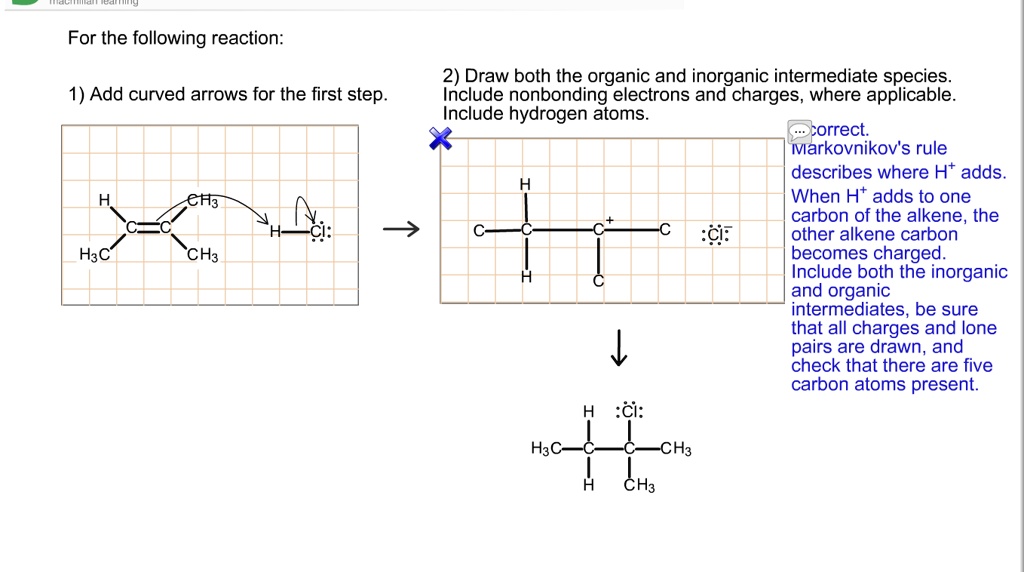
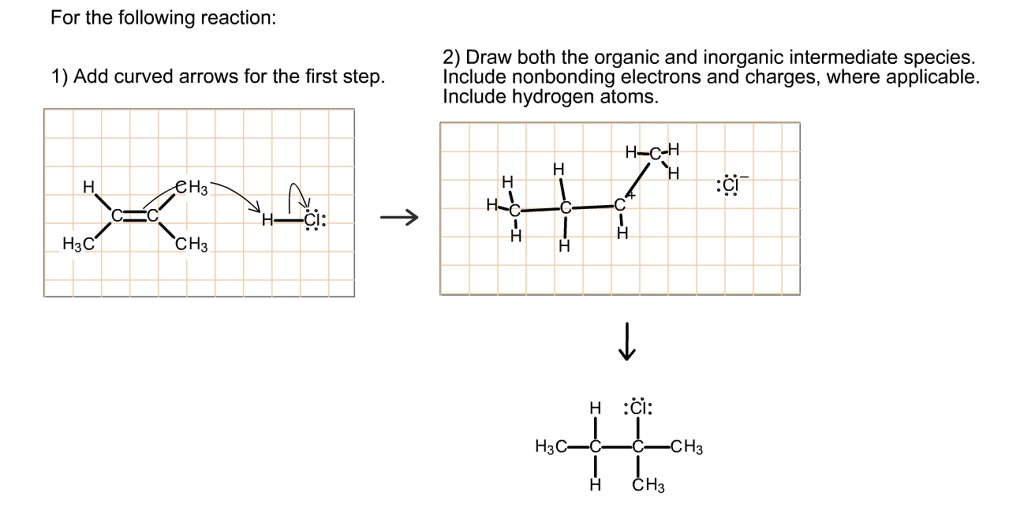
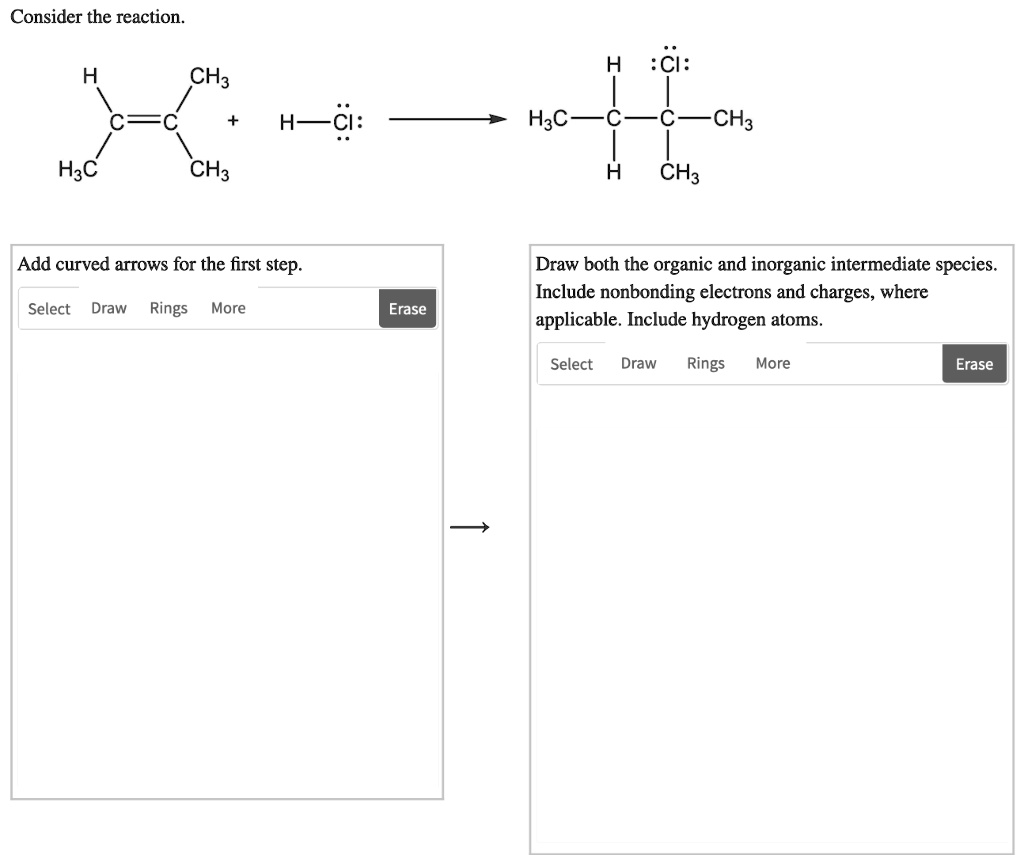
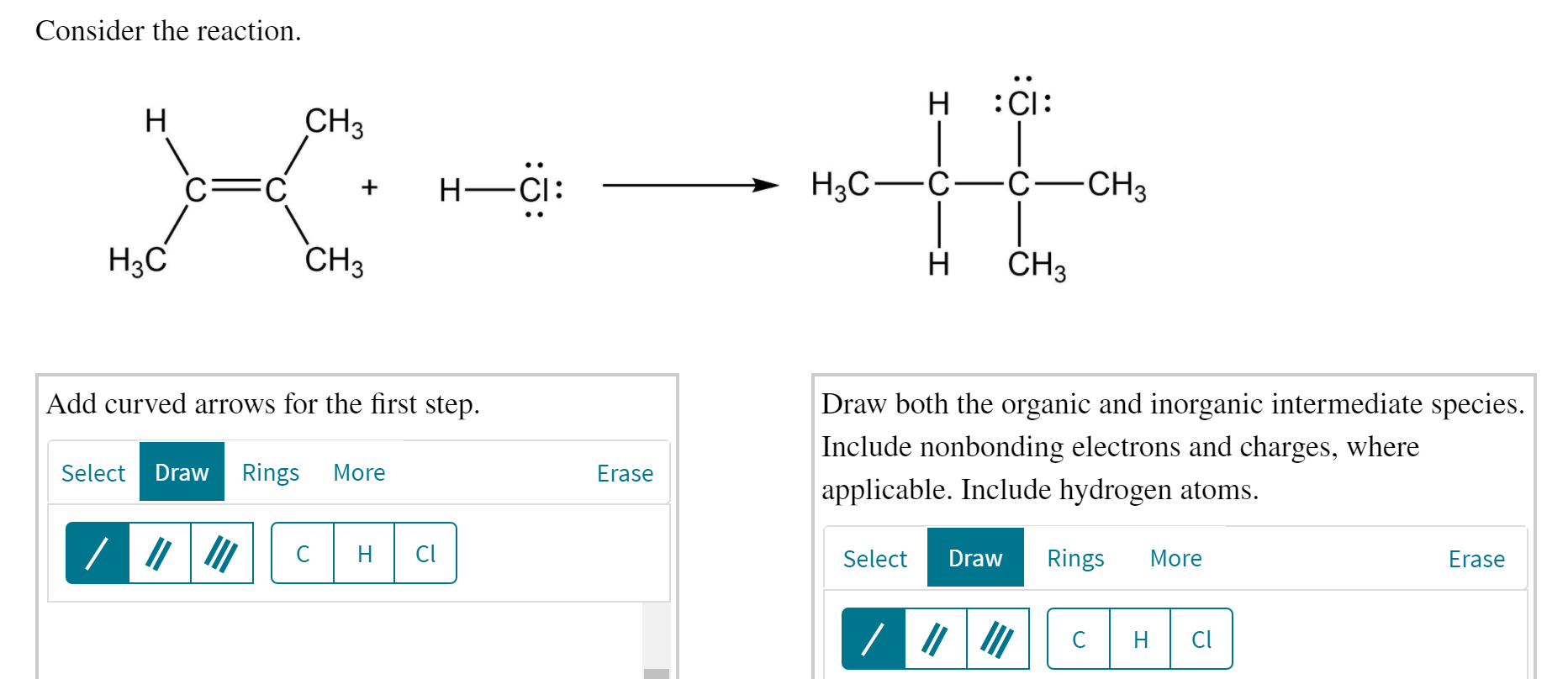
Draw Both The Organic And Inorganic Intermediate Species
Draw Both The Organic And Inorganic Intermediate Species - H2o + h+ → h3o+. Solution for for the following reaction: The organic compound and inorganic intermediate species. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. Web both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Web many important organic reactions do not occur in a single step; Web 2) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. This is a popular solution! Web draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first?
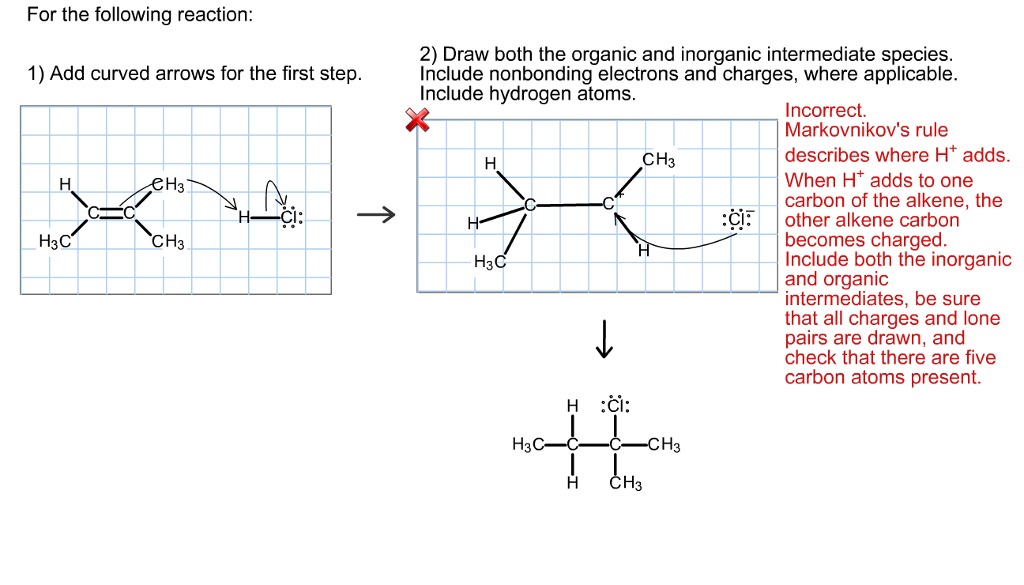
Web many important organic reactions do not occur in a single step; Solved in 4 steps with 2 images. Complete the steps in the mechanism to produce the product shown. Web 2) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. We are asked to show our mechanism arrows when we have an additional reaction, hydrochloric acid, to alkene. Web both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Carbon double bond, carbon c, h, 3 c, h, 3 h, plus h, c, l, n g s, and 3 s 3 positive charge c, h, plus chlorine, were the organic and inorganic intermediate. Draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. H3c—c—c—ch3 ch3 ch3 add curved arrows for the first step. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable.
Complete the steps in the mechanism to produce the product shown. By now you are familiar with a range of reaction types in organic, inorganic,. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where. Web both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Our chlorine will go in our most. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. H3c—c—c—ch3 ch3 ch3 add curved arrows for the first step. Draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. Web 1) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species.
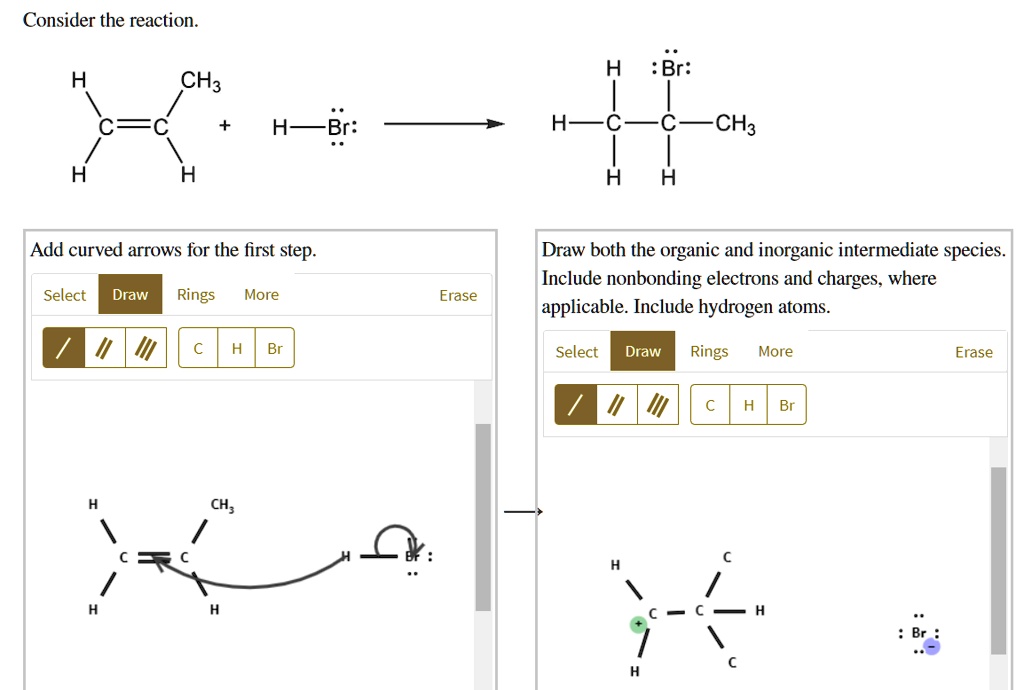
SOLVED Consider the reaction Br CH3 HBr H Add curved arrows for the
No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first? Draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. Draw each species (organic and inorganic) resulting from the previous step. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable.
OneClass For the following reaction 1) Add curved arrows for the
The organic compound and inorganic intermediate species. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. Complete the steps in the mechanism to produce the product shown. Solution for for the following reaction: Draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species.
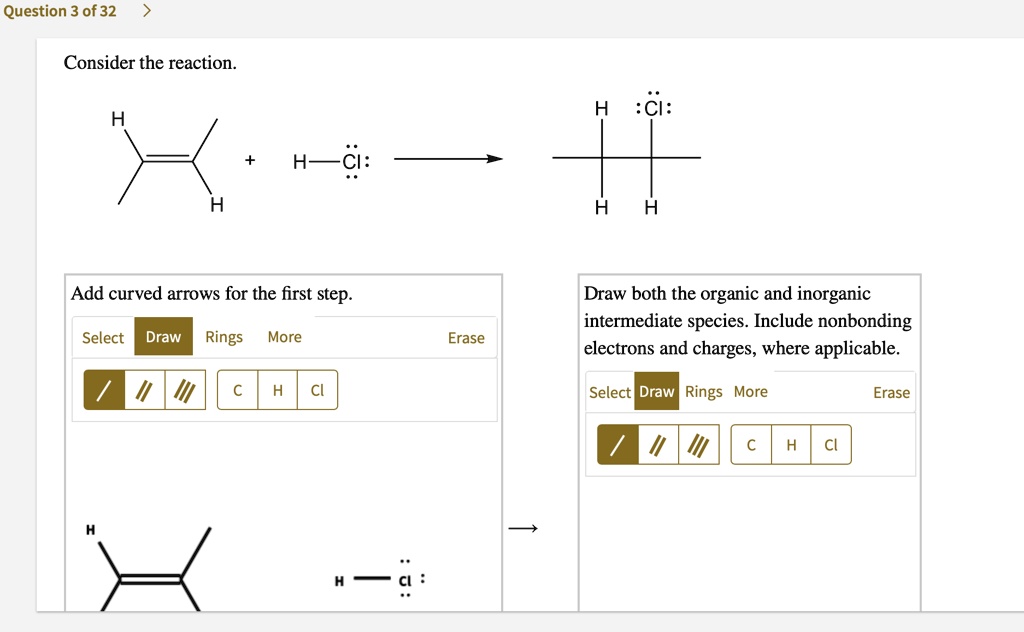
SOLVED Question 3 of 32 Consider the reaction CI HCI Add curved
Web 1) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Web 2) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species: Submitted by christian p., sep. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable.
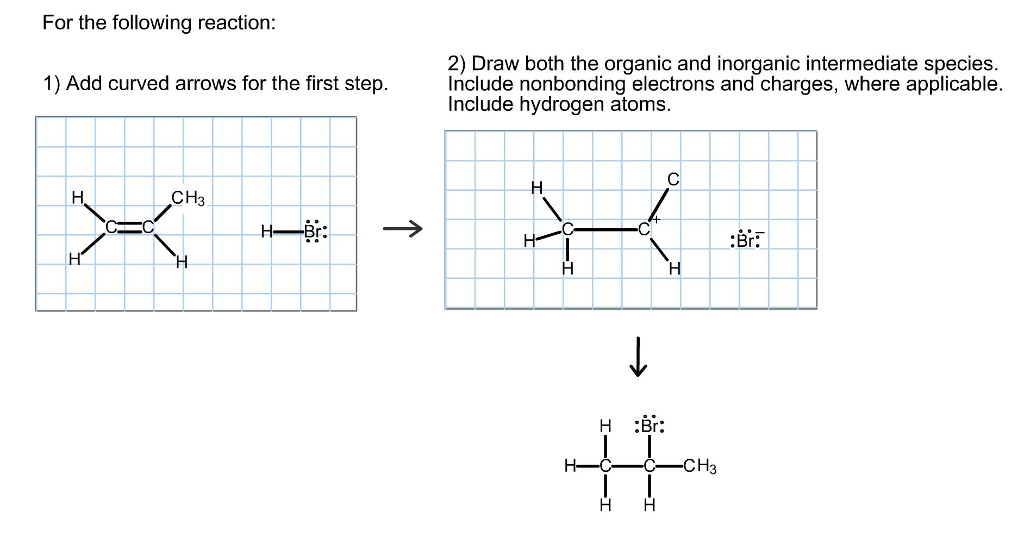
Solved For the following reaction 2) Draw both the organic
Submitted by christian p., sep. H2o + h+ → h3o+. The organic compound and inorganic intermediate species. Carbon double bond, carbon c, h, 3 c, h, 3 h, plus h, c, l, n g s, and 3 s 3 positive charge c, h, plus chlorine, were the organic and inorganic intermediate. Our chlorine will go in our most.
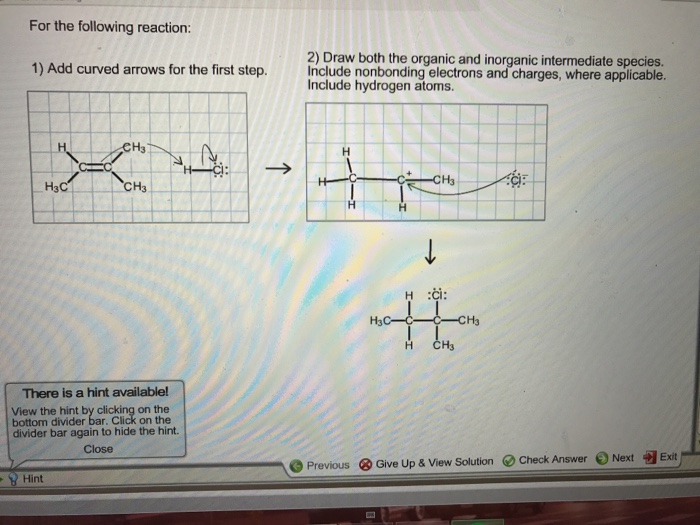
Solved For The Following Reaction 1) Add Curved Arrows F...
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images. Web for the following reaction: Web draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Carbon double bond, carbon c, h, 3 c, h, 3 h, plus h, c, l, n g s, and 3 s 3 positive charge c, h, plus chlorine, were the organic and inorganic intermediate. 2) draw both the organic.
SOLVED For the following reaction 2) Draw both the organic and
This is a popular solution! Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. H2o + h+ → h3o+. We are asked to show our mechanism arrows when we have an additional reaction, hydrochloric acid, to alkene. 2) draw both the organic and inorganic.
SOLVED For the following reaction 2) Draw both the organic and
We are asked to show our mechanism arrows when we have an additional reaction, hydrochloric acid, to alkene. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first? Draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Solved in 4 steps with 2 images.
SOLVED Consider the reaction CI CH3 HCI H3C CH3 HzC CH3 Add curved
The organic compound and inorganic intermediate species. Web 1) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Web many important organic reactions do not occur in a single step; Web 2) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species:
Solved Draw both the organic and intermediate
Web 1) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. We are asked to show our mechanism arrows when we have an additional reaction, hydrochloric acid, to alkene. No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first? Ch2 add curved arrows for the first step.
Solved For the following reaction 2) Draw both the organic
Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. The atom's negatively charged particles are called. Complete the steps in the mechanism to produce the product shown. Draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable.
Include Nonbonding Electrons And Charges, Where Applicable.
2) draw both the organic and inorganic. Ch3ch2ch2oh + h+ → ch3ch2ch2oh2+ inorganic intermediate species: This is a popular solution! Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable.
Solution For For The Following Reaction:
H2o + h+ → h3o+. Include nonbonding electrons and charges, where applicable. By now you are familiar with a range of reaction types in organic, inorganic,. 1) add curved arrows for the first step.
Include Nonbonding Electrons And Charges, Where Applicable.
Our chlorine will go in our most. Web 1) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. Web 2) draw both the organic and inorganic intermediate species. The atom's negatively charged particles are called.
No One Rated This Answer Yet — Why Not Be The First?
College of saint benedict/saint john's university. The organic compound and inorganic intermediate species. Solved in 4 steps with 2 images. Web for the following reaction: