Epidermis Drawing
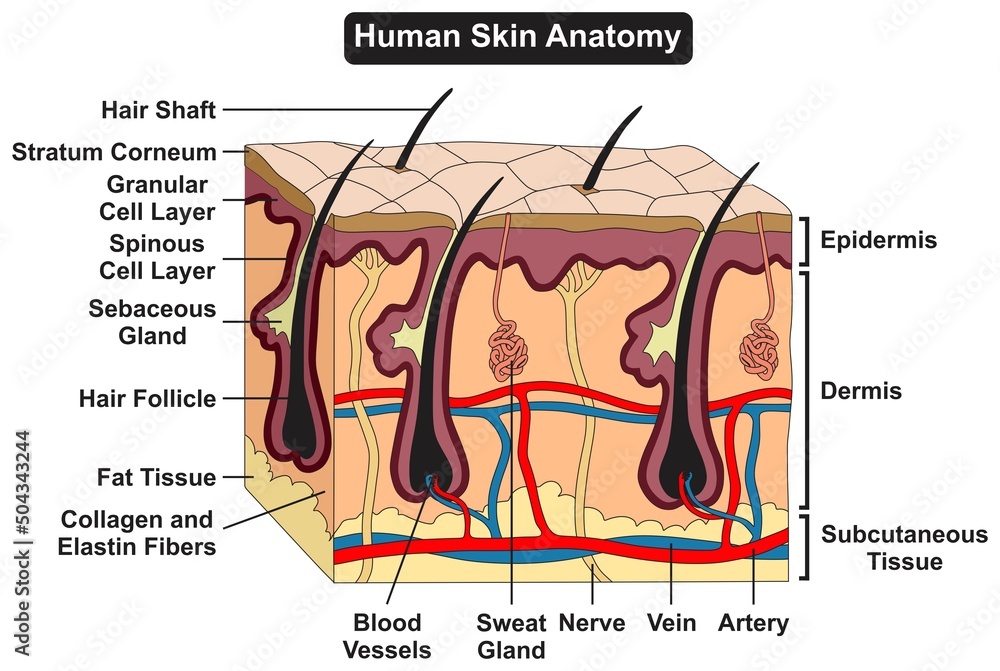
Epidermis Drawing - Drawing shows normal skin anatomy, including the epidermis, dermis, hair follicles, sweat glands, hair shafts, veins, arteries, fatty tissue, nerves, lymph vessels, oil glands, and subcutaneous tissue. Web diagram of human skin structure. The epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. The epidermis includes five main layers: The skin is composed of two main layers: Web your drawing with the epidermis, dermis (papillary layer), blood vessels, and dermis (reticular layer). It forms the outer covering for the entire body and protects the internal tissues from the external environment. Sectional view of the skin.comparison. Anatomy of the skin with merkel cells; Web the skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area.
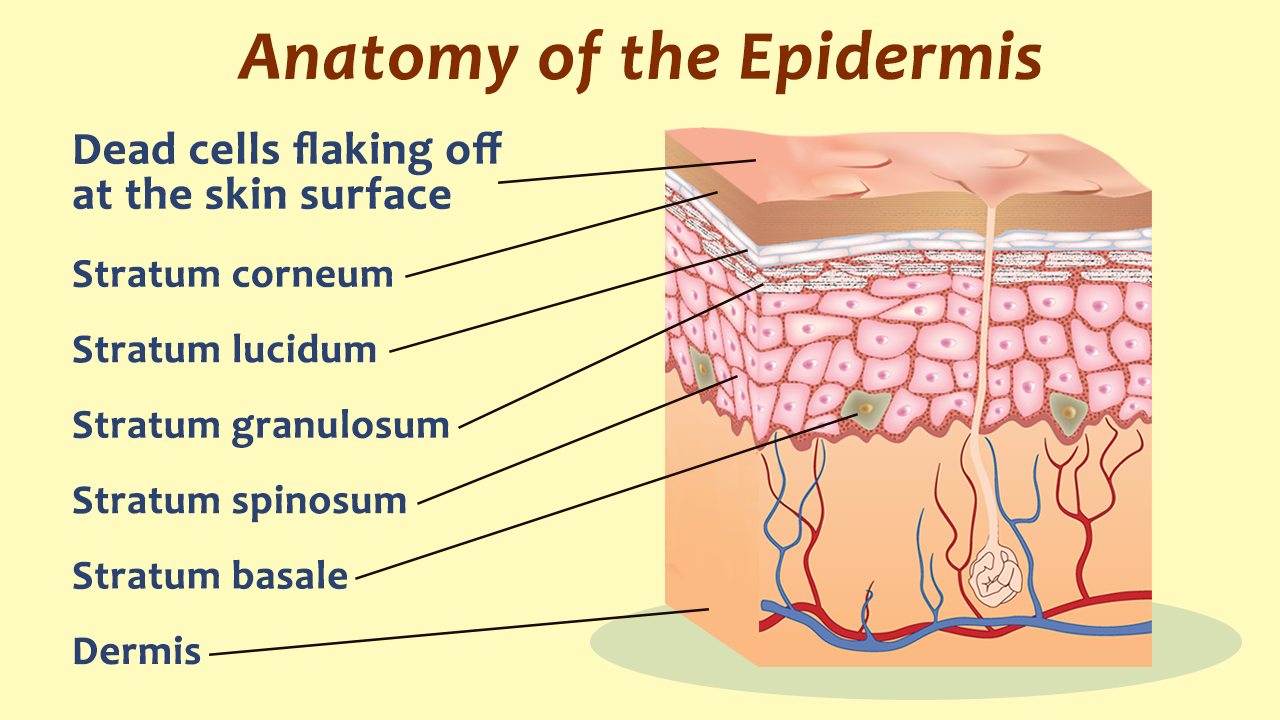
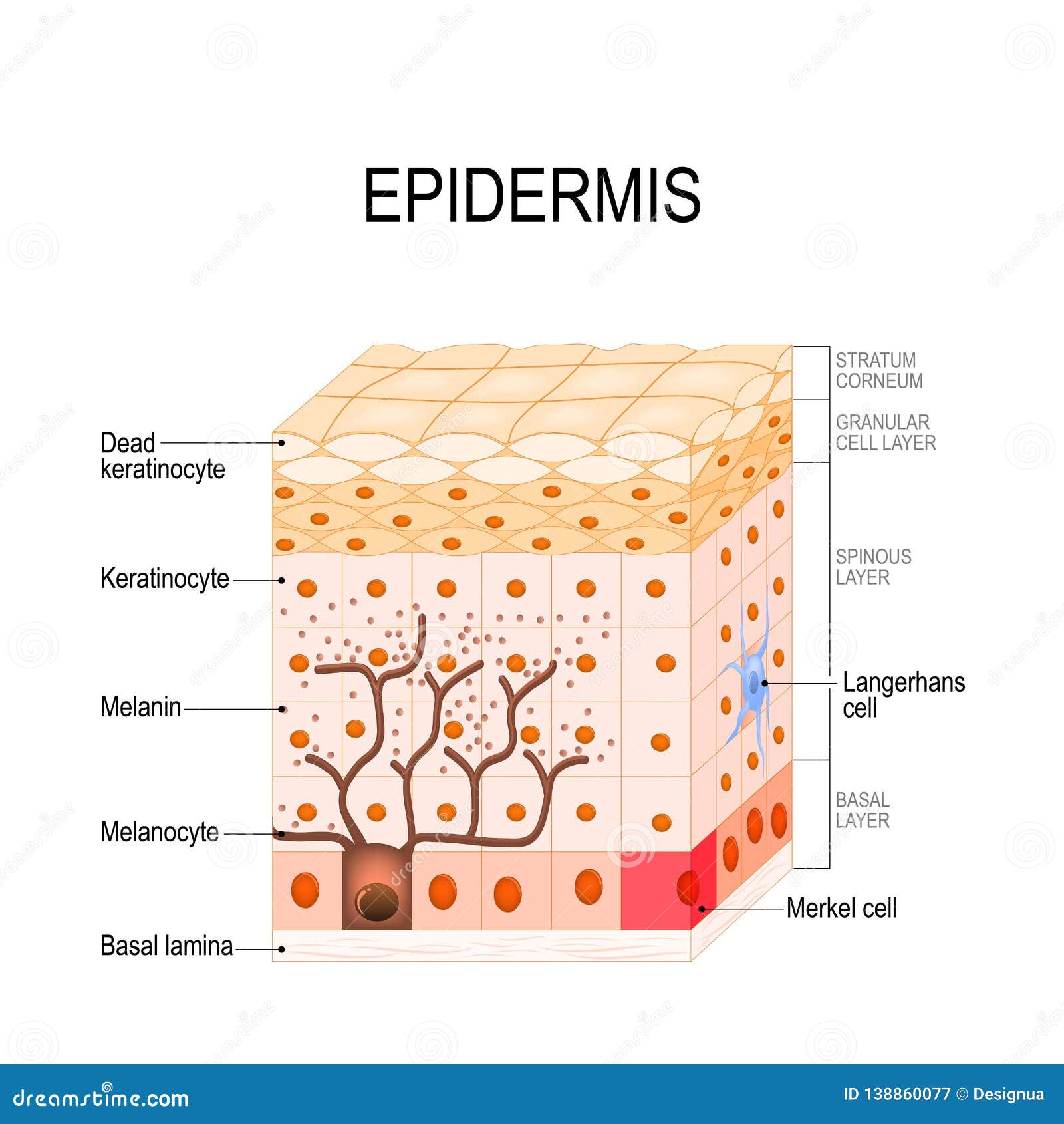
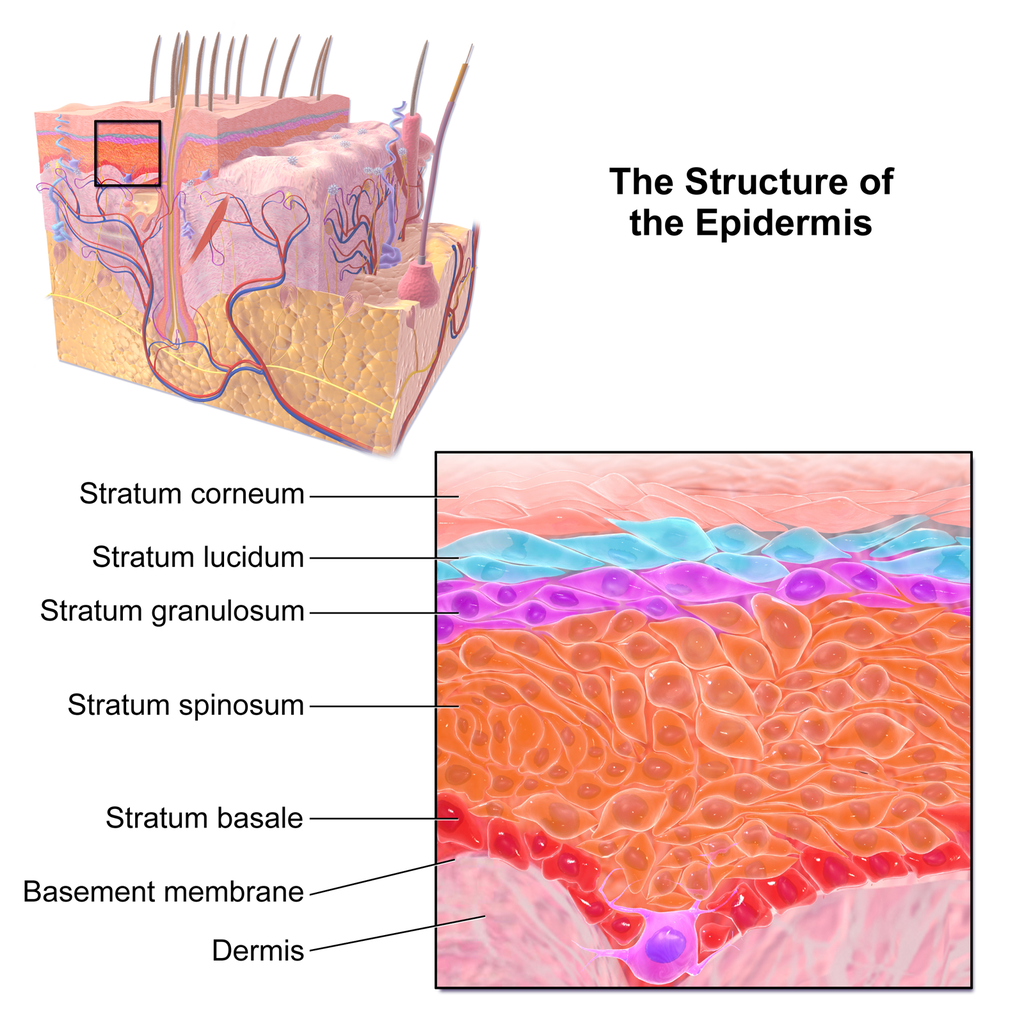
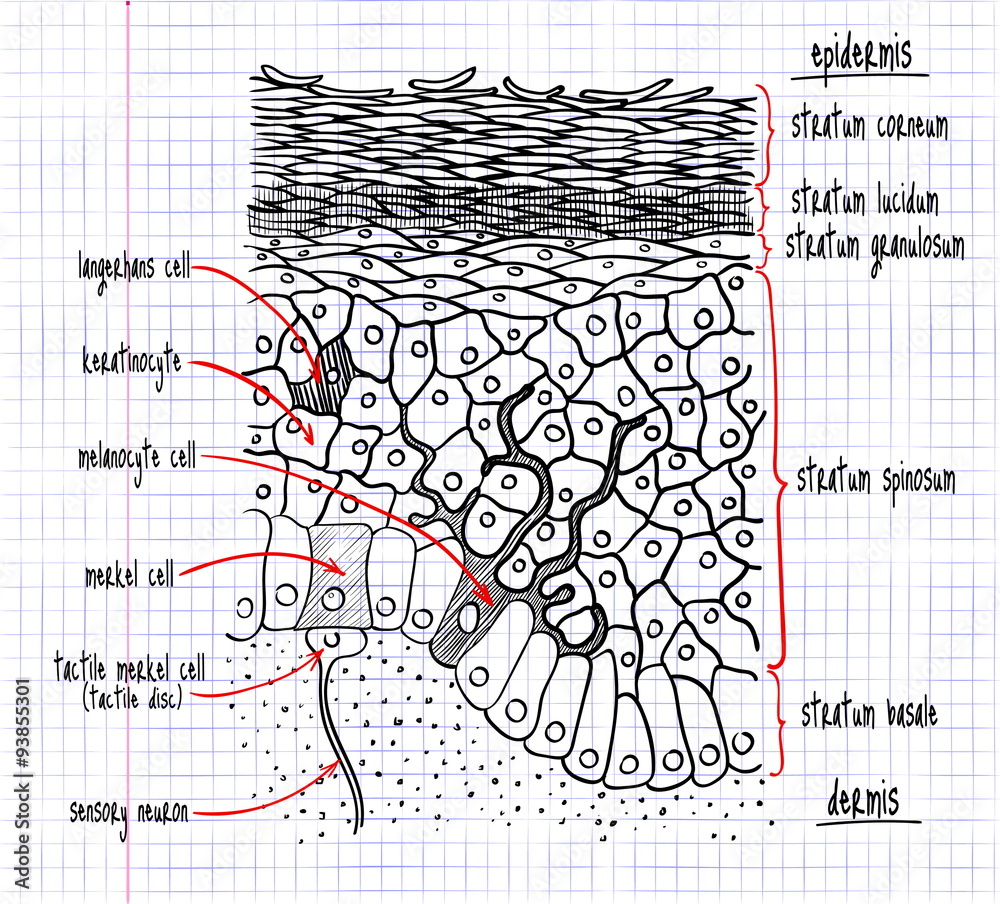
Web skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface. Anatomy of the skin with merkel cells; The cells in the stratum basale bond to the dermis via intertwining collagen fibers, referred to as the basement membrane. They are far away from any blood supply, causing a lack of nutrients. Skin w/ hair using colored pens/pencils, draw the histology image b from the “skin w/ hair” chart in the space below. The stratum basale (also called the stratum germinativum) is the deepest epidermal layer and attaches the epidermis to the basal lamina, below which lie the layers of the dermis. Web the skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. It is made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in their anatomy and function. They're exposed to harsh chemicals contained in soaps, lotions, and other products.
The epidermis includes five main layers: Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose. Using image a as a reference, label your drawing with the epidermis, dermis, hypodermis, hair follicle, and hair. Skin w/ hair using colored pens/pencils, draw the histology image b from the “skin w/ hair” chart in the space below. Literally covering you from head to toe. The thickness of the epidermis varies from 31.2μm for the penis to 596.6μm for the sole of the foot with most being. The cells in the stratum basale bond to the dermis via intertwining collagen fibers, referred to as the basement membrane. Web skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface. Sectional view of the skin.comparison illustration of protection effect between healthy skin and wounded skin. They are far away from any blood supply, causing a lack of nutrients.
Do You Know Your Skin? Layers of the Epidermis and their Functions
The epidermis is composed of layers of skin cells called keratinocytes. They are far away from any blood supply, causing a lack of nutrients. Drawing shows layers of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue including hair shafts and follicles, oil glands, lymph vessels, nerves, fatty tissue, veins, arteries, and a sweat gland. It forms the outer covering for the entire.
Vector illustration of Epidermis layers. Skin anatomy. Medical diagram
Sectional view of the skin.comparison illustration of protection effect between healthy skin and wounded skin. Web the skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area. The skin consists of two distinct layers: It forms the outer covering for the.
Structure of the epidermis medical vector illustration, dermis anatomy
It is made up of three layers, the epidermis, dermis, and the hypodermis, all three of which vary significantly in their anatomy and function. Web hello friends, this is my youtube channel and in this channel i used to share videos of different diagrams in easy way and step by step tutorials. Anatomy of the skin with merkel cells; Web.
Layers of the Epidermis Sketchy Medicine
The university of waikato te whare wānanga o waikato published 1 february 2011 size: The epidermis includes five main layers: Web your drawing with the epidermis, dermis (papillary layer), blood vessels, and dermis (reticular layer). Anatomy of the skin with merkel cells; So, five layers or strata, and each strata or.
Epidermis Structure. Cell, And Layers Of A Human Skin. Illustration
They're exposed to harsh chemicals contained in soaps, lotions, and other products. It forms the outer covering for the entire body and protects the internal tissues from the external environment. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose connective and fatty tissues. The skin is composed of two main layers: Web this article will describe the.
Human skin anatomy structure and parts infographic diagram epidermis
The university of waikato te whare wānanga o waikato published 1 february 2011 size: Literally covering you from head to toe. The skin's structure is made up of an intricate network which serves as the body’s initial barrier against pathogens, uv. A layer of our skin that is found on the palms of our hands and the soles of our.
Epidermis Definition, Anatomy and Function
100 kb referencing hub media. The epidermis is a tough coating formed from overlapping layers of dead skin cells. The skin consists of two distinct layers: A layer of our skin that is found on the palms of our hands and the soles of our feet. The epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense,.
10.3 Epidermis Human Biology
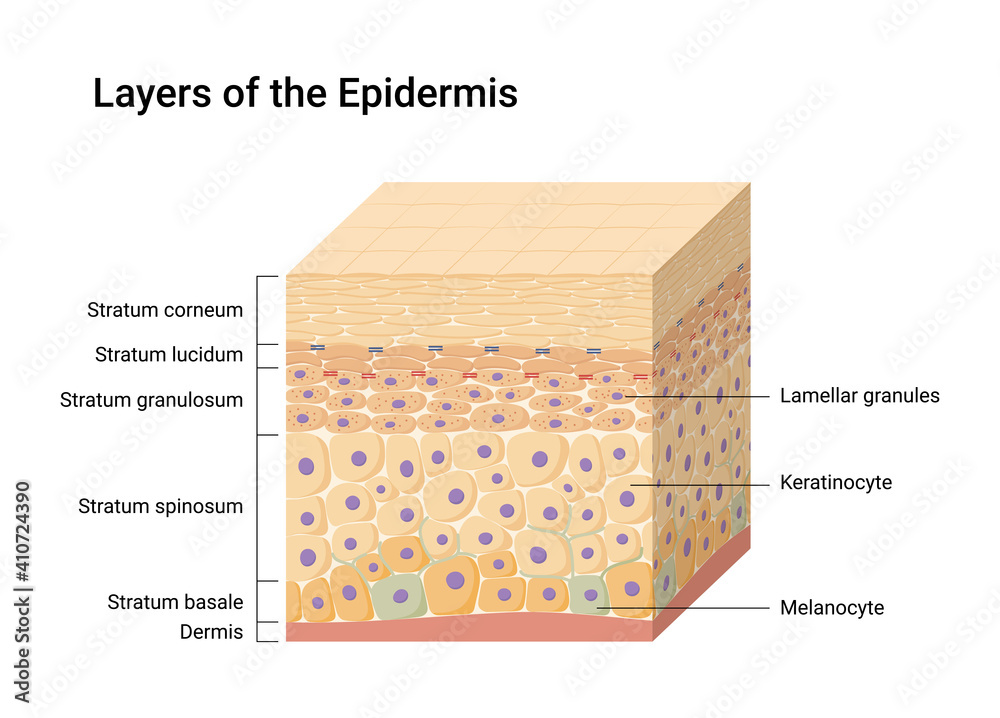
The cells in the stratum basale bond to the dermis via intertwining collagen fibers, referred to as the basement membrane. In addition, the epidermis continuously makes new skin that replaces the old skin cells and produces melanin that provides skin color. The stratum basale (also called the stratum germinativum) is the deepest epidermal layer and attaches the epidermis to the.
Epidermis Structure. Cell, And Layers Of A Human Skin. Stock Vector
Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose. A layer of our skin that is found on the palms of our hands and the soles of our feet. The epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures..
drawing of the structure of the human epidermis Stock Vector Adobe Stock
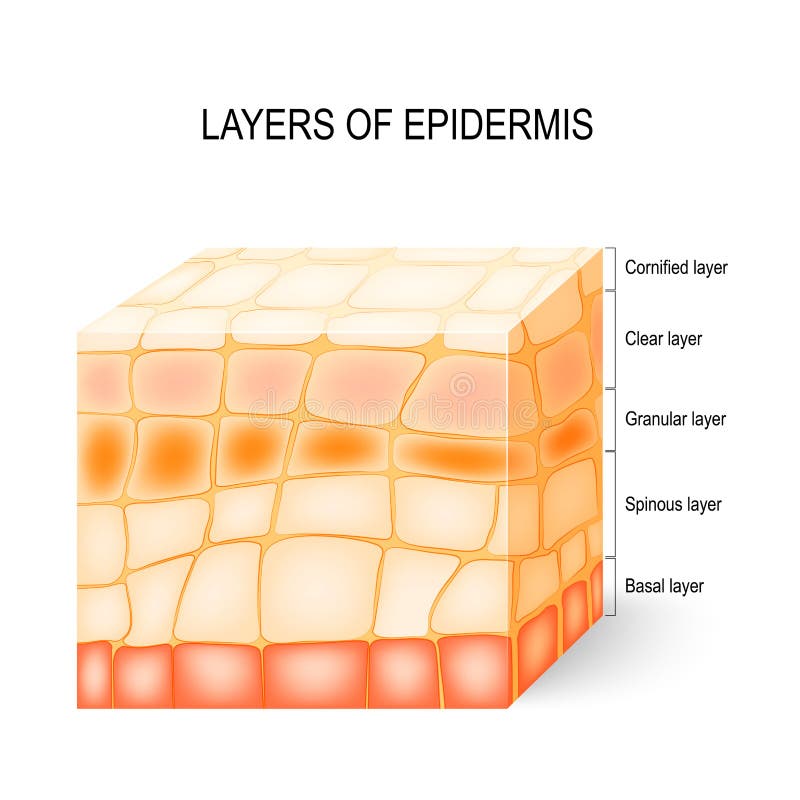
The epidermis is the topmost layer of skin, and itself is comprised of five layers or as we call them, strata. Your skin has four layers of skin cells in the epidermis and an additional fifth layer in areas of thick skin. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. So, five layers or strata, and.
Beneath The Dermis Lies The Hypodermis, Which Is Composed Mainly Of Loose.
The skin consists of two distinct layers: The epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. The epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Web skin is the largest organ in the body and covers the body's entire external surface.
It Is Made Up Of Three Layers, The Epidermis, Dermis, And The Hypodermis, All Three Of Which Vary Significantly In Their Anatomy And Function.
A layer of our skin that is found on the palms of our hands and the soles of our feet. Web they're exposed to oxygen in the air, causing them to age faster. Anatomy of the skin with merkel cells; Web your drawing with the epidermis, dermis (papillary layer), blood vessels, and dermis (reticular layer).
The Epidermis Is A Tough Coating Formed From Overlapping Layers Of Dead Skin Cells.
B&w, medical illustration (jpeg format) source: Sectional view of the skin.comparison illustration of protection effect between healthy skin and wounded skin. Web hello friends, this is my youtube channel and in this channel i used to share videos of different diagrams in easy way and step by step tutorials. Anatomy of the skin, showing the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue.
Literally Covering You From Head To Toe.
The four layers of cells, beginning at the bottom, are the stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, and stratum corneum. The epidermis includes five main layers: The thickness of the epidermis varies from 31.2μm for the penis to 596.6μm for the sole of the foot with most being. Web the epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells [4] that overlie a base layer ( stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly.