Draw The Structure Of A Nucleotide And Label The Parts
Draw The Structure Of A Nucleotide And Label The Parts - Phosphate is associated with the sugar of nucleoside by an ester bond with the 5 th c hydroxyl group. Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Label the 3' and 5' carbons. The most commonly occurring purines in dna are adenine and guanine: Here’s the best way to solve it. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like use a venn diagram to compare and contrast dna and rna, explain the base pairing rules of dna. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. Take a look at what a nucleotide is, its structure, and its function in biological processes. In contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers.
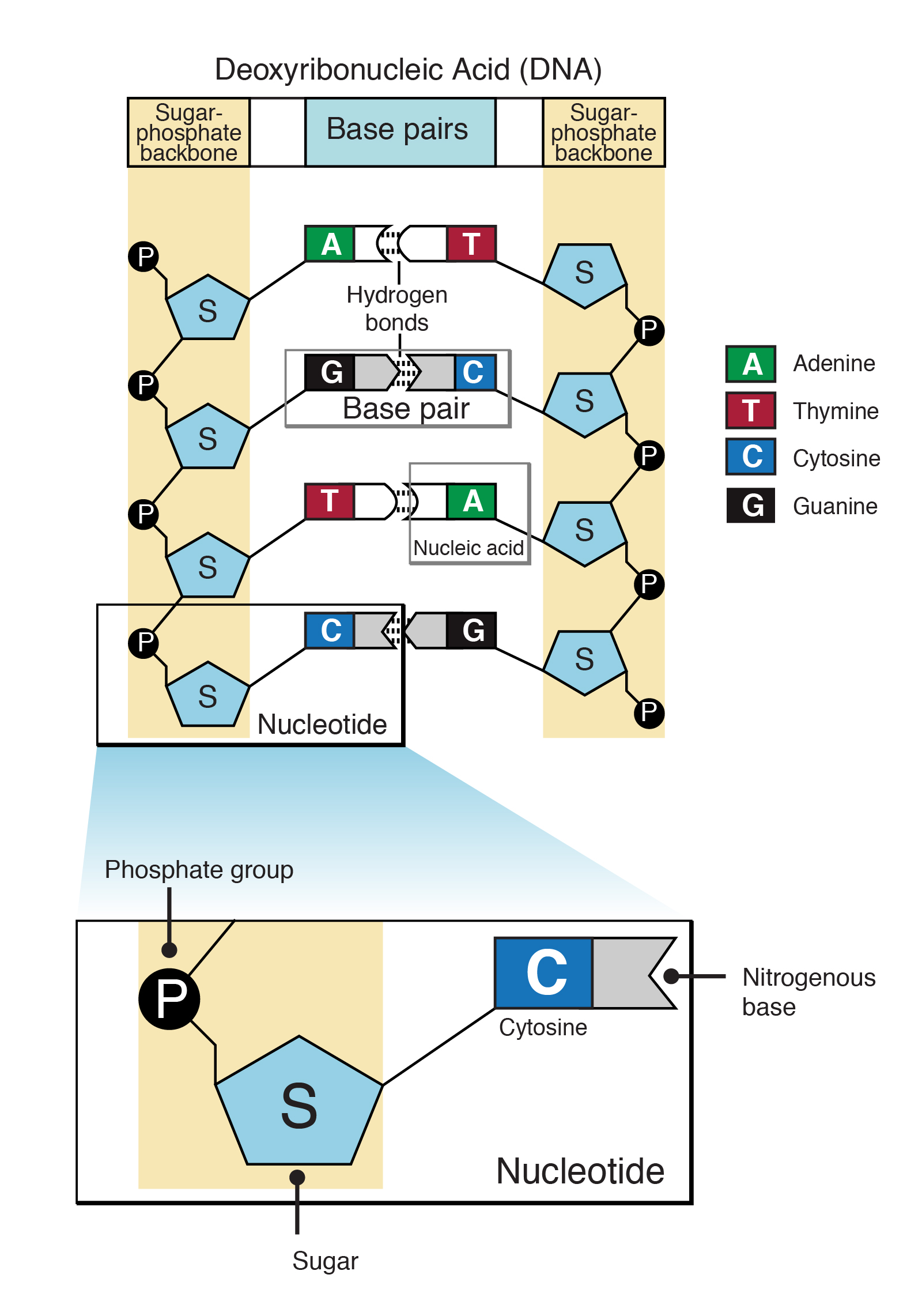
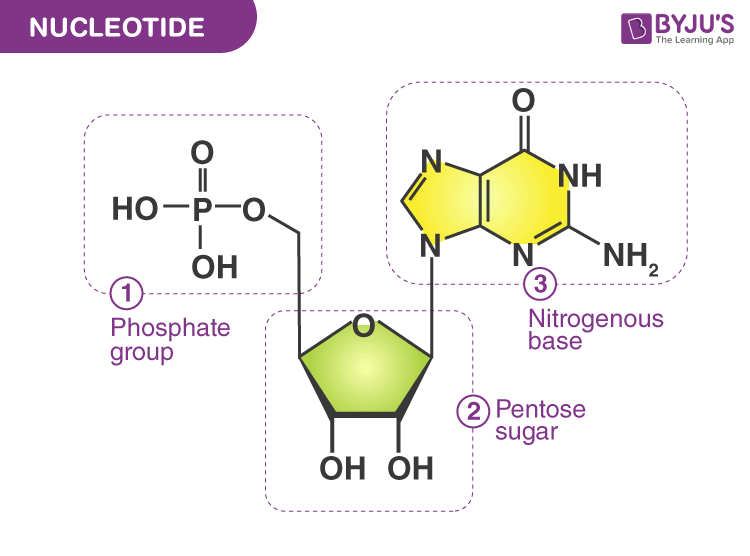
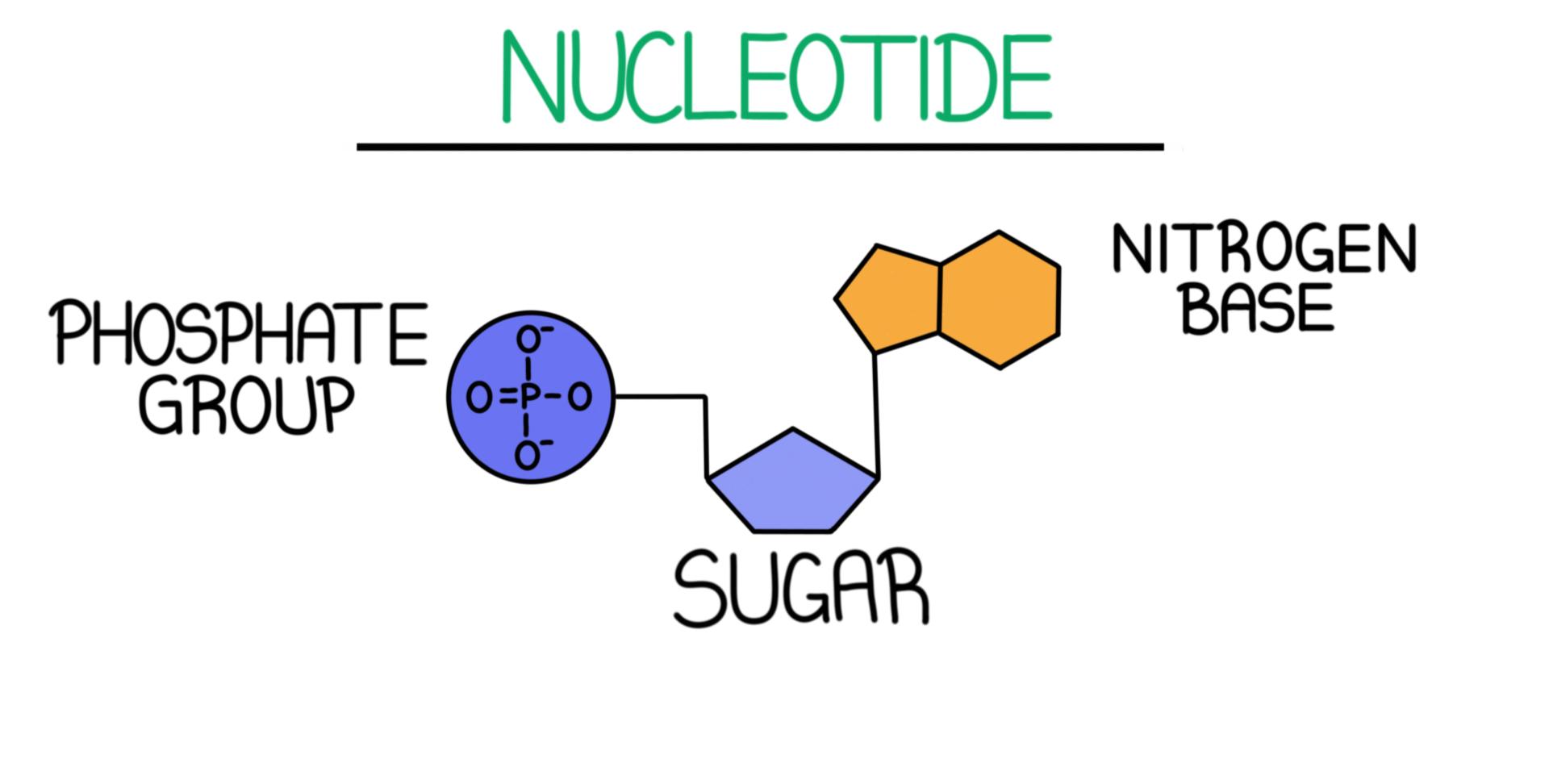
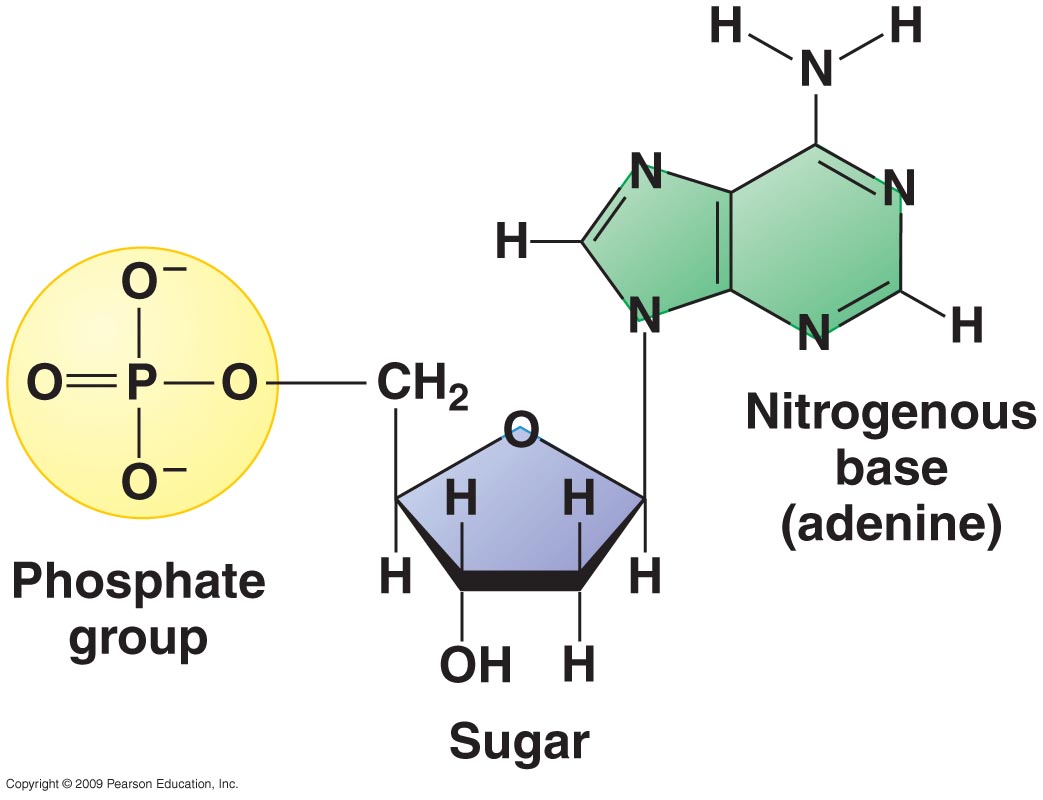
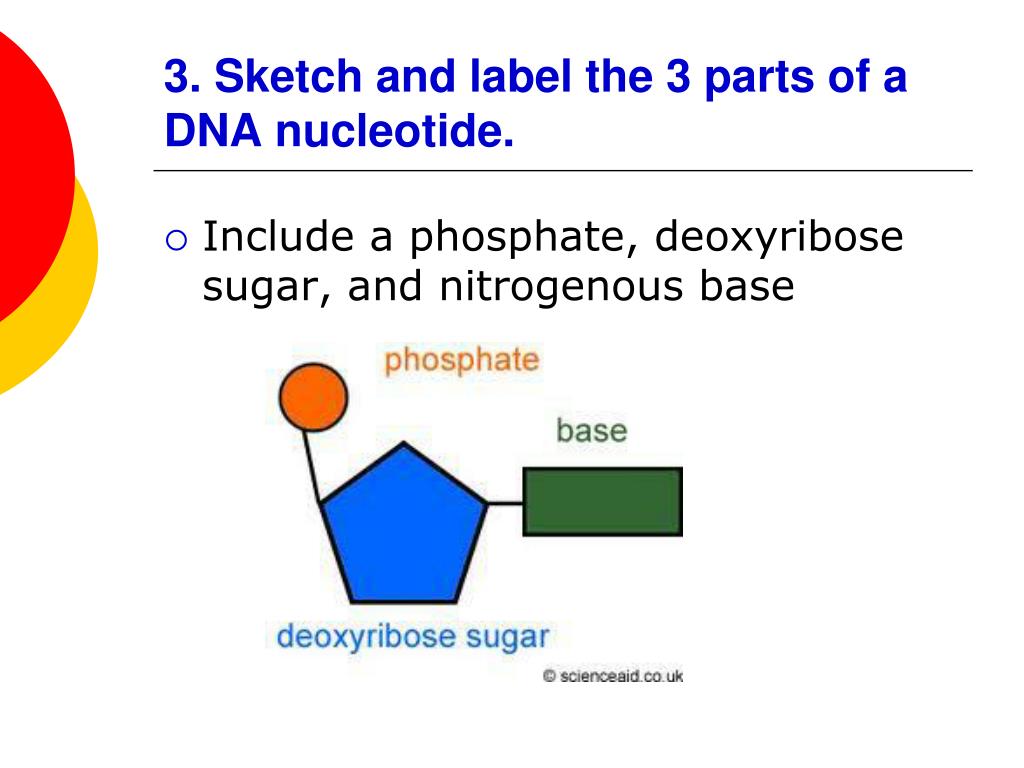
A sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase. The major groove is a wider gap that. Adenosine diphosphate (adp) and adenosine triphosphate (atp), shown in figure 7.10.3 7.10. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. Take a look at what a nucleotide is, its structure, and its function in biological processes. Include all parts of the dna molecule. Label the sugar, phosphate, and base. 2 the pyrimidine and purine nucleotides. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: The four nitrogenous bases in dna are adenine,.
A sugar, a phosphate group, and a nucleobase. Label the 5′ and 3′ ends of your mrna strand. Adenine and guanine are purines. (see lecture notes) learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the oh group on the 3' carbon atom of the sugar unit of a second nucleotide. Adenine (a), guanine (g) cytosine (c), and thymine (t). 3, have a role in cell metabolism. Draw a nucleotide and label all parts. Web using this strand of dna as a template, draw a picture of the complete dna molecule. Dna and rna code genetic information, transport energy throughout cells, and serve as cell signaling molecules.
Nucleic Acids Function, Examples, and Monomers
Now draw a complete picture of the mrna strand that will be made from this dna. Dna and rna code genetic information, transport energy throughout cells, and serve as cell signaling molecules. 2 the pyrimidine and purine nucleotides. Here is a closer look at the components of a nucleotide. Nucleotides are ubiquitous in biology, serving as the foundation of genetic.
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the oh group on the 3' carbon atom of the sugar unit of a second nucleotide. Now draw a complete picture of the mrna strand that will be made from this dna. The four nitrogenous bases in dna are adenine,. Here’s the best.
Nucleotide Structure, Examples and Function
Here is a closer look at the components of a nucleotide. Dna, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of nucleotides forming a double helix structure. Adenine and guanine are purines. The most commonly occurring pyrimidines in dna are cytosine and thymine: Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains deoxyribose sugar and rna (ribonucleic acid) contains a ribose sugar.
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
Web a nucleotide is an organic molecule made of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate group. Label the sugar, phosphate, and base. The sugar molecule has a central position in the nucleotide, with the base attached to one of its carbons and the phosphate group (or groups) attached to another. Include all parts of the dna molecule. Adenosine diphosphate.
DNA Structure — Overview & Diagrams Expii
The above structure is a #color (magenta)nucleotide#. Web the three parts of a nucleotide are the base, the sugar, and the phosphate. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. This unit joins to a third nucleotide, and the process is repeated to produce a long nucleic acid chain (figure. Color (orange)phosphate group color (red)5.
What is Three Parts of Nucleotide ? DNA and RNA
In contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like use a venn diagram to compare and contrast dna and rna, explain the base pairing rules of dna. Adenosine diphosphate (adp) and adenosine triphosphate (atp), shown in figure 16.6.3 16.6. Web the three parts of a nucleotide.
What Are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide?
Draw a nucleotide and label all parts. The most commonly occurring purines in dna are adenine and guanine: A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains deoxyribose sugar and rna (ribonucleic acid) contains a ribose sugar. In dna, the bases are adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g), and cytosine.
Draw And Label Three Parts Of Nucleotide
The major groove is a wider gap that. Web now let’s consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). A nitrogenous base attached with the sugar is called “nucleoside”. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: Draw the structure for the ump nucleotide.
What Are Three Parts Of A Dna Nucleotide And How Are They Connected
Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. The most commonly occurring purines in dna are adenine and guanine: The major groove is a wider gap that. Web now let’s consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Apart from being the monomer units of dna and rna, the nucleotides and some of.
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected
2 the pyrimidine and purine nucleotides. Adenosine diphosphate (adp) and adenosine triphosphate (atp), shown in figure 7.10.3 7.10. The sugar molecule has a central position in the nucleotide, with the base attached to one of its carbons and the phosphate group (or groups) attached to another. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and.
Take A Look At What A Nucleotide Is, Its Structure, And Its Function In Biological Processes.
(see lecture notes) learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Adenine (a), guanine (g) cytosine (c), and thymine (t). Here’s the best way to solve it. Adenosine diphosphate (adp) and adenosine triphosphate (atp), shown in figure 16.6.3 16.6.
A Nucleotide Is Made Up Of Three Parts:
See below the above structure is a color (magenta)nucleotide. Web each nucleotide is made up of three parts: Nucleotides contain a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. A nucleotide comprises a pentose sugar.
Web Now Let’s Consider The Structure Of The Two Types Of Nucleic Acids, Deoxyribonucleic Acid (Dna) And Ribonucleic Acid (Rna).
Adenosine diphosphate (adp) and adenosine triphosphate (atp), shown in figure 7.10.3 7.10. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like use a venn diagram to compare and contrast dna and rna, explain the base pairing rules of dna. This unit joins to a third nucleotide, and the process is repeated to produce a long nucleic acid chain (figure. Apart from being the monomer units of dna and rna, the nucleotides and some of their derivatives have other functions as well.
Web Now Let’s Consider The Structure Of The Two Types Of Nucleic Acids, Deoxyribonucleic Acid (Dna) And Ribonucleic Acid (Rna).
The building blocks of dna are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: Adenine and guanine are purines. Dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains deoxyribose sugar and rna (ribonucleic acid) contains a ribose sugar. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)


/what-are-the-parts-of-nucleotide-606385-FINAL-5b76fa94c9e77c0025543061.png)
/Nucleotide-58e518d35f9b58ef7e62834d.jpg)