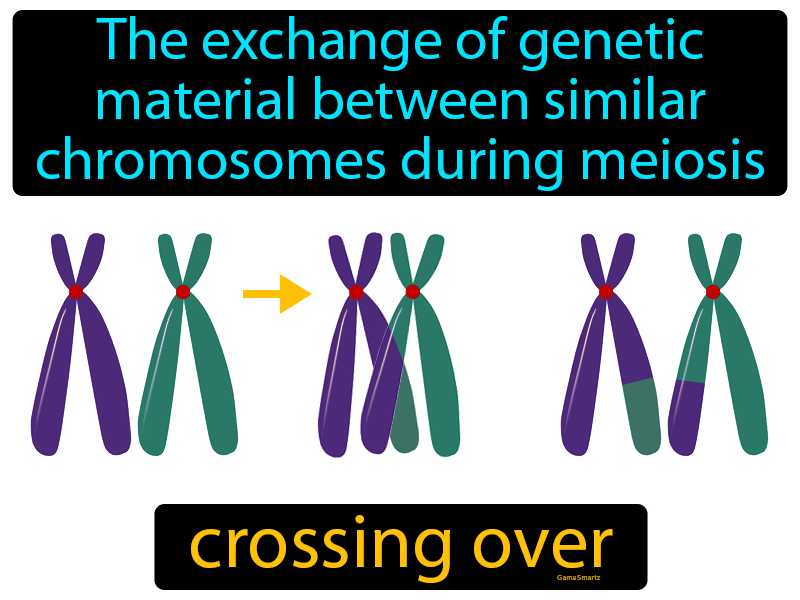
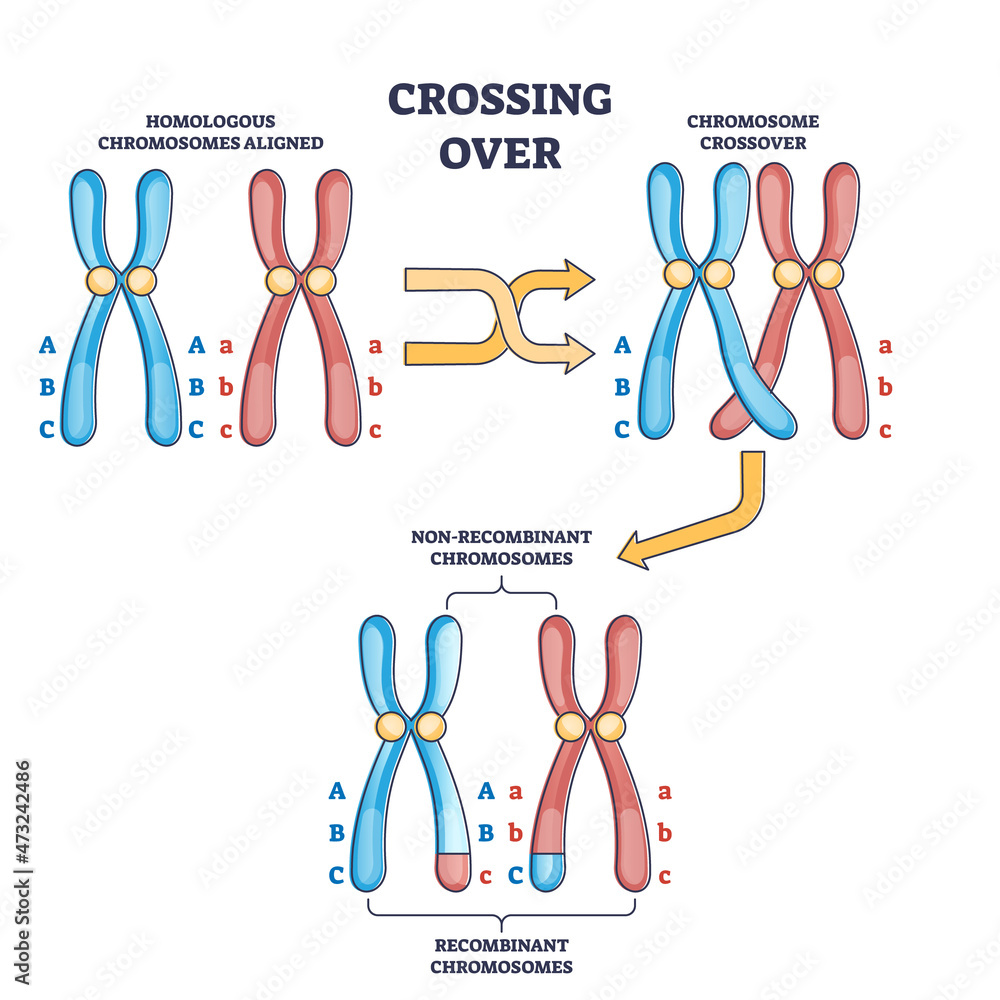
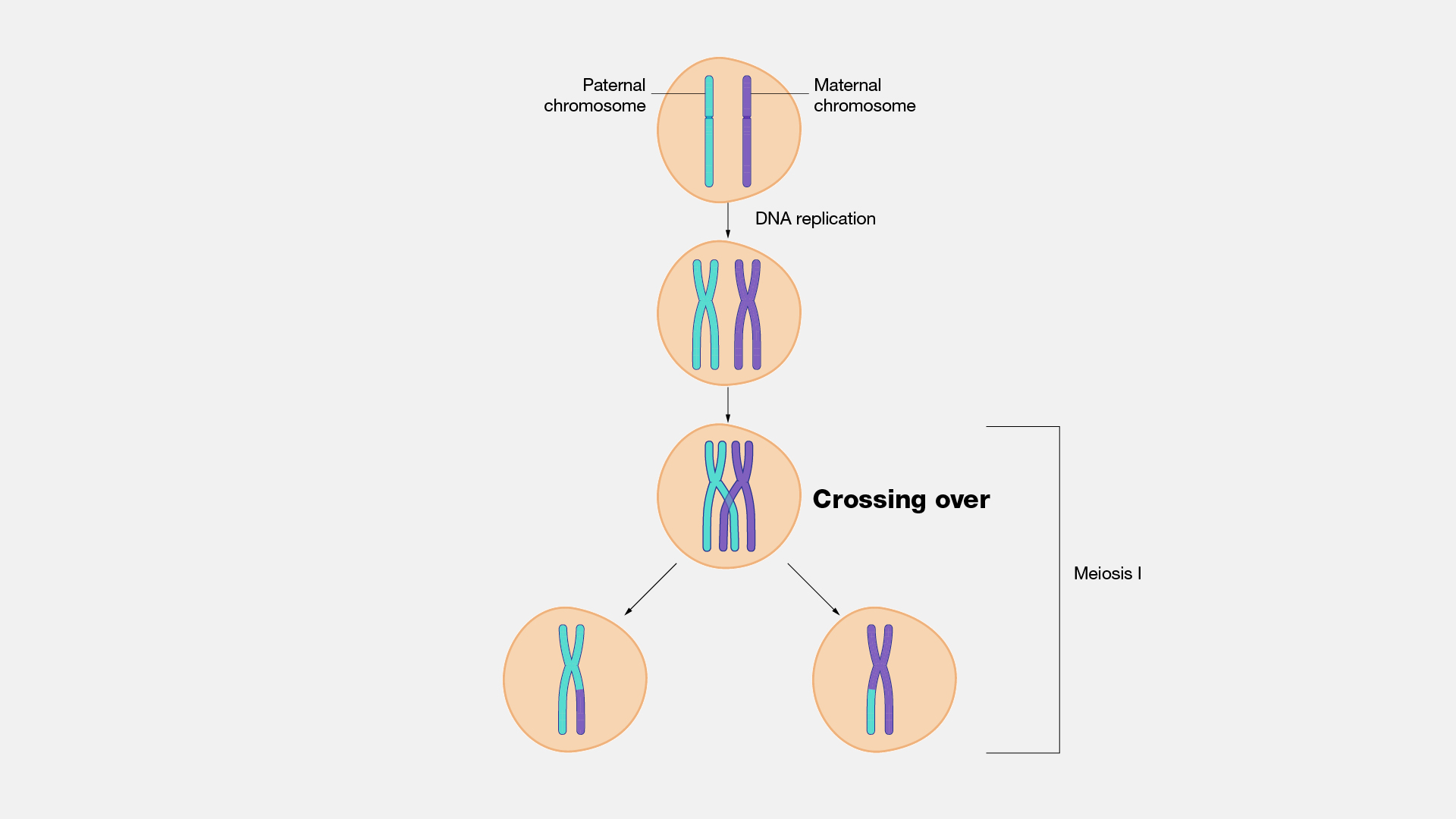
Crossing Over Drawing
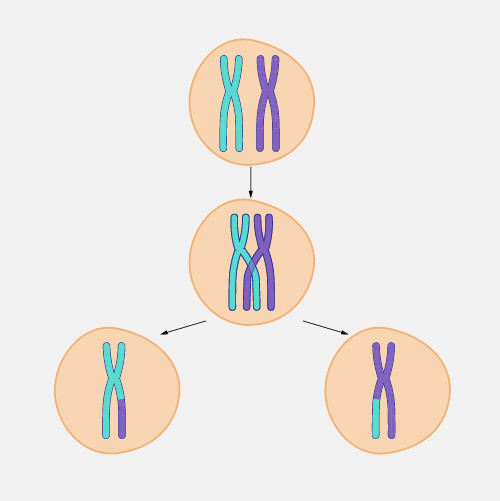
Crossing Over Drawing - This animation shows crossing over, which is the process by which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis. Though both happen in prophase i, synapsis happens before the chromosomes can cross over. Web cross hatching is a type of shading technique, whereby artists will draw parallel lines at two angles that cross one another to create the impression of light and shadow. Web crossing over is when bits of dna are exchanged from each chromosome to produce genetically unique chromosomes. The process, which produces recombination of genes by interchanging the corresponding segments between nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, is. The points where homologues cross over and exchange genetic material are chosen more or less at random, and they will be different in each cell that goes through meiosis. Crossing over is a process that happens between homologous chromosomes in order to increase genetic diversity. 9.7k views 4 years ago how to draw traffic and road safety topics. Web draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of new allele combinations as a results of crossing over. When genes are far apart, crossing over happens often enough that all types of gametes are produced with 25 % frequency.
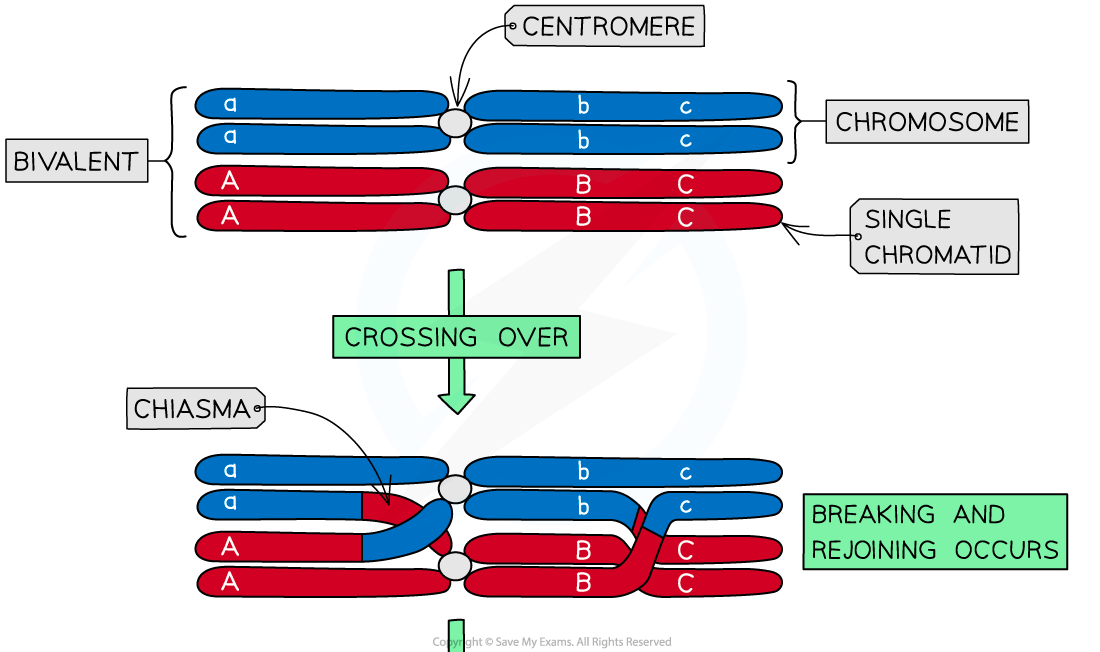
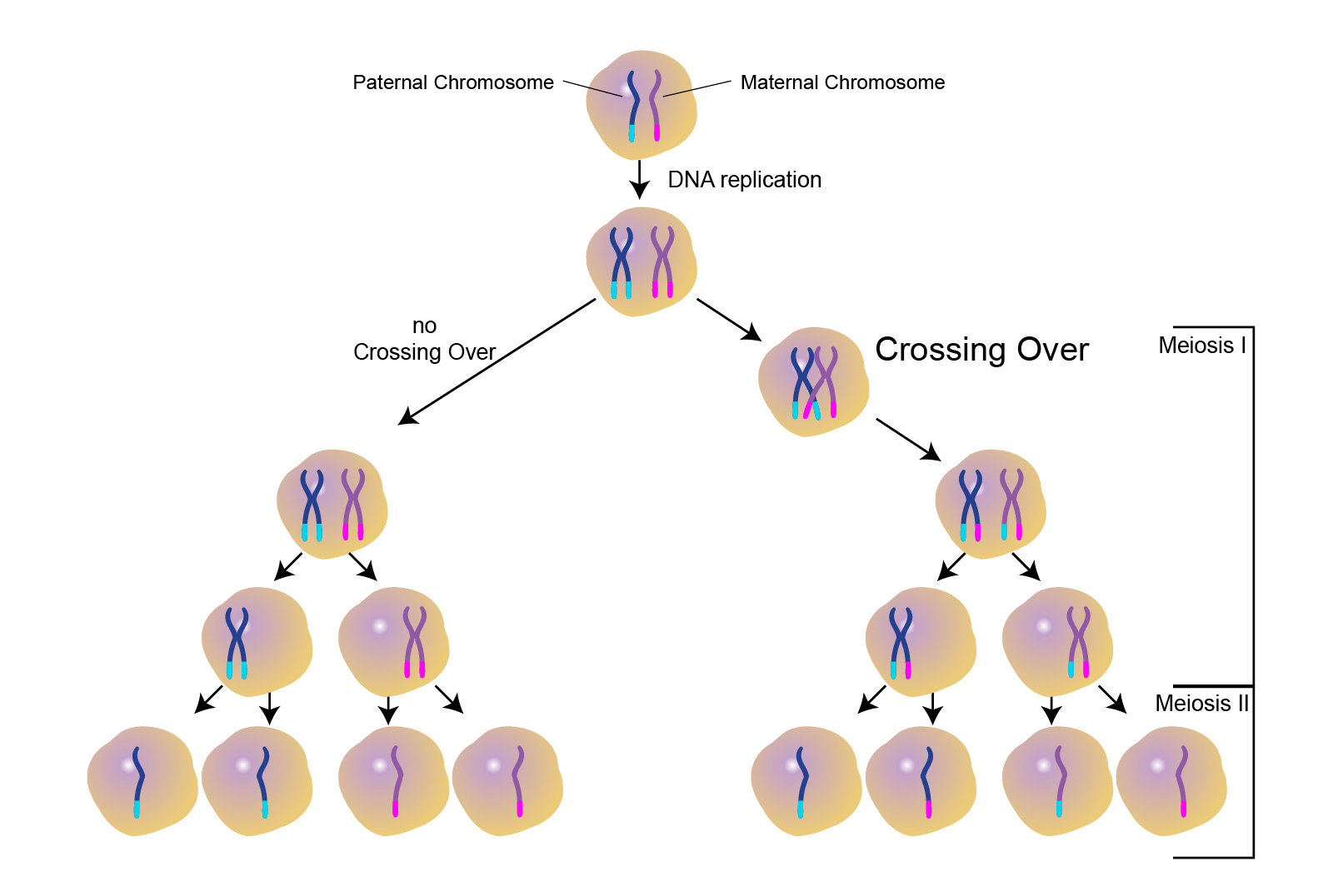
If meiosis happens many times, as in humans, crossovers will happen at many different points. Crossing over, as related to genetics and genomics, refers to the exchange of dna between paired homologous chromosomes (one from each parent) that occurs during. The exchange of segments between the inner situated chromatids of homologous chromosomes is called crossing over. The process of recombination involves the breakage and rejoining of parental chromosomes (m, f). The purpose of the cross hatching technique is to create a value range in a drawing. Meiosis has several mechanisms that increase the genetic diversity of gametes produced. Though both happen in prophase i, synapsis happens before the chromosomes can cross over. This results in the generation of novel chromosomes (c1, c2) that share dna from both parents. Web crossovers and genetic mapping. 136k views 4 years ago cell biology.
The exchange of segments between the inner situated chromatids of homologous chromosomes is called crossing over. As you can see, crossing over results in new combinations of genetic information, thus affecting inheritance and increasing genetic diversity. Crossing over, as related to genetics and genomics, refers to the exchange of dna between paired homologous chromosomes (one from each parent) that occurs during. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. The result is a hybrid chromosome with a unique pattern of genetic material. Each diploid cell contains two copies of every chromosome, one derived from the maternal gamete and. If meiosis happens many times, as in humans, crossovers will happen at many different points. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: The process of recombination involves the breakage and rejoining of parental chromosomes (m, f). Its occurrence depends on specific events early in prophase i, and it has important consequences for the rest of meiosis and beyond.
Crossing Over Diagram Diagram Quizlet
Web crossing over can put new alleles together in combination on the same chromosome, causing them to go into the same gamete. 136k views 4 years ago cell biology. Web use this to evaluate the student’s familiarity with the core concepts in crossing over and independent assortment. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. During crossing over, part.
Crossing Over and Independent Assortment Cell Division Ep 5 Zoë
Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Web the exchange of information between homologous chromosomes (through crossing over) happens during meiosis i when the maternal and paternal chromosomes associate to form tetrads. This results in the generation of novel chromosomes (c1, c2) that share dna from both parents. Web crossing over is the exchange of genetic _____ between.
🌱 Crossing over occurs during which of the following phases. Crossing
When genes are far apart, crossing over happens often enough that all types of gametes are produced with 25 % frequency. As you can see, crossing over results in new combinations of genetic information, thus affecting inheritance and increasing genetic diversity. Web crossovers and genetic mapping. The purpose of the cross hatching technique is to create a value range in.
AQA A Level Biology复习笔记7.3.1 Variation翰林国际教育
Web crossovers and genetic mapping. Its occurrence depends on specific events early in prophase i, and it has important consequences for the rest of meiosis and beyond. This results in the generation of novel chromosomes (c1, c2) that share dna from both parents. If meiosis happens many times, as in humans, crossovers will happen at many different points. Web crossing.
Linkage and (Part 1) Chromosomal Theory, Linkage
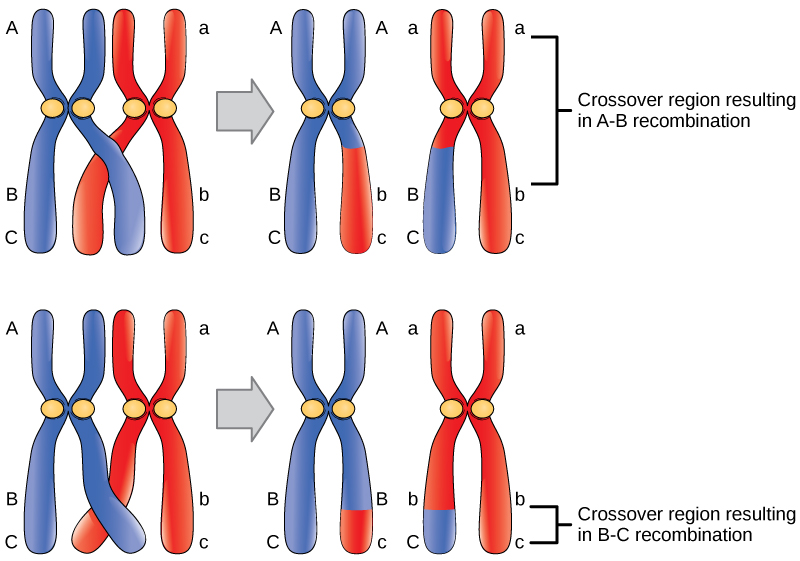
Web draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of new allele combinations as a results of crossing over. As you can see, crossing over results in new combinations of genetic information, thus affecting inheritance and increasing genetic diversity. Crossing over is unique to meiosis. This works on the basis that if two genes are present far apart on the chromosome,.
5.12 Sexual Reproduction, Meiosis, and Gametogenesis Human Biology
Web crossing over produces two chromosomes that have not previously existed. This works on the basis that if two genes are present far apart on the chromosome, the frequency of crossing over between the two will be greater. The purpose of the cross hatching technique is to create a value range in a drawing. Web courses on khan academy are.
What Stage Do Crossing Over Occurs? Mastery Wiki
Web use this to evaluate the student’s familiarity with the core concepts in crossing over and independent assortment. The purpose of the cross hatching technique is to create a value range in a drawing. Web crossing over can put new alleles together in combination on the same chromosome, causing them to go into the same gamete. The formation of recombinants.
Crossing Over Definition Easy to Understand
When genes are far apart, crossing over happens often enough that all types of gametes are produced with 25 % frequency. The process, which produces recombination of genes by interchanging the corresponding segments between nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, is. Though both happen in prophase i, synapsis happens before the chromosomes can cross over. Crossing over, as related to genetics.
Plakat Crossing over chromosomes and homologous division process
Web crossing over can put new alleles together in combination on the same chromosome, causing them to go into the same gamete. The purpose of the cross hatching technique is to create a value range in a drawing. The points where homologues cross over and exchange genetic material are chosen more or less at random, and they will be different.
🌱 Crossing over occurs during which of the following phases. Crossing
The process, which produces recombination of genes by interchanging the corresponding segments between nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, is. Web cross hatching is a type of shading technique, whereby artists will draw parallel lines at two angles that cross one another to create the impression of light and shadow. Web the exchange of information between homologous chromosomes (through crossing over).
During Crossing Over, Part Of One Chromosome Is Exchanged With Another.
Web draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of new allele combinations as a results of crossing over. This results in the generation of novel chromosomes (c1, c2) that share dna from both parents. Each diploid cell contains two copies of every chromosome, one derived from the maternal gamete and. Web crossing over is when bits of dna are exchanged from each chromosome to produce genetically unique chromosomes.
This Works On The Basis That If Two Genes Are Present Far Apart On The Chromosome, The Frequency Of Crossing Over Between The Two Will Be Greater.
Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Crossing over is a process that happens between homologous chromosomes in order to increase genetic diversity. The process, which produces recombination of genes by interchanging the corresponding segments between nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes, is. When genes are far apart, crossing over happens often enough that all types of gametes are produced with 25 % frequency.
Its Occurrence Depends On Specific Events Early In Prophase I, And It Has Important Consequences For The Rest Of Meiosis And Beyond.
Crossing over is unique to meiosis. The process of recombination involves the breakage and rejoining of parental chromosomes (m, f). If meiosis happens many times, as in humans, crossovers will happen at many different points. Web the exchange of information between homologous chromosomes (through crossing over) happens during meiosis i when the maternal and paternal chromosomes associate to form tetrads.
Web Crossing Over Produces Two Chromosomes That Have Not Previously Existed.
The exchange of segments between the inner situated chromatids of homologous chromosomes is called crossing over. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. The points where homologues cross over and exchange genetic material are chosen more or less at random, and they will be different in each cell that goes through meiosis. Web crossovers and genetic mapping.