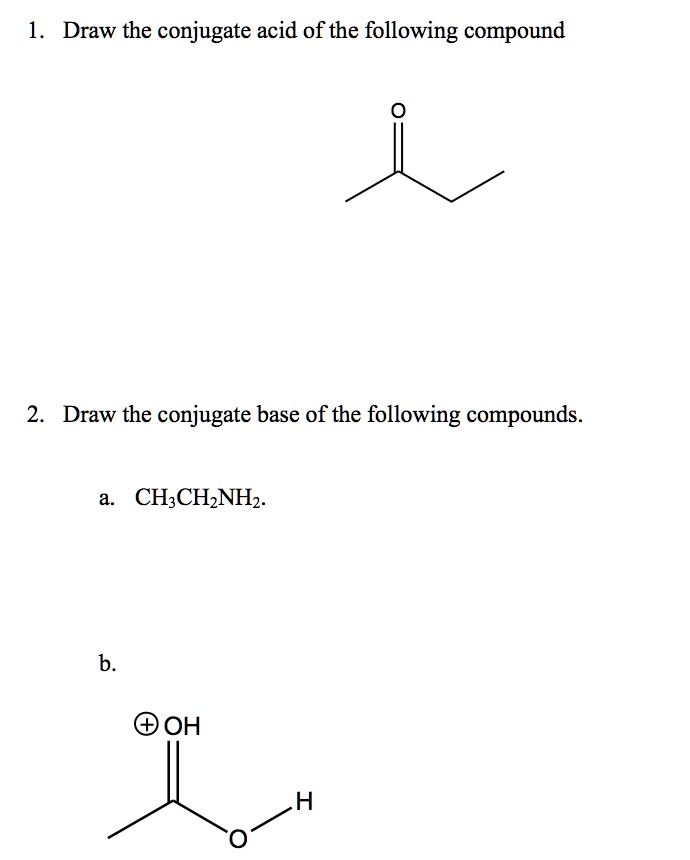
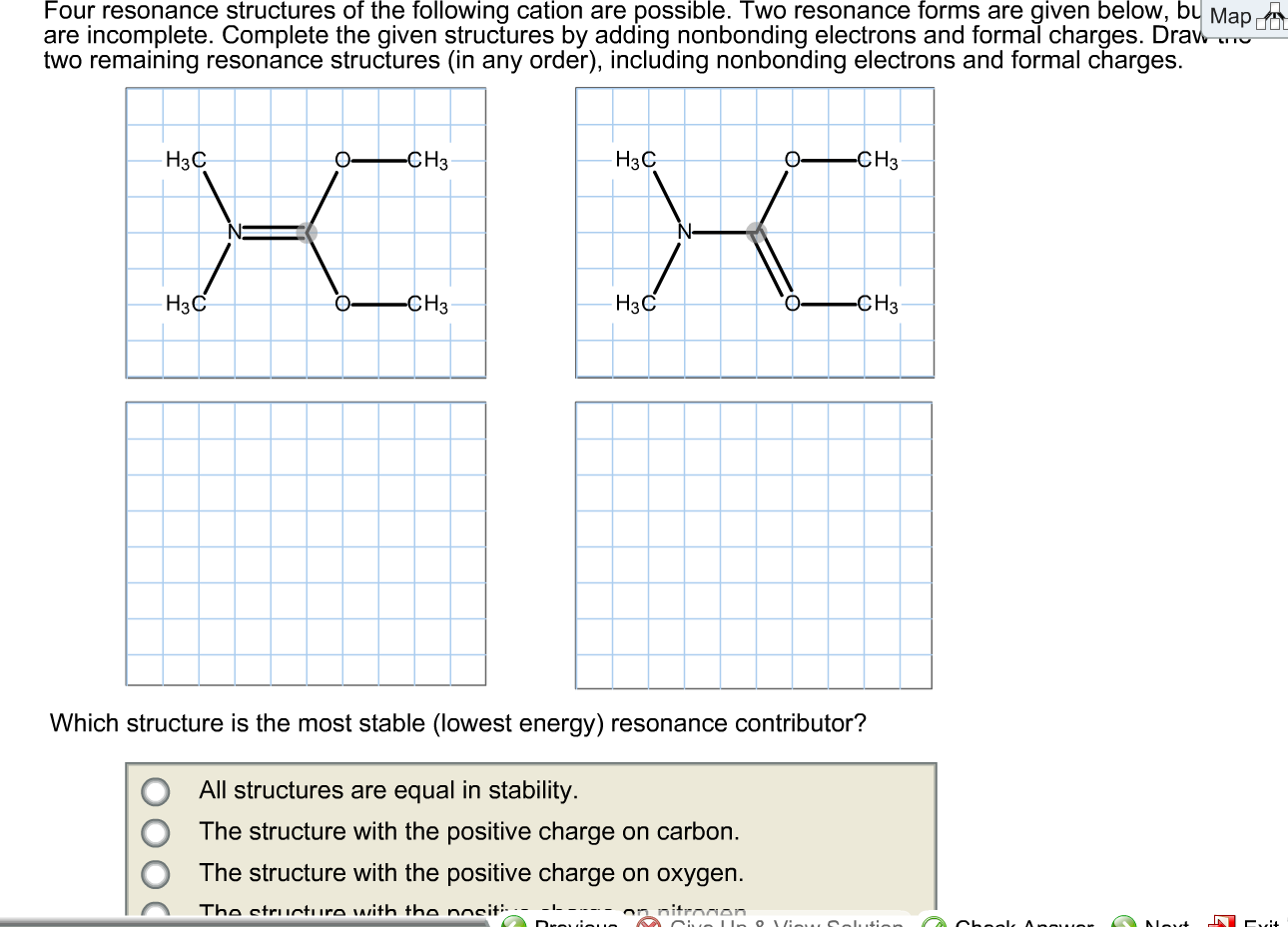
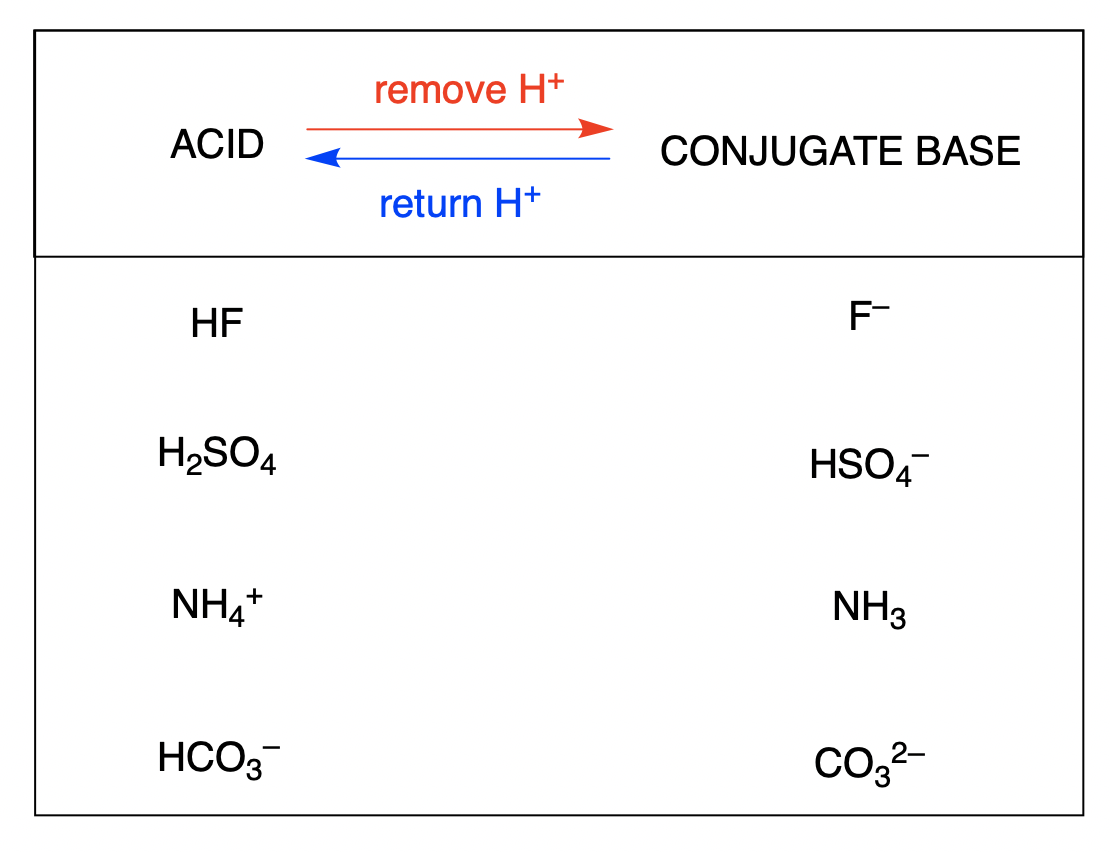
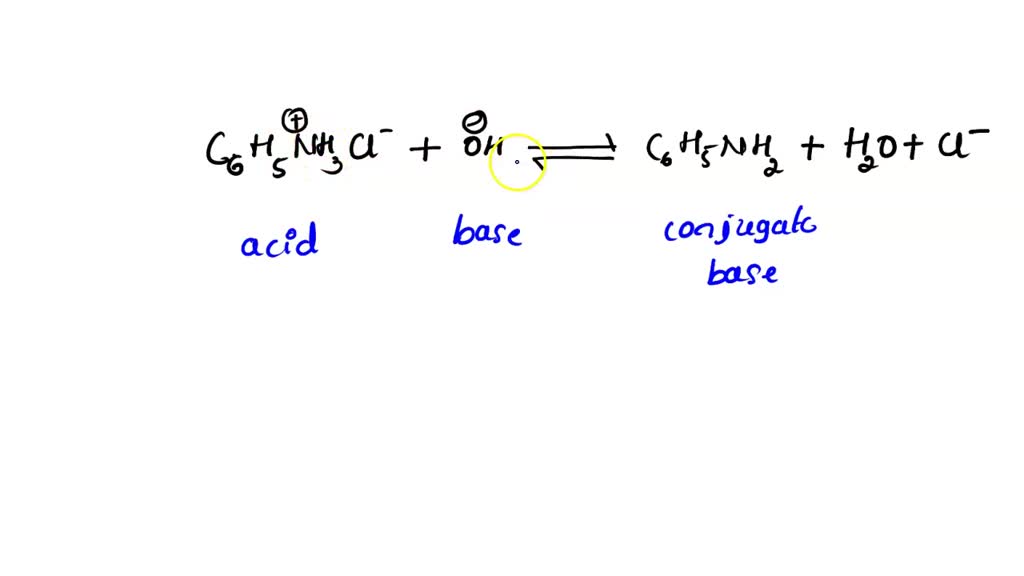Draw The Conjugate Base For The Following Acid
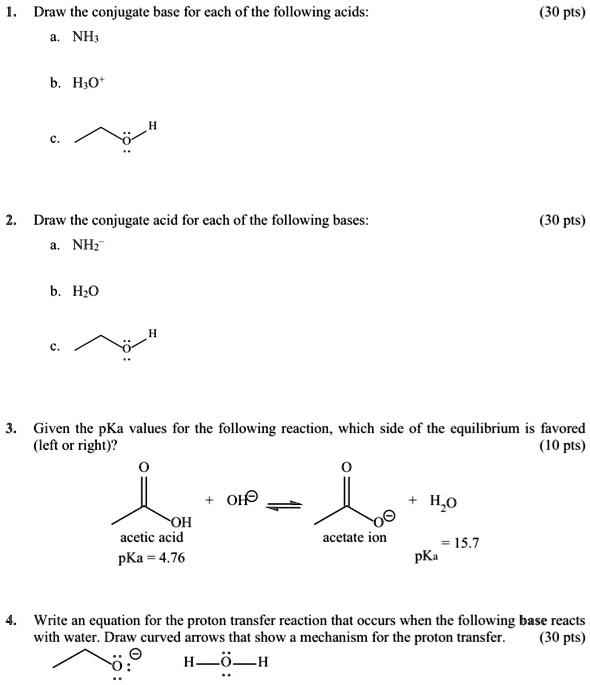
Draw The Conjugate Base For The Following Acid - Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids: Web how would you identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and the conjugate base in the following equation: The conjugate base of hts is ts⁻. 3.36 draw the conjugate base for each of the following acid. There are 3 steps to solve this one. Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids (a). Web tennessine is a halogen, so it should form the following acid (probably called hydrotennessic acid): Draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases. If acetic acid donates this proton, then the electrons in magenta are left behind on the oxygen, so the conjugate base would have a. (a) (b) (c) nh3 (d) h3o+ (e) (f) (g) nh4+ 3.38 draw the conjugate.
Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids: Web draw the conjugate acid of each of the following: 2) draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases: If acetic acid donates this proton, then the electrons in magenta are left behind on the oxygen, so the conjugate base would have a. Web let's draw the conjugate base for acetic acid. Web how would you identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and the conjugate base in the following equation: $\mathrm {nh}_4 { }^ {+}$. Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids (a). (a) (b) (c) nh3 (d) h3o+ (e) (f) (g) nh4+ 3.38 draw the conjugate. The conjugate base of hts is ts⁻.
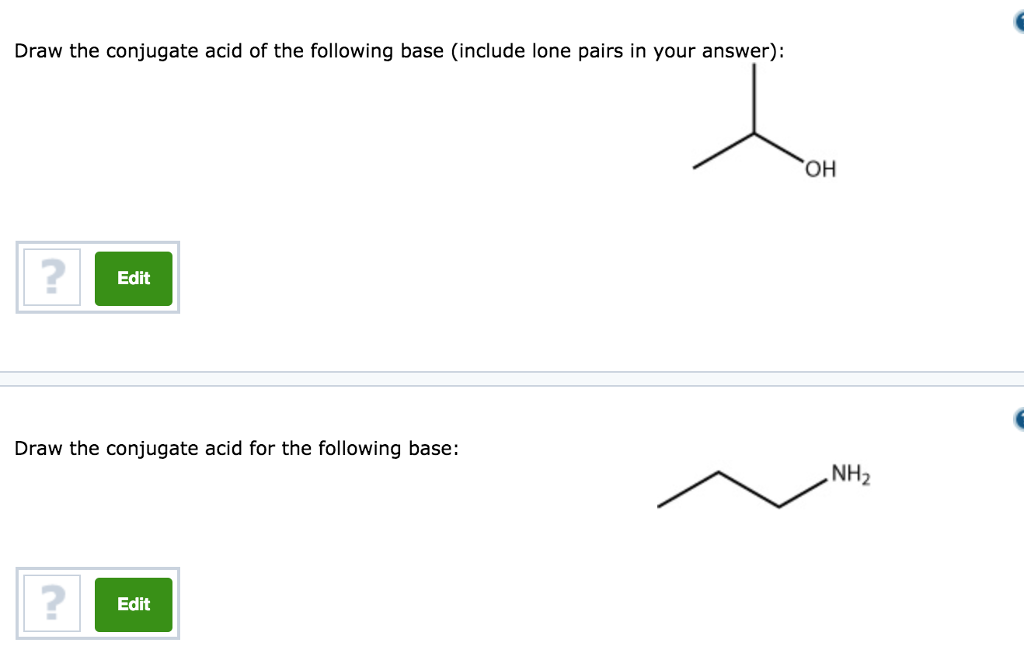
Web draw the conjugate acid of each of the following: If acetic acid donates this proton, then the electrons in magenta are left behind on the oxygen, so the conjugate base would have a. Oh draw the conjugate base for the following acid (lone pairs do not have to. Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids: Web hcl is a strong acid. Web how would you identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and the conjugate base in the following equation: 3.35 draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases 2. Draw the conjugate acid for the following base: Web let's draw the conjugate base for acetic acid. Draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases.
SOLVED Draw the conjugate acid of the following compound CH3CH2NH2
Draw the conjugate acid for the following base: Web let's draw the conjugate base for acetic acid. This problem has been solved!. Acids and bases acids and bases. 3.36 draw the conjugate base for each of the following acid.
Solved Draw the conjugate base for the following acid.
If acetic acid donates this proton, then the electrons in magenta are left behind on the oxygen, so the conjugate base would have a. Draw the conjugate acid for the following base: There are 3 steps to solve this one. 3.36 draw the conjugate base for each of the following acid. The conjugate base of hts is ts⁻.
Write the Formula for the Conjugate Acid of Each Base
Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids: 3.35 draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases 2. Draw the conjugate base for the following acid (lone pairs do not have to be drawn): Oh draw the conjugate base for the following acid (lone pairs do not have to. Web let's draw the conjugate base for.
[Solved] Draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases . a
Draw the conjugate base for the following acid (lone pairs do not have to be drawn): Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids (a). Draw the conjugate acid for the following base: $\mathrm {nh}_4 { }^ {+}$. Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids:
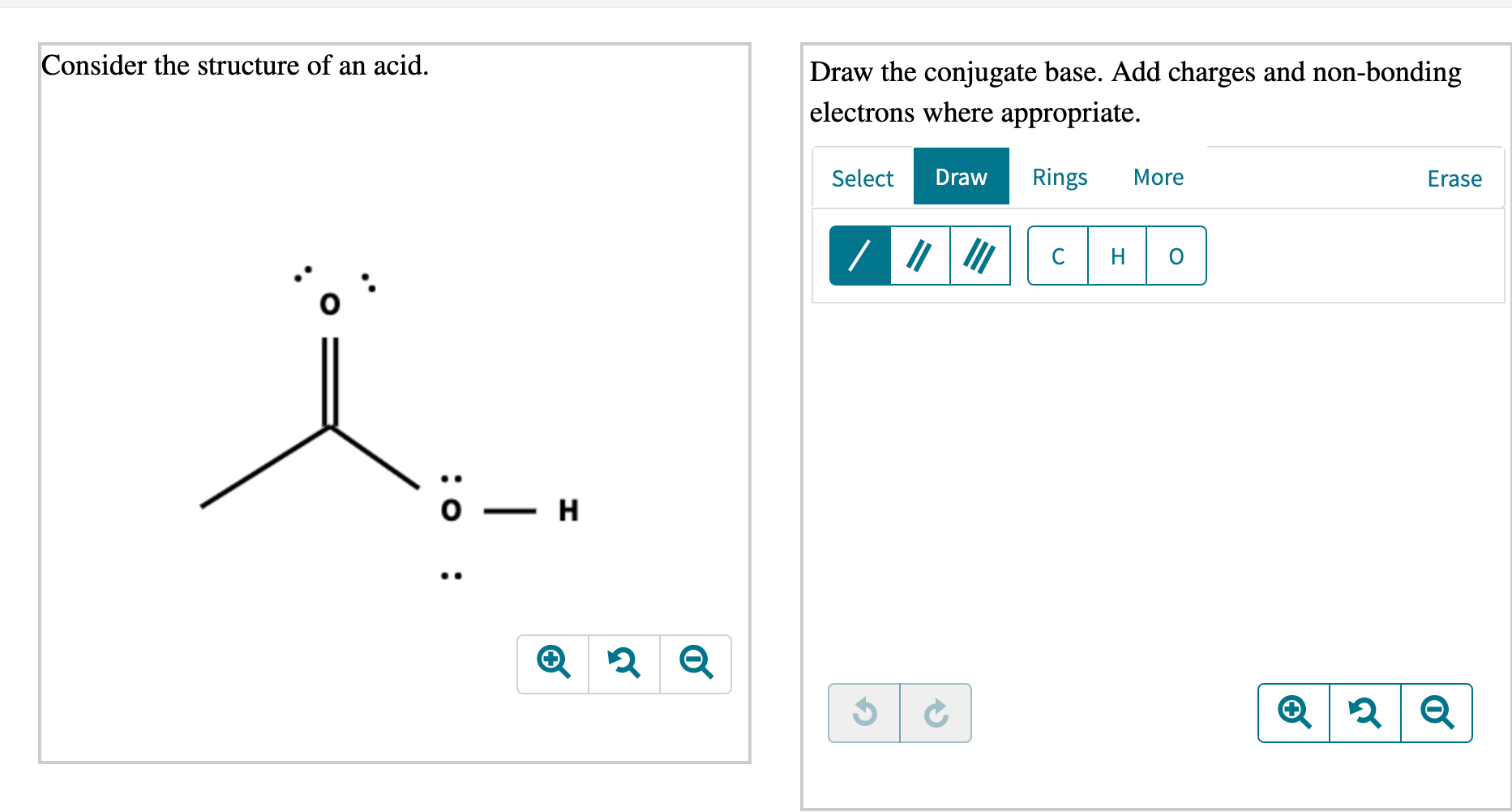
Solved Consider the structure of an acid. Draw the conjugate
Web hcl is a strong acid. $\mathrm {nh}_4 { }^ {+}$. 2) draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases: Web let's draw the conjugate base for acetic acid. Ch 3 nh 2 is an amine and therefore a weak base.
Solved Draw the conjugate base for the following acid
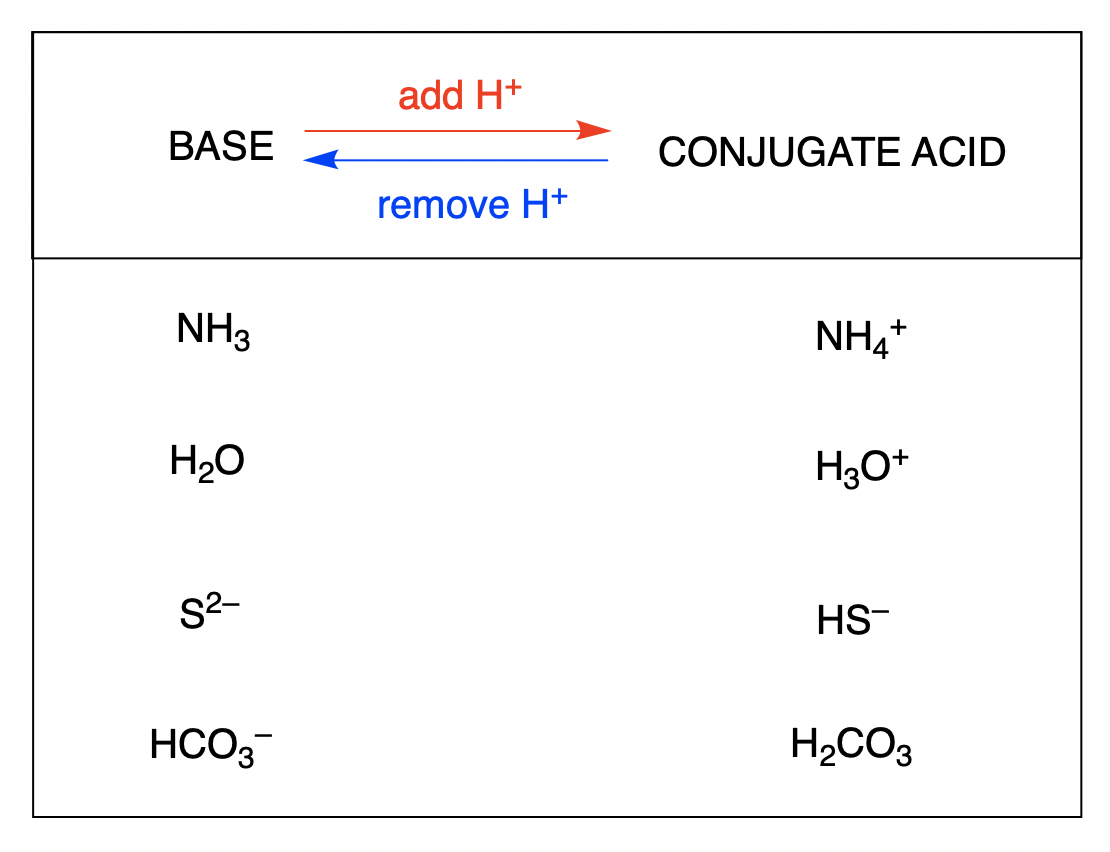
3.37 draw the conjugate base for. Web here are the conjugate bases for some common acids: Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids: Acids and bases acids and bases. The conjugate base of hts is ts⁻.
SOLVED Draw the acidbase reaction between the following acids and
2) draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases: This problem has been solved!. Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids (a). Oh draw the conjugate base for the following acid (lone pairs do not have to. 3.36 draw the conjugate base for each of the following acid.
Enter the Conjugate Base for Each Acid.
Acids and bases acids and bases. Web tennessine is a halogen, so it should form the following acid (probably called hydrotennessic acid): 3.37 draw the conjugate base for. Draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases. Web draw the conjugate acid of each of the following:
SOLVED Draw the conjugate base for cach of the following acids NH
Oh draw the conjugate base for the following acid (lone pairs do not have to. Draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases. Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids: 3.37 draw the conjugate base for. If acetic acid donates this proton, then the electrons in magenta are left behind on the oxygen, so the.
Solved Draw the conjugate acid of the following base
Draw the conjugate acid for the following base: Web tennessine is a halogen, so it should form the following acid (probably called hydrotennessic acid): Web here are the conjugate bases for some common acids: Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids: Web let's draw the conjugate base for acetic acid.
Draw The Conjugate Acid For Each Of The Following Bases.
(a) (b) (c) nh3 (d) h3o+ (e) (f) (g) nh4+ 3.38 draw the conjugate. Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids (a). This problem has been solved!. 3.35 draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases 2.
There Are 3 Steps To Solve This One.
Web tennessine is a halogen, so it should form the following acid (probably called hydrotennessic acid): Web how would you identify the acid, base, conjugate acid, and the conjugate base in the following equation: Web hcl is a strong acid. Draw the conjugate base for the following acid (lone pairs do not have to be drawn):
$\Mathrm {Nh}_4 { }^ {+}$.
2) draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases: The conjugate base of hts is ts⁻. Ch 3 nh 2 is an amine and therefore a weak base. Oh draw the conjugate base for the following acid (lone pairs do not have to.
3.37 Draw The Conjugate Base For.
Web let's draw the conjugate base for acetic acid. Web draw the conjugate acid of each of the following: If acetic acid donates this proton, then the electrons in magenta are left behind on the oxygen, so the conjugate base would have a. Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids: