Drawing Of Phospholipid
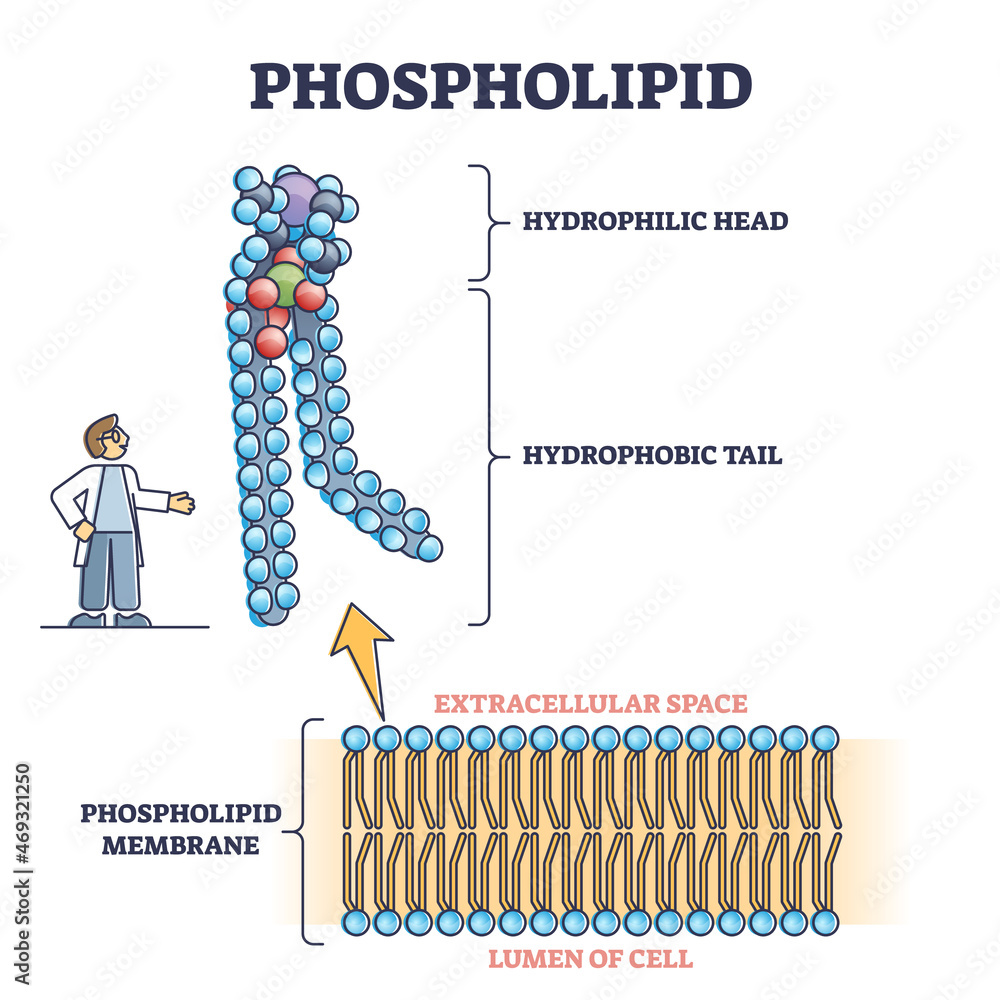
Drawing Of Phospholipid - The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water ( hydrophilic ). The phospholipid bilayer with hydrophobic 'tails' and hydrophilic 'heads' of the phospholipid.more. Their hydrophobic tails facing inwards and hydrophilic heads outwards. Phospholipids are amphipathic (they have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts) It is made of a phospholipid bilayer, along with other various lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Explain how the phospholipid molecules form the bilayer of the cell membrane. Lipids are molecules that include fats, waxes, and some vitamins, among others. Web (a) an electron micrograph of unfixed, unstained phospholipid vesicles—liposomes—in water rapidly frozen to liquid nitrogen temperature. Web the cell membrane provides a barrier around the cell, separating its internal components from the extracellular environment. Web a phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane.
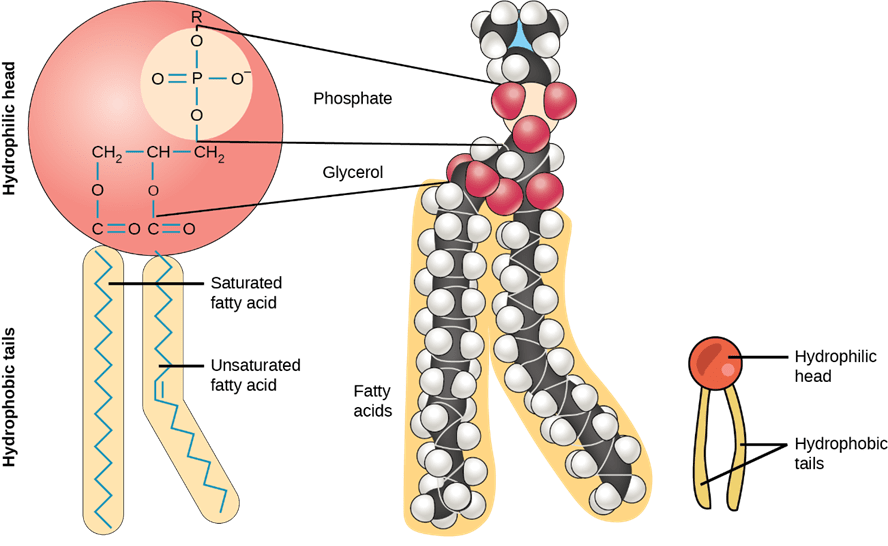
The two tails are made up of fatty acids (chains of carbon atoms) that aren’t compatible with, or repel, water ( hydrophobic ). The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water ( hydrophilic ). Just to briefly remind us, our phospholipid is often drawn like this. Created by william tsai.watch the next lesson: Web phospholipids are a very important class of lipids containing phosphorous bound in a diester linkage. It has that polar phosphate head group, and it has two fatty acid chains. Web a phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule which means it has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic component. The bilayer structure of the liposomes is readily apparent. They have fatty acid tails that are hydrophobic and a phosphate head, that is hydrophilic, attached to a glycerol molecule. Web phospholipids are the major components of cell surface membranes.
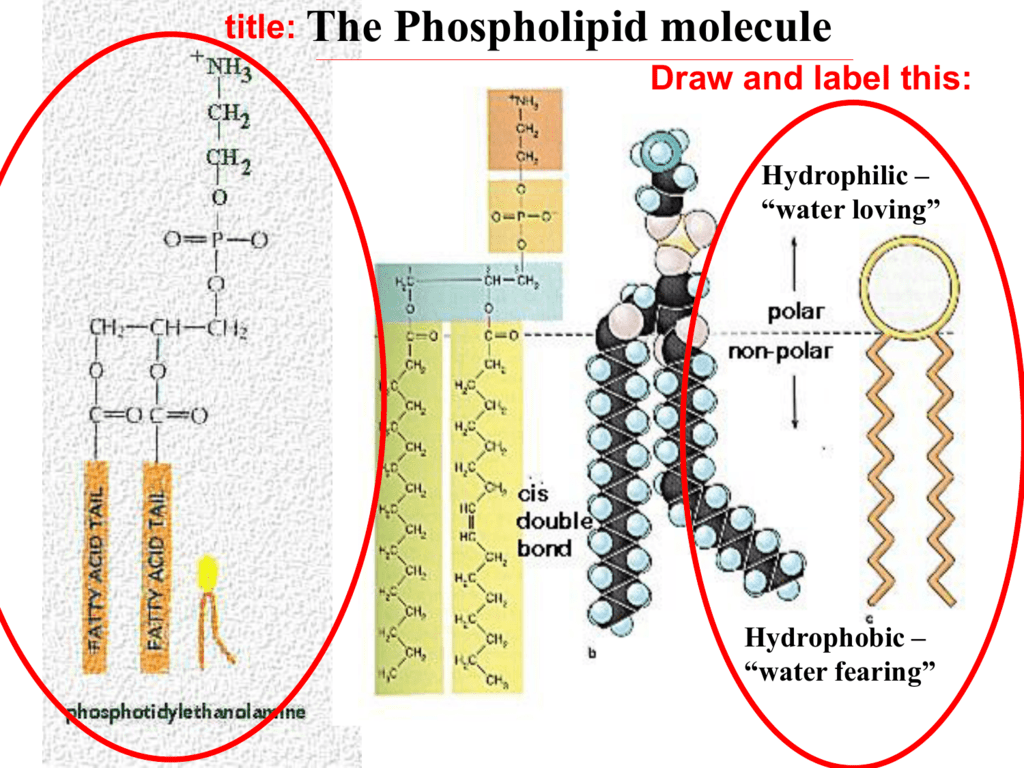
Phospholipids are compound/complex lipids containing lipid molecules attached to a phosphate group. Web a diagram of a plasma membrane shows a phospholipid bilayer with 3 proteins embedded in the bilayer. Web phospholipids [1] are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic head containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic tails derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Created by william tsai.watch the next lesson: Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic sections. The two layers of phospholipids are loosely held together by weak hydrophobic interactions between the hydrocarbon tails allowing some membrane fluidity. Phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phospholipid molecules. Explain how the phospholipid molecules form the bilayer of the cell membrane. The head and the two tails. Web phospholipids are the major components of cell surface membranes.
Phospholipid Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Web phospholipids [1] are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic head containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic tails derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). The head and the two tails. Web a phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule which means it has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic component. Web.
On the back of it draw and label the phospholipid
There are two important parts of a phospholipid: A bilayered membrane consisting of phospholipids arranged in two layers, with their heads pointing out and their tails sandwiched in the middle, is also. The phospholipids are very important structural components of all cell membranes including those of the cell organelles. Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic sections. Web (a) an electron micrograph.
Lipids Microbiology
One of the proteins is shown with a channel in it. Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic sections. Web in this video, we're going to actually explore in detail the structure of phospholipids in our cell membrane. Web phospholipids [1] are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic head containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic tails derived from.
Phospholipid or phosphatides lipids microscopical structure outline
They have fatty acid tails that are hydrophobic and a phosphate head, that is hydrophilic, attached to a glycerol molecule. Web structure of a phospholipid, showing hydrophobic fatty acid tails and hydrophilic head (including ester linkages, glycerol backbone, phosphate group, and attached r group on phosphate group). It is made of a phospholipid bilayer, along with other various lipids, proteins,.
14.3 Phospholipids in Cell Membranes Chemistry LibreTexts
Web when drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include: Explain how the phospholipid molecules form the bilayer of the cell membrane. Web describe the structure of a phospholipid. There are two important parts of a phospholipid: Web phospholipids [1] are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic head containing a.
Phospholipid Structure Labeling Diagram Quizlet
Web structure of a phospholipid, showing hydrophobic fatty acid tails and hydrophilic head (including ester linkages, glycerol backbone, phosphate group, and attached r group on phosphate group). Web the cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). Web learn about the detailed structure of phospholipids in the cell membrane. Just to briefly remind us, our phospholipid is often drawn like this..
How to Draw a Phospholipid Bilayer YouTube
1.3.u1 phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phosphlipid molecules. Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic sections. Web the cell membrane provides a barrier around the cell, separating its internal components from the extracellular environment. Web it discusses the basic structure and functions of lipids such as fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, terpenes, waxes, and eicosanoids which include.
3.5C Phospholipids Biology LibreTexts
A bilayered membrane consisting of phospholipids arranged in two layers, with their heads pointing out and their tails sandwiched in the middle, is also. The two layers of phospholipids are loosely held together by weak hydrophobic interactions between the hydrocarbon tails allowing some membrane fluidity. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, with hydrophobic internal lipid “tails” and hydrophilic external.
Phospholipid or phosphatides lipids head and tail structure outline
Web when drawing and labeling a diagram of the plasma membrane you should be sure to include: Web structure of a phospholipid, showing hydrophobic fatty acid tails and hydrophilic head (including ester linkages, glycerol backbone, phosphate group, and attached r group on phosphate group). Web (a) an electron micrograph of unfixed, unstained phospholipid vesicles—liposomes—in water rapidly frozen to liquid nitrogen.
Phospholipid Structure Diagram
The head and the two tails. Web draw the general structure of a phosphoglyceride. Explain how the phospholipid molecules form the bilayer of the cell membrane. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. Phospholipids are amphipathic (they have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts)
Click The Card To Flip 👆.
Created by william tsai.watch the next lesson: Web phospholipids are a very important class of lipids containing phosphorous bound in a diester linkage. Web a phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule which means it has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic component. Just to briefly remind us, our phospholipid is often drawn like this.
Web Describe The Structure Of A Phospholipid.
Explain how the phospholipid molecules form the bilayer of the cell membrane. (b) a drawing of a small spherical liposome The bilayer structure of the liposomes is readily apparent. The phospholipid bilayer with hydrophobic 'tails' and hydrophilic 'heads' of the phospholipid.more.
They Have Fatty Acid Tails That Are Hydrophobic And A Phosphate Head, That Is Hydrophilic, Attached To A Glycerol Molecule.
The hydrophilic (polar) head group and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains) are depicted in. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. Web the cell membrane is semipermeable (or selectively permeable). The head and the two tails.
Web The Cell Membrane Provides A Barrier Around The Cell, Separating Its Internal Components From The Extracellular Environment.
1.3.u1 phospholipids form bilayers in water due to the amphipathic properties of phosphlipid molecules. Web in this video, we're going to actually explore in detail the structure of phospholipids in our cell membrane. Web draw a diagram of a single phospholipid molecule. Describe the occurrence and importance of phosphoglycerides in plant and animal tissues.