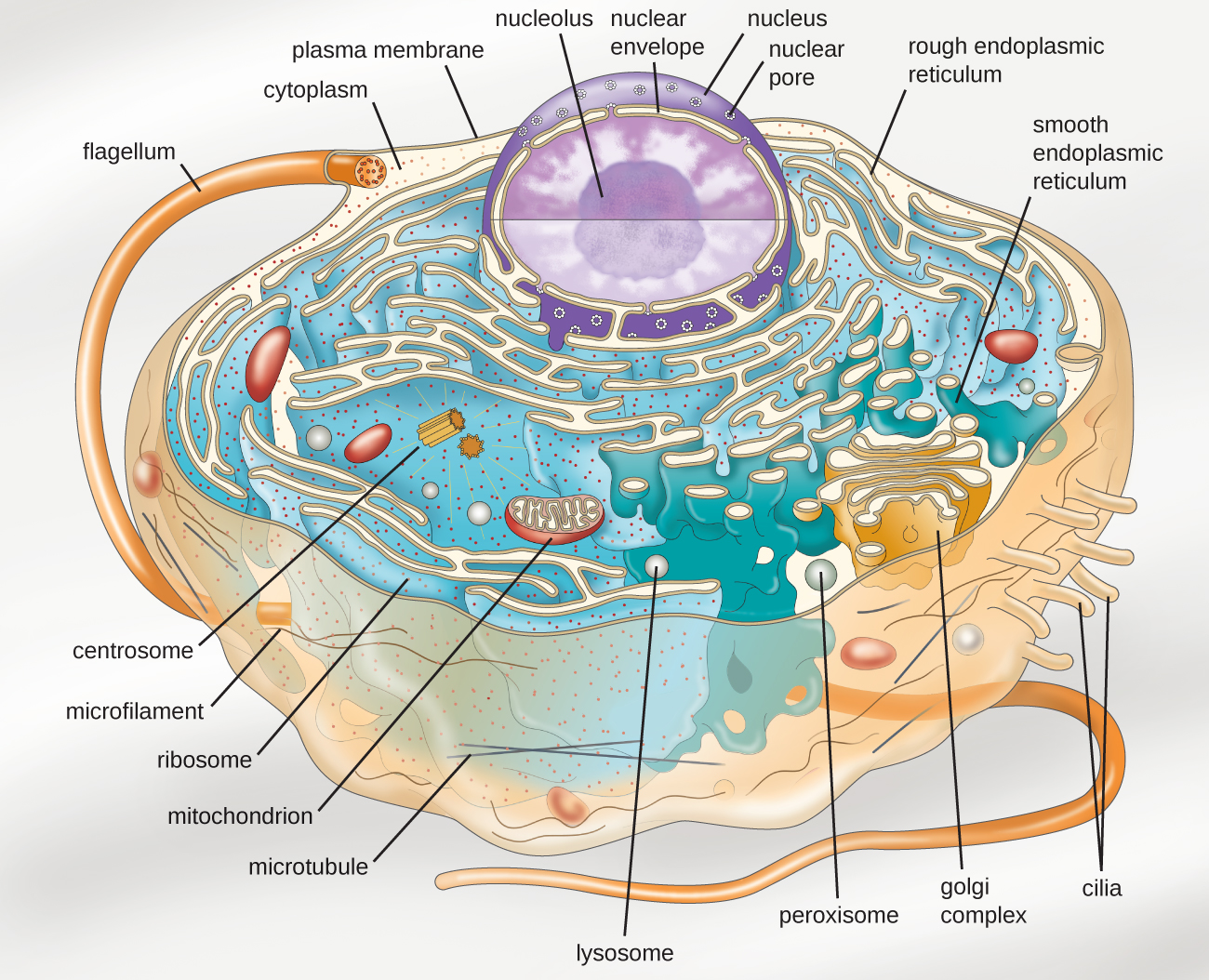
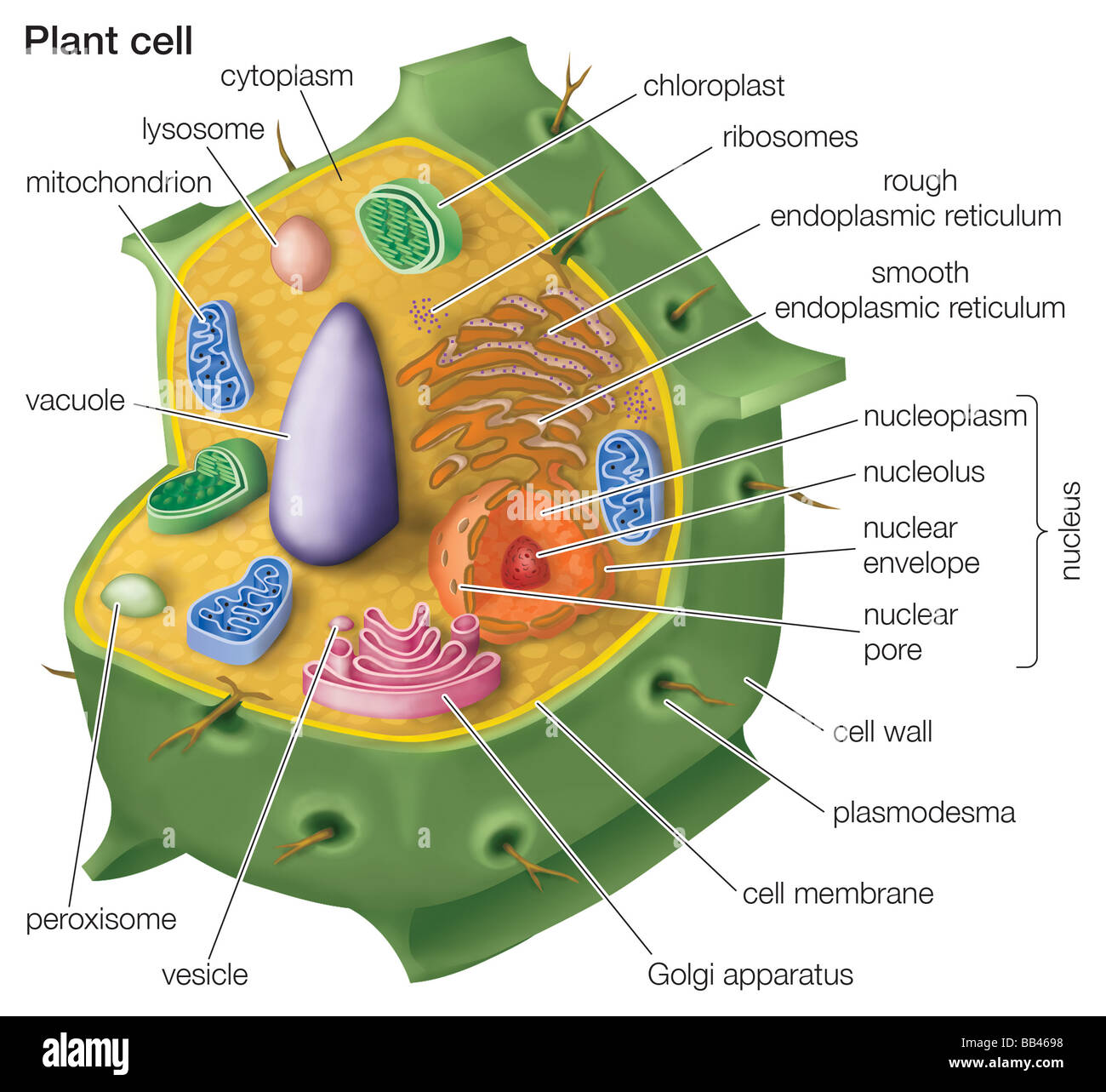
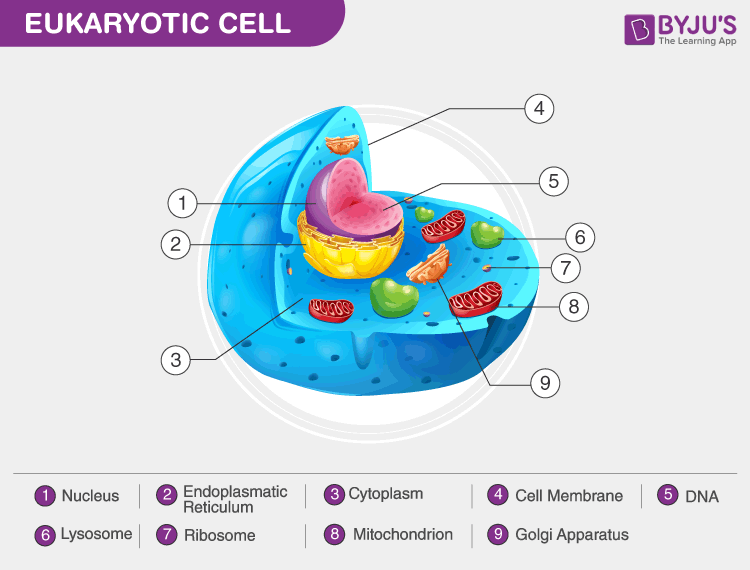
Eukaryotic Drawing
Eukaryotic Drawing - For the purpose of this article, the primary focus will be the structure and histology of the animal cell. Eukaryotic cells, with their much larger genomes, have multiple, linear chromosomes. Web figure 4.8 these figures show the major organelles and other cell components of (a) a typical animal cell and (b) a typical eukaryotic plant cell. Rough er (contains ribosomes) and smooth er (does not. Structure and function is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by libretexts. A phospholipid is a lipid molecule composed of two fatty acid chains, a glycerol backbone,. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. The most notable feature of a eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. The possession of a nucleus is the main distinction between prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria. Also identifying the difference between the plant and animal cell structure.
Of course, a cell is ever so much more than just a bag of goo. Web eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Cell walls give strength and rigidity to the cell. As previously stated, the fundamental components of a cell are its organelles. And the plasma membrane and cytoplasm are actually pretty sophisticated. Web eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. Web how to draw eukaryotic cell/ step by step drawing for beginnerseukaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell diagram, step by step drawing for beginners, biology diagram,. For the purpose of this article, the primary focus will be the structure and histology of the animal cell. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells. Like prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane (figure 3.3.2 3.3.
The location of the dna is highlighted in each. The eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeletal structure. Flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs in a eukaryotic cell. Of course, a cell is ever so much more than just a bag of goo. Endoplasmic reticulum (er) network of tubes and membranes that carry material through the cell and play a role in protein modification and lipid synthesis; Web drawing eukaryotic cells and annotating the functions of each of the organelles. Cell walls give strength and rigidity to the cell. Most prokaryotic cells contain a single circular chromosome. A diagram showing the basic structure of a eukaryotic cell and prokaryotic cell. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells.
Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
Web eukaryotic cells have the nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells. Rough er (contains ribosomes) and smooth er (does not. Web chromosomes are long strands of dna in cells that carry genetic information. A 3d model of a eukaryote including the major components, while missing a few smaller structures:
3.4 Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology 201
They're also the more complex of the two. A phospholipid is a lipid molecule composed of two fatty acid chains, a glycerol backbone,. Web in this video showing how to draw a eukaryotic cell in easy steps. Web eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The length and linear nature of eukaryotic chromosomes increase the challenge.
Cutaway drawing of a eukaryotic plant cell Stock Photo Alamy
Web eukaryotic cells have the nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane. The plant cell has a cell wall, chloroplasts, plastids, and a central vacuole—structures not in animal cells. Web eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. Web eukaryotic genes are a combination of introns and exons. Found either floating free in the cytoplasm or attached to.
Eukaryotic Cell Definition, Characteristics, Structure and Examples
Web how to draw eukaryotic cell/ step by step drawing for beginnerseukaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell diagram, step by step drawing for beginners, biology diagram,. The cells divide by a process called mitosis. Eukaryotic cells, with their much larger genomes, have multiple, linear chromosomes. The endoplasmic reticulum in a eukaryotic cell is the transport network of the cell and it extends.
Cell Biology Glossary Cell Architecture of Animals (Eukaryotes) Draw
A phospholipid is a lipid molecule composed of two fatty acid chains, a glycerol backbone,. Like prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane (figure 3.3.2 3.3. The eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeletal structure. Year 10 • edexcel • higher. Most cells do not have lysosomes or centrosomes.
Eukaryotic Cells Definition, Characteristics, Structure, & Examples
Year 10 • edexcel • higher. Web i draw a plant cell to show you how to make an accurate biological drawing of a eukaryotic cell. Flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs in a eukaryotic cell. 2.3.2 annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with the functions of each named structure. A phospholipid is a lipid molecule composed of two fatty.
How to Draw an Animal Cell Really Easy Drawing Tutorial
The most notable feature of a eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. Web eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria (cellular energy exchangers), a. Most cells do not have lysosomes or centrosomes. Of course, a cell is ever so much more than just a bag of goo.
Diagram Of A Eukaryotic Cell Drivenheisenberg
Web gene regulation is the process of controlling which genes in a cell's dna are expressed (used to make a functional product such as a protein). Web eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Web eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. Web figure 4.8 these figures show the major organelles and other cell components of (a) a typical.
Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Cellular Structures ALevel Biology
These organisms are grouped into the biological domain eukaryota. Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria (cellular energy exchangers), a. Web eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. Web the eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi. Most cells do not have lysosomes or centrosomes.
EUKARYOTE, DRAWING Stock Photo Alamy
And the plasma membrane and cytoplasm are actually pretty sophisticated. I can use a light microscope to observe and produce scientific drawings of cells. Web eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The nucleus is centrally placed which is a double membranous structure. The set of genes expressed in a cell determines the set of proteins.
The Length And Linear Nature Of Eukaryotic Chromosomes Increase The Challenge Of Keeping The Genetic Material.
Web how to draw eukaryotic cell/ step by step drawing for beginnerseukaryotic cell, eukaryotic cell diagram, step by step drawing for beginners, biology diagram,. Web eukaryotic genes are a combination of introns and exons. Please note, that usually the cells are so densely packed with structures, that if this was an accurate representation of the amount of components, it would be didactically. As previously stated, the fundamental components of a cell are its organelles.
Like Prokaryotes, Eukaryotic Cells Have A Plasma Membrane (Figure 3.3.2 3.3.
Different cells in a multicellular organism may express very different sets of genes, even though they contain the same dna. Web eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Flagella and cilia are the locomotory organs in a eukaryotic cell. A cell wall is the outermost layer of the eukaryotic cells.
Most Cells Do Not Have Lysosomes Or Centrosomes.
They're also the more complex of the two. The cells divide by a process called mitosis. Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria (cellular energy exchangers), a. The location of the dna is highlighted in each.
Web Figure 4.8 These Figures Show The Major Organelles And Other Cell Components Of (A) A Typical Animal Cell And (B) A Typical Eukaryotic Plant Cell.
This video help's you to draw eukaryotic cell of class 11th bio, ncert.don't forget to sha. A diagram showing the basic structure of a eukaryotic cell and prokaryotic cell. The most notable feature of a eukaryotic cell is the nucleus. Endoplasmic reticulum (er) network of tubes and membranes that carry material through the cell and play a role in protein modification and lipid synthesis;