Draw An Amino Acid
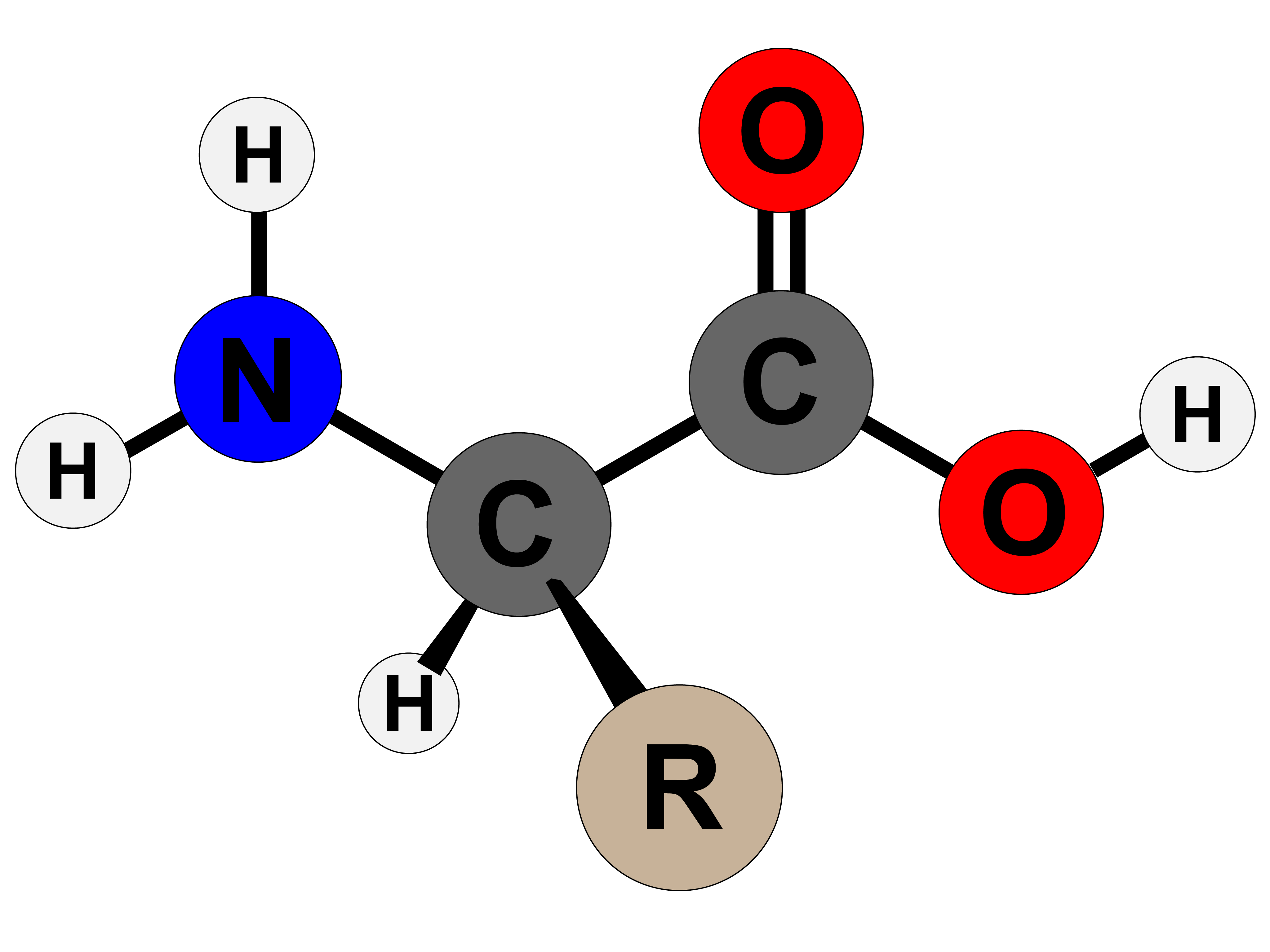
Draw An Amino Acid - Reversing or inverting the structure will have implications on the wedge or hashed ( dashed) marked bonds (figure 3). Draw the zwitterion form of a given amino acid. Describe the structure of an amino acid and the features that confer its specific properties. Amino acids share a basic structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group ( nh 2 ), a carboxyl group ( cooh ), and a hydrogen atom. Ala (a) arg (r) asn (n) asp (d) cys (c) gln (q) glu (e) gly (g) his (h) ile (i) leu (l) lys (k) met (m) phe (f) pro (p) ser (s) thr (t) trp (w) tyr (y) val (v) special amino acids; Web course instructors will draw structures many different ways. Different amino acids have the same basic structure and only differ in the r group. This will become the attachment point for the amine end of the next amino acid. This page was last updated: Web how to draw amino acids and peptide bonds to make a protein.
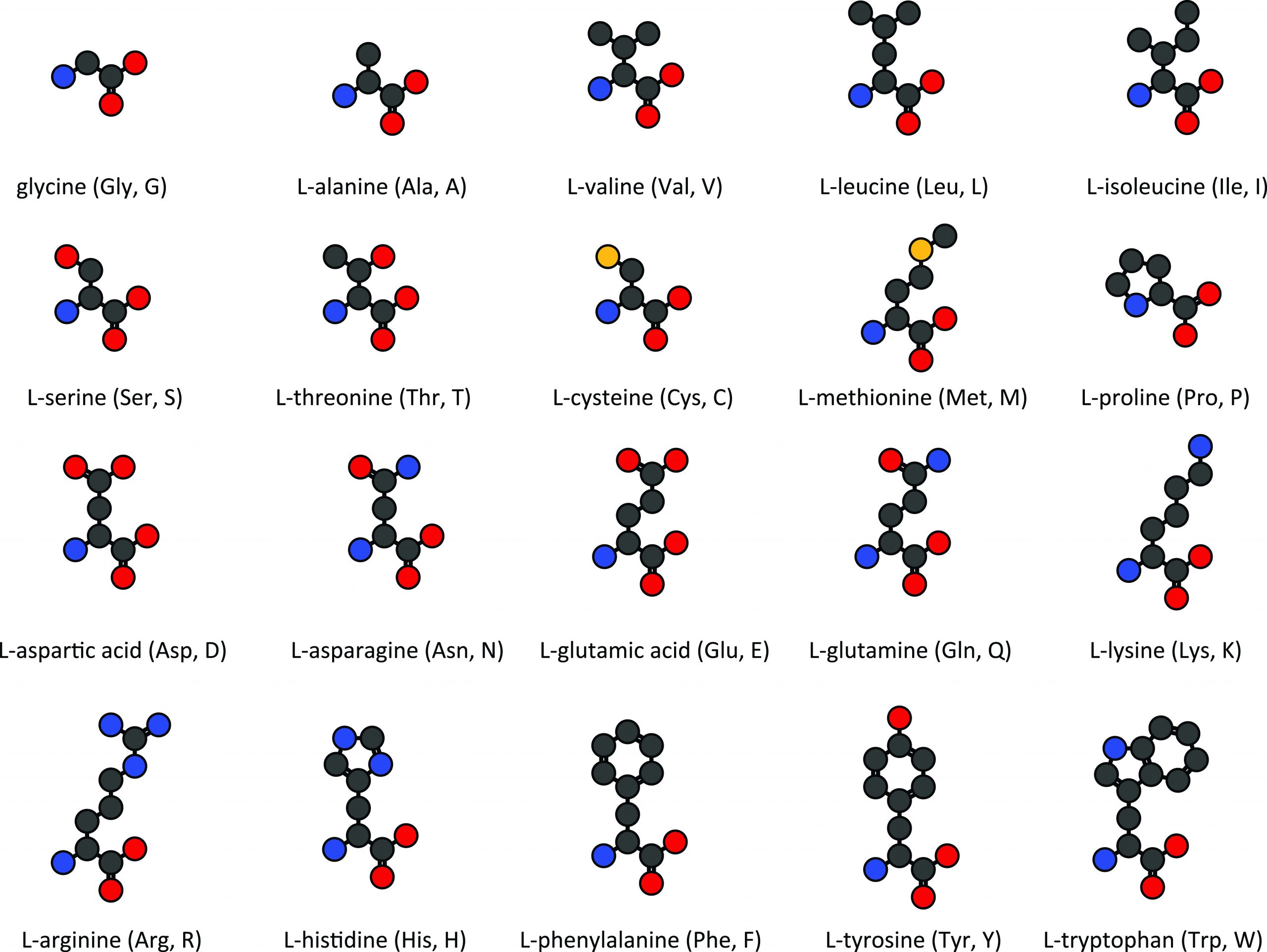
Arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and lysine. See solution check out a sample q&a here. Then from c1, draw a line down and to the right to create another point called c2. Reversing or inverting the structure will have implications on the wedge or hashed ( dashed) marked bonds (figure 3). A downloadable study sheet of this information is available here. Alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, and valine. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Account for some of the typical properties of amino acids (e.g., high melting points, solubility in water) in terms of zwitterion formation. There are 22 amino acids that are found in proteins and of these, only 20 are specified by the universal genetic code. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom.
There are 22 amino acids that are found in proteins and of these, only 20 are specified by the universal genetic code. Starting with the amine end, write nh3+ and from there, draw a line up to the right, creating a point called c1 to represent carbon 1. Web step by step. Arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and lysine. Web there are 20 types of amino acids commonly found in proteins. Most amino acids have a chiral carbon, which allows them to rotate polarized light. Ask the instructor to provide the stereochemistry whenever possible. Alpha carbon with a r group. Web the building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and. Draw the predominant form of a given amino acid in a solution of known ph, given the isoelectric point of the amino acid.
General Structure Of Amino Acid
Table of 20 amino acids derived from proteins with the. After completing this section, you should be able to. Web how to draw amino acids and peptide bonds to make a protein. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Different amino acids have the same basic structure and only differ in the r group.
Amino acids. 2D chemical structures of the 20 common amino acids REP ONE
Table of 20 amino acids derived from proteins with the. The others, selenocysteine and pyrrolysine use trnas that are able to base pair with stop codons in the mrna during translation. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and lysine. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins.
Amino Acids Facts for Kids
Draw a single amino acid. Solution for given an amino acid, be able to draw the structure when it is placed in water at ph = 2, ph = 7, or ph = 13. When an amino acid contains both a plus and a minus charge in the backbone, it is called a zwitterion and has an overall neutral charge..
Amino Acid Structure Chart
Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, which is shown in figure 2.1. Ala (a) arg (r) asn (n) asp (d) cys (c) gln (q) glu (e) gly (g) his (h) ile (i) leu (l) lys (k) met (m) phe (f) pro (p) ser (s) thr (t) trp (w) tyr (y) val (v) special amino acids; There are.
How To Draw Amino Acids Structures Learn Mnemonics YouTube
Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, which is shown in figure 2.1. This will become the attachment point for the amine end of the next amino acid. Ask the instructor to provide the stereochemistry whenever possible. Hence it is important for us to identify the r group so that we can identify the amino acid. Solution for.
How to draw AMINO ACID Biology IB Biology Bio Draw YouTube
Then from c1, draw a line down and to the right to create another point called c2. Solution for given an amino acid, be able to draw the structure when it is placed in water at ph = 2, ph = 7, or ph = 13. Different amino acids have the same basic structure and only differ in the r.
Amino_Acid_Structure
Ala (a) arg (r) asn (n) asp (d) cys (c) gln (q) glu (e) gly (g) his (h) ile (i) leu (l) lys (k) met (m) phe (f) pro (p) ser (s) thr (t) trp (w) tyr (y) val (v) special amino acids; Ask the instructor to provide the stereochemistry whenever possible. After completing this section, you should be able.
Amino Acid Classification and Structure ( Read ) Chemistry CK12
Hence it is important for us to identify the r group so that we can identify the amino acid. Web amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Solution for given an amino acid, be able to draw the structure when it is placed in water at ph = 2, ph = 7, or ph = 13. Web classify an.
Trick To Draw Structure Of Amino Acids YouTube
Alpha carbon with a r group. Arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, and lysine. The zwitterion of an amino acid exists at a ph equal to the isoelectric point. Then from c1, draw a line down and to the right to create another point called c2. Draw a single amino acid.
Drawing Generalized Amino Acid YouTube
Amino acids share a basic structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group ( nh 2 ), a carboxyl group ( cooh ), and a hydrogen atom. Web step by step. The protein builder constructs text representations for simple peptides and proteins from a library of 20 standard.
Draw The Predominant Form Of A Given Amino Acid In A Solution Of Known Ph, Given The Isoelectric Point Of The Amino Acid.
Web the building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and. To connect amino acids together, a peptide bond (also called an amide. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (nh2), a carboxyl group (cooh), and a hydrogen atom. A downloadable study sheet of this information is available here.
Account For Some Of The Typical Properties Of Amino Acids (E.g., High Melting Points, Solubility In Water) In Terms Of Zwitterion Formation.
Most amino acids have a chiral carbon, which allows them to rotate polarized light. Alpha carbon with a r group. After completing this section, you should be able to. Describe the structure of an amino acid and the features that confer its specific properties.
This Will Become The Attachment Point For The Amine End Of The Next Amino Acid.
Amino acids share a basic structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group ( nh 2 ), a carboxyl group ( cooh ), and a hydrogen atom. Describe, briefly, how a mixture of amino acids may be separated by paper electrophoresis. Starting with the amine end, write nh3+ and from there, draw a line up to the right, creating a point called c1 to represent carbon 1. Alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, and valine.
Arginine, Aspartic Acid, Glutamic Acid, And Lysine.
Is the amine group protonated or not?…. Web classify an amino acid as being acidic, basic or neutral, given its kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure. Draw a single amino acid. Draw the zwitterion form of a given amino acid.