Drawing Of Cell Cycle
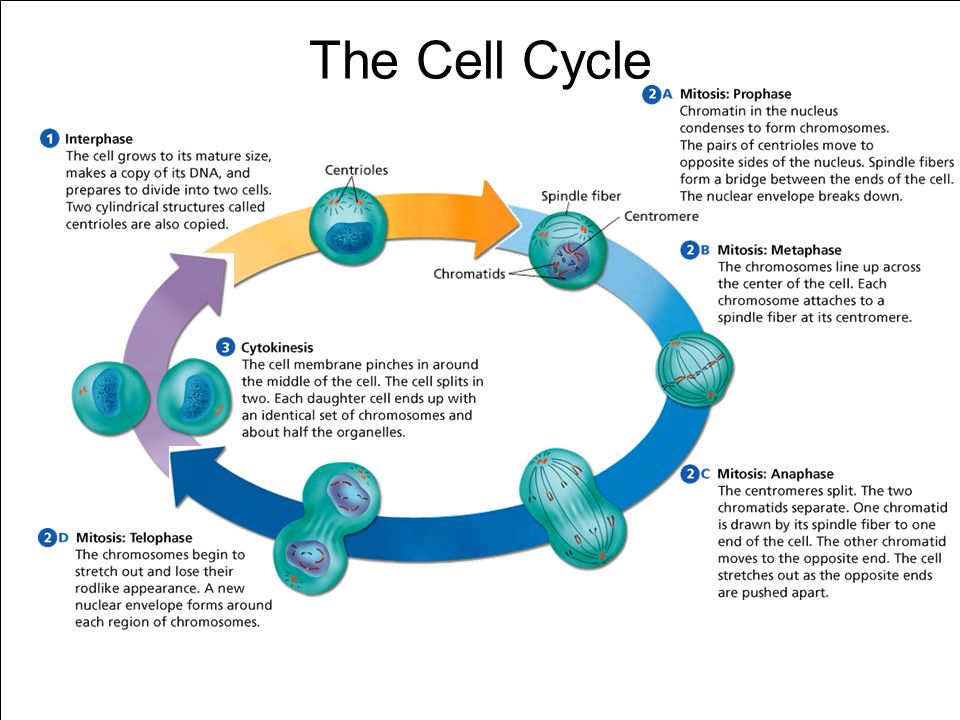
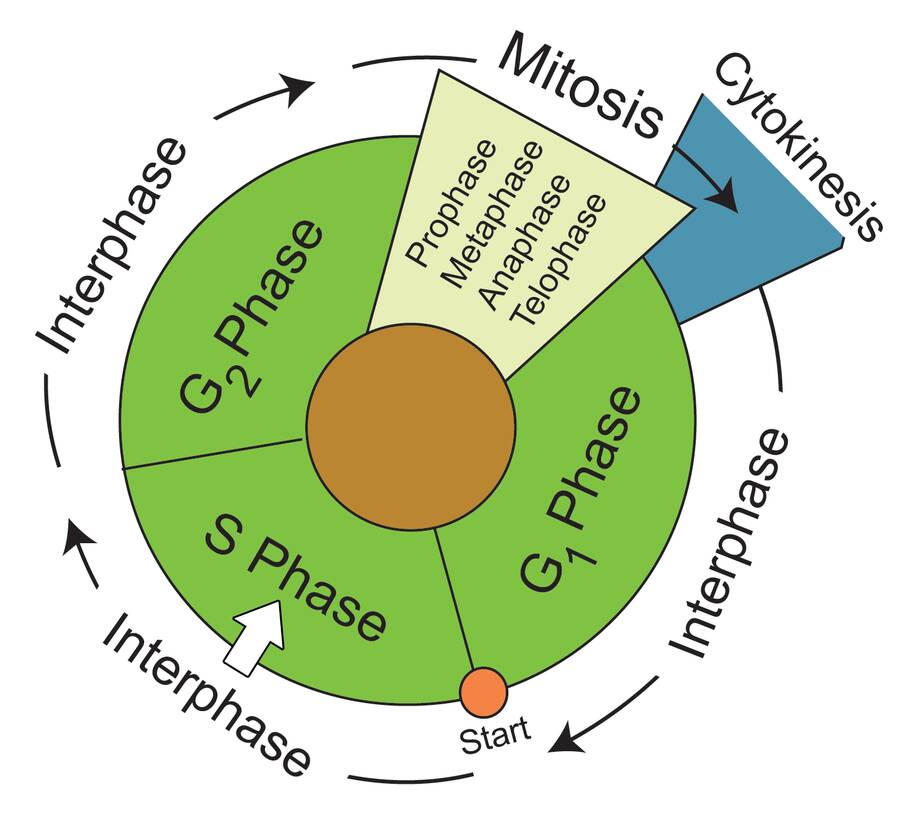
Drawing Of Cell Cycle - The cycle begins at the end of each nuclear division and ends with the beginning of the next. From g0, the cell can undergo terminal differentiation. Web mitosis consists of four basic phases: During mitosis, chromosomes will align, separate, and move into new daughter cells. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated, and the cell divides. Web cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). The first stages of the cell cycle involve cell growth, then. The g 1, s, and g 2 phases.
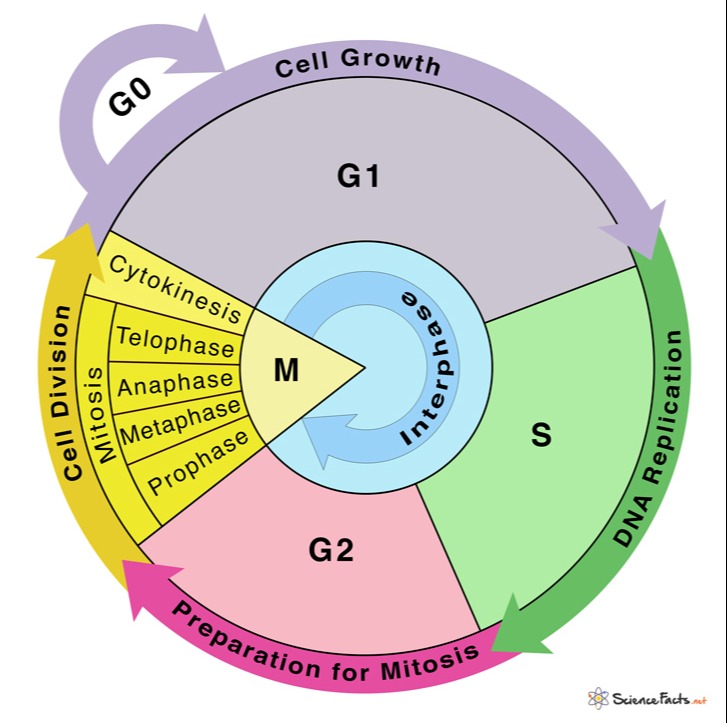
Web the cell cycle has two major phases: A cell spends most of its life in interphase, which has three phases: Web practice identifying the various stages of the cell cycle, using the drawings of the stages as a guide (figure 10.6). Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. During the mitotic phase, the replicated dna and cytoplasmic contents are separated, and the cell divides. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. Cells perform these tasks in an organized, predictable series of steps that make up the cell cycle. The two broad phases of the cell cycle are interphase and mitosis. The video quality is not the greatest but if you follow along i highlight some key features fo. Web define the quiescent g 0 phase.
In the g1 phase, the cell grows and takes in nutrients. The two broad phases of the cell cycle are interphase and mitosis. Web the cell cycle is defined as the events that enable cells to proceed from one cell division event to the next. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle. After completing the cycle it either starts the process again from g1 or exits through g0. A cell spends most of its life in interphase, which has three phases: Web an overview of the cell cycle. This is when the cell grows and copies its dna before moving into mitosis. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. The single strand of dna that makes up each chromosome produces an exact copy of itself.
Cell Cycle Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
Cells perform these tasks in an organized, predictable series of steps that make up the cell cycle. Web an overview of the cell cycle. A cell cycle is thus a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides to produce new cells. The video quality is not the greatest but if you follow along i.
6.2 The Cell Cycle Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
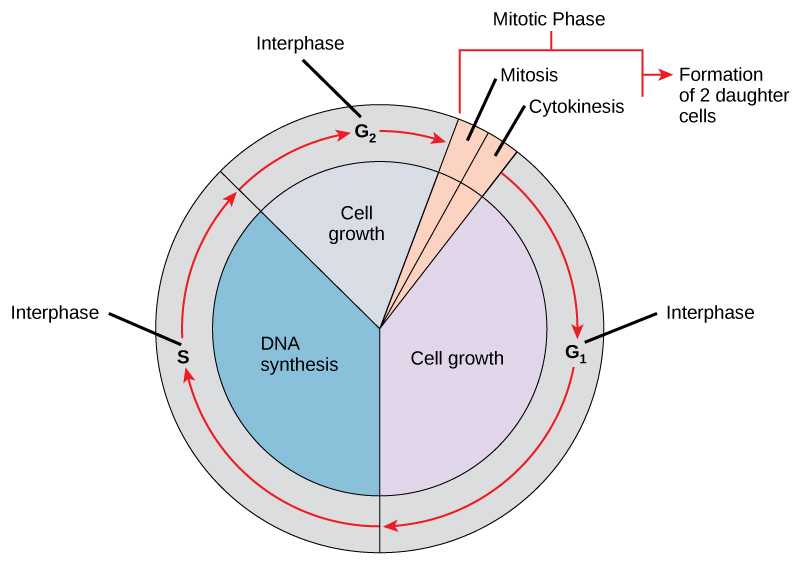
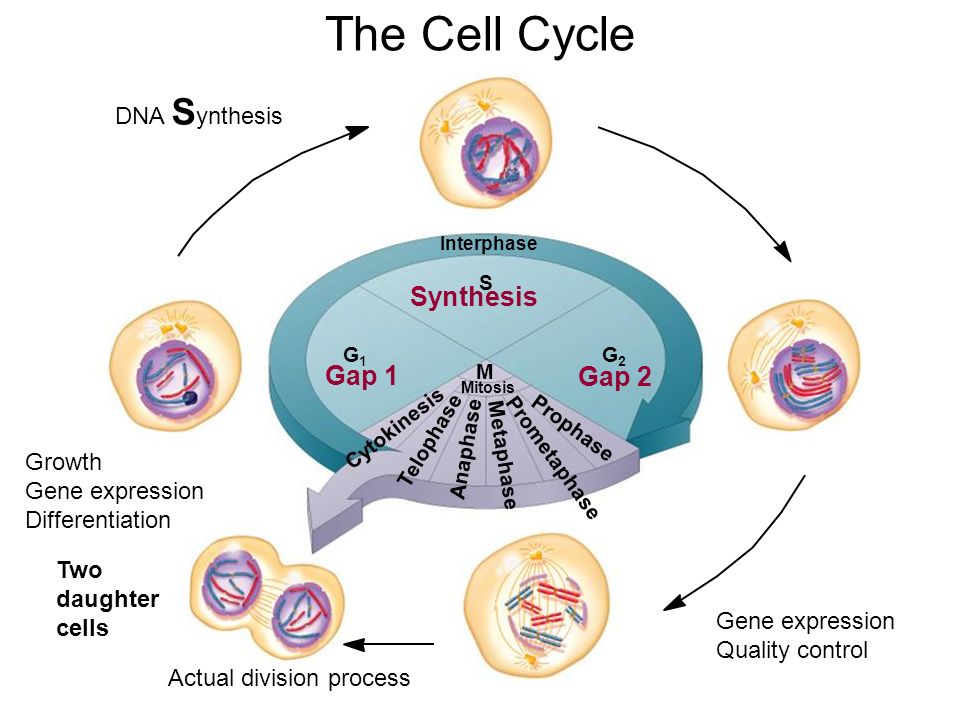
In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Interphase steps are the first gap phase (g 1 ), the synthesis phase (s), and the second gap phase (g 2 ). This cell cycle is used.
The Cell Cycle Study Guide Inspirit
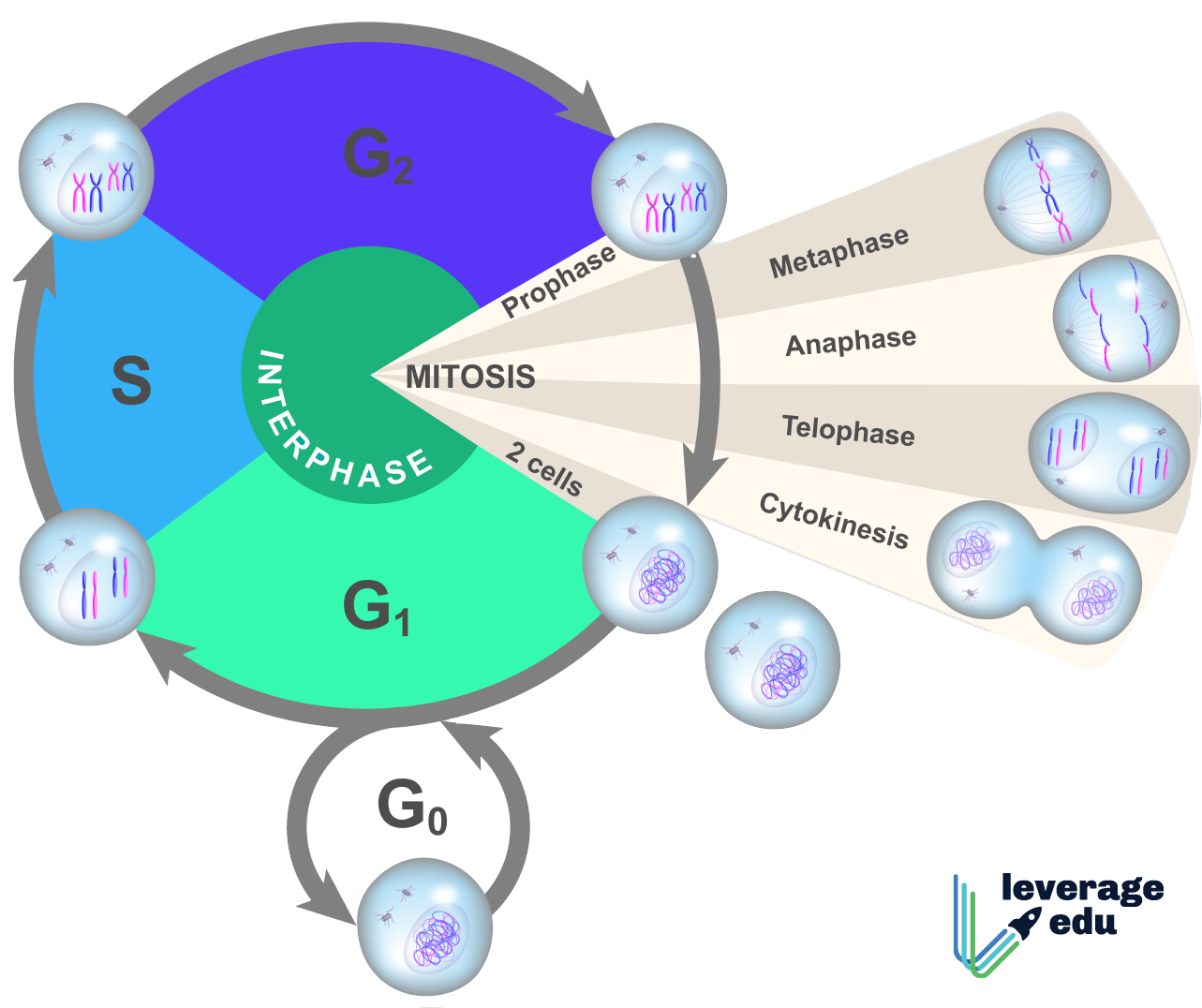
From g0, the cell can undergo terminal differentiation. Web the cell cycle has two major phases: Each replicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere. Web the cell cycle is defined as the events that enable cells to proceed from one cell division event to the next. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2.
Phases of the cell cycle 6894530 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Web in eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of four discrete phases: Once you are confident about your identification, begin to record the stage of each cell you encounter as you scan left to right, and top to bottom across the blastula section. Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). Web an overview of the cell cycle. The single strand of.
Cell Cycle Diagram Quizlet
Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages. The cycle begins at the end of each nuclear division and ends with the beginning of the next. Web mitosis consists of four basic phases: Cells divide during mitosis (m).
Cell Division An Intro AmoebaMike
It must grow, copy its genetic material (dna), and physically split into two daughter cells. The video quality is not the greatest but if you follow along i highlight some key features fo. Web overview of the cell cycle phases. The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter.
Cell Biology, Mitosis Cell Cycle
Each replicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere. Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. Web the cell cycle has two major phases: In eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle is divided into two major phases: From g0, the cell can undergo terminal differentiation.
Regulation of the cell cycle, DNA synthesis phase, Interphase & Mitosis
Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). Cells perform these tasks in an organized, predictable series of steps that make up the cell cycle. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Some textbooks list five, breaking prophase into an early phase (called prophase) and a late phase (called prometaphase). Web practice identifying the various stages of.
The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology
The single strand of dna that makes up each chromosome produces an exact copy of itself. Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). From g0, the cell can undergo terminal differentiation. Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). During mitosis, chromosomes will align, separate, and move into new daughter cells.
Phases of Cell Cycle01 Leverage Edu
In the g1 phase, the cell grows and takes in nutrients. Once you are confident about your identification, begin to record the stage of each cell you encounter as you scan left to right, and top to bottom across the blastula section. The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in.
Interphase Steps Are The First Gap Phase (G 1 ), The Synthesis Phase (S), And The Second Gap Phase (G 2 ).
During interphase, the cell grows and dna is replicated. This cell cycle is used by all eukaryotic cells to produce new cells. Each replicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere. This video walks through drawing the stages of the cell cycle.
During Interphase, The Cell Grows And Dna Is Replicated.
The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. During mitosis, chromosomes will align, separate, and move into new daughter cells. Web overview of the cell cycle phases. The products formed in each round replicate the process in the next round.
Web Practice Identifying The Various Stages Of The Cell Cycle, Using The Drawings Of The Stages As A Guide (Figure 2).
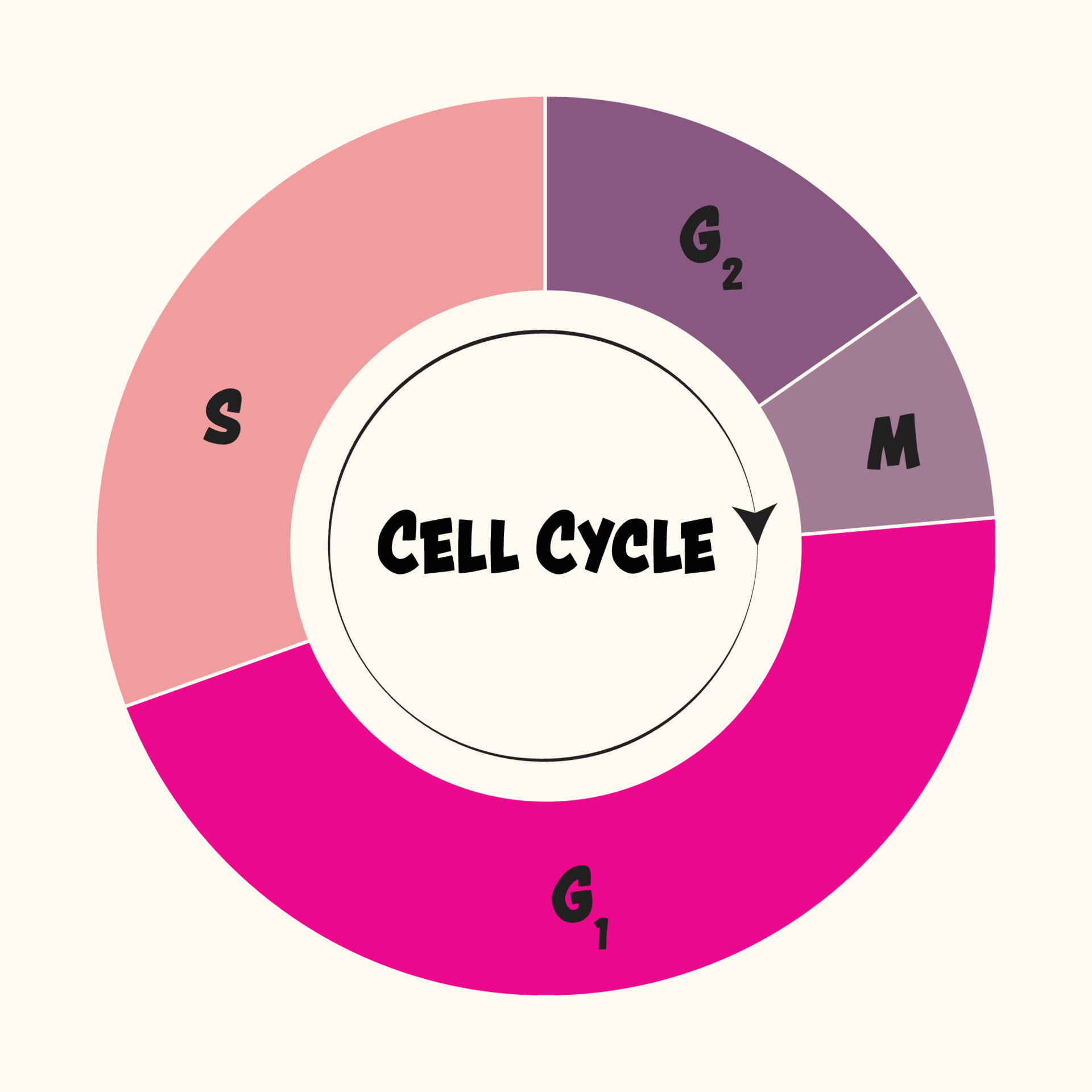
Learn more about the cell cycle and the proteins that regulate its progression. Interphase and the mitotic phase (figure 1). In the g1 phase, the cell grows and takes in nutrients. The small section labeled “m” represents mitosis, while interphase is shown subdivided into its major components:
Interphase And Mitosis (Or The Mitotic (M) Phase).
The first stages of the cell cycle involve cell growth, then. The g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Web © 2024 google llc. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle.