests, an integral protein is a protein that is embedded in the. Web the cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds the cytoplasm of all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including plant and animal cells. Web the plasma membrane—the outer boundary of the cell—is the bag, and the cytoplasm is the goo.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png)