Exocytosis Drawing
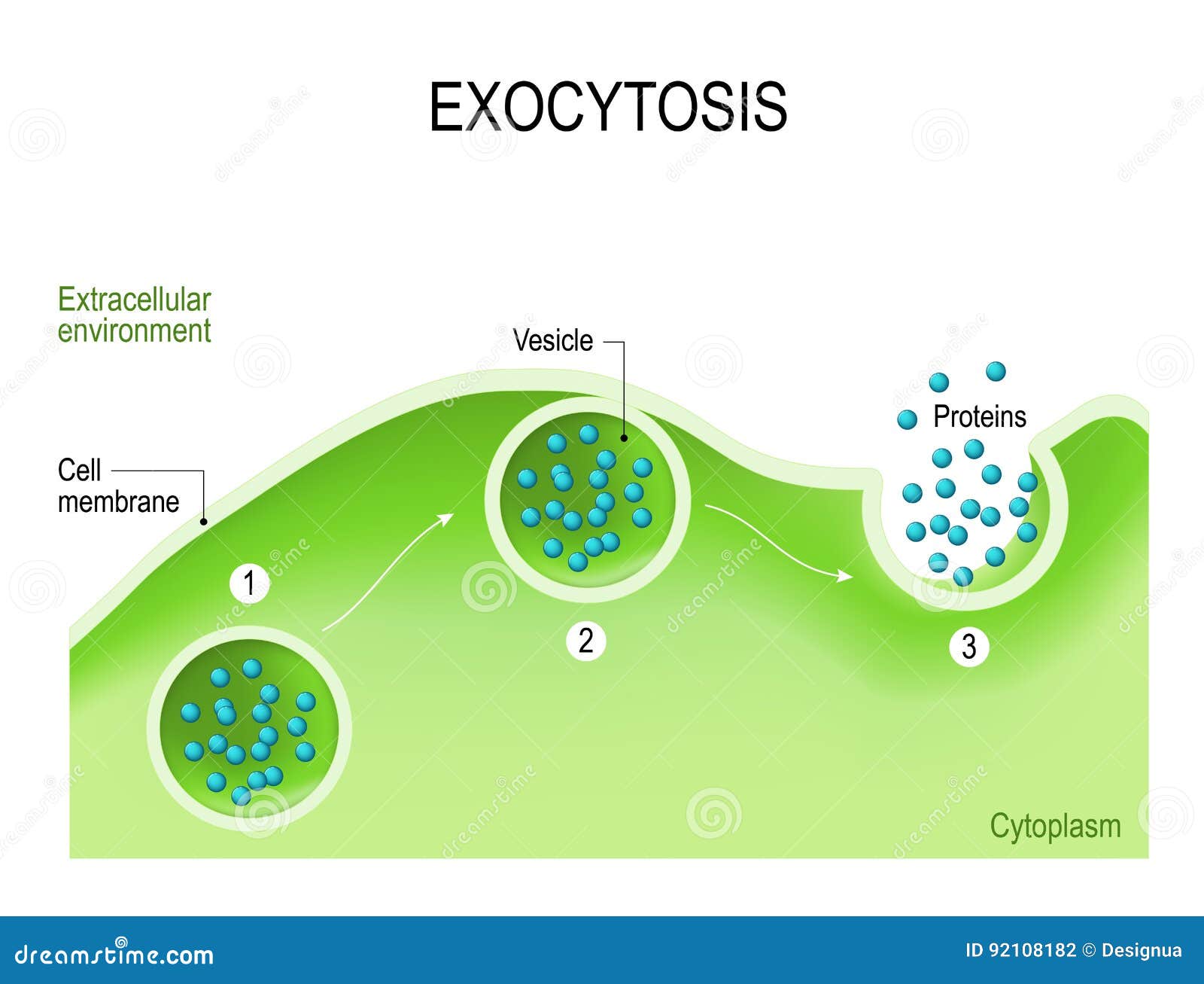
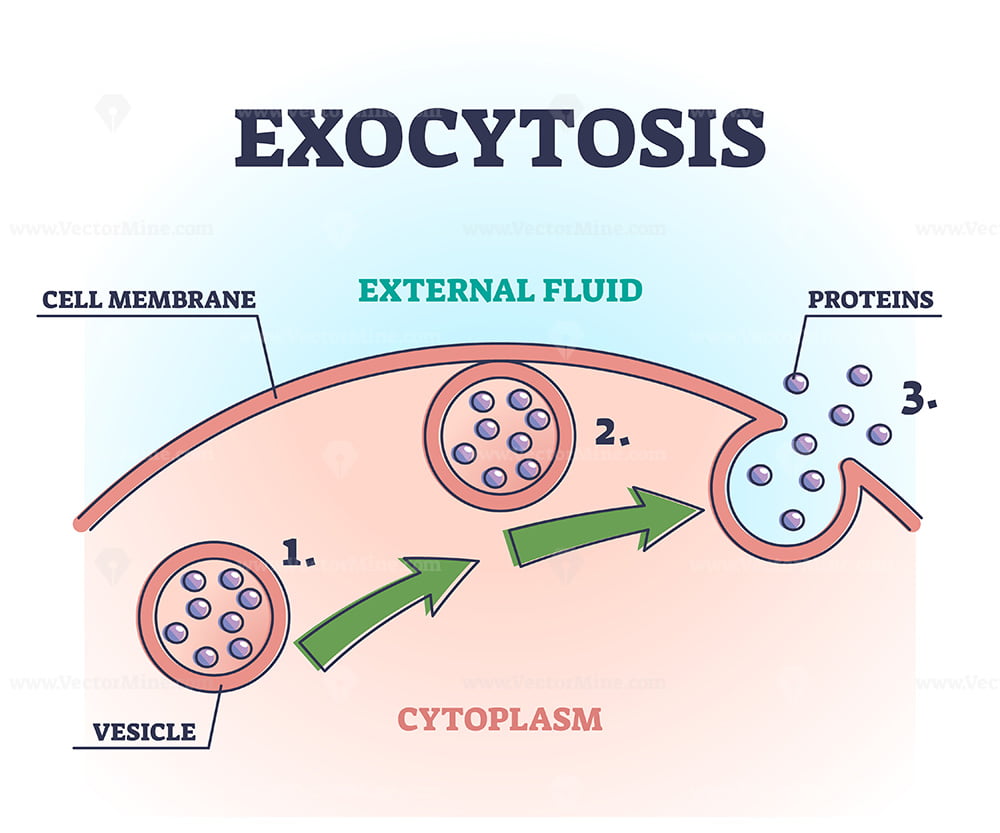
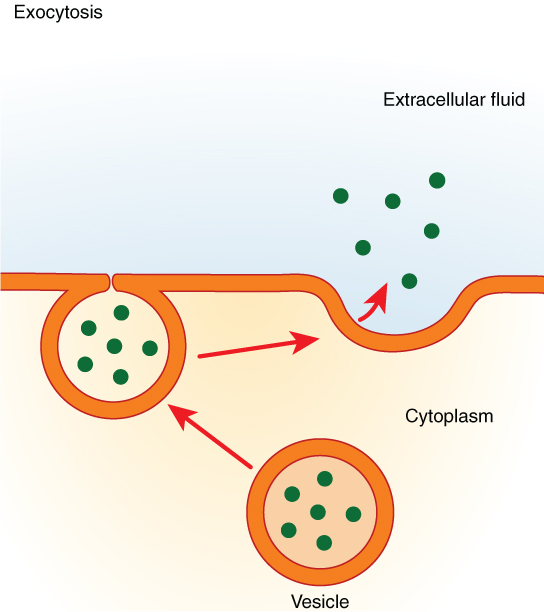
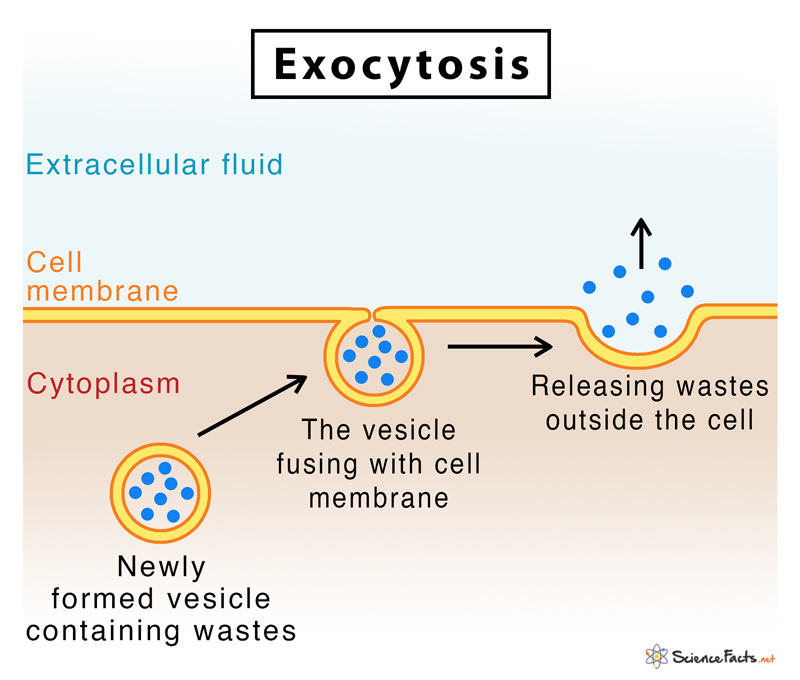
Exocytosis Drawing - Exocytosis illustration figure drawing diagram image. Exocytosis occurs via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. The contents are then released to the exterior of the cell. Exocytosis is a form of bulk transport during which large numbers of molecules are transported out of the cell. These processes allow larger molecules that cannot diffuse through the lipid bilayer to cross the membrane. In this process, the vesicles containing the fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. New users enjoy 60% off. Exocytosis is the natural process of transporting molecules from within a cell to the outside space. Can transport soluble proteins or plasma. It is a type of active transport mechanism that makes the use of atp.
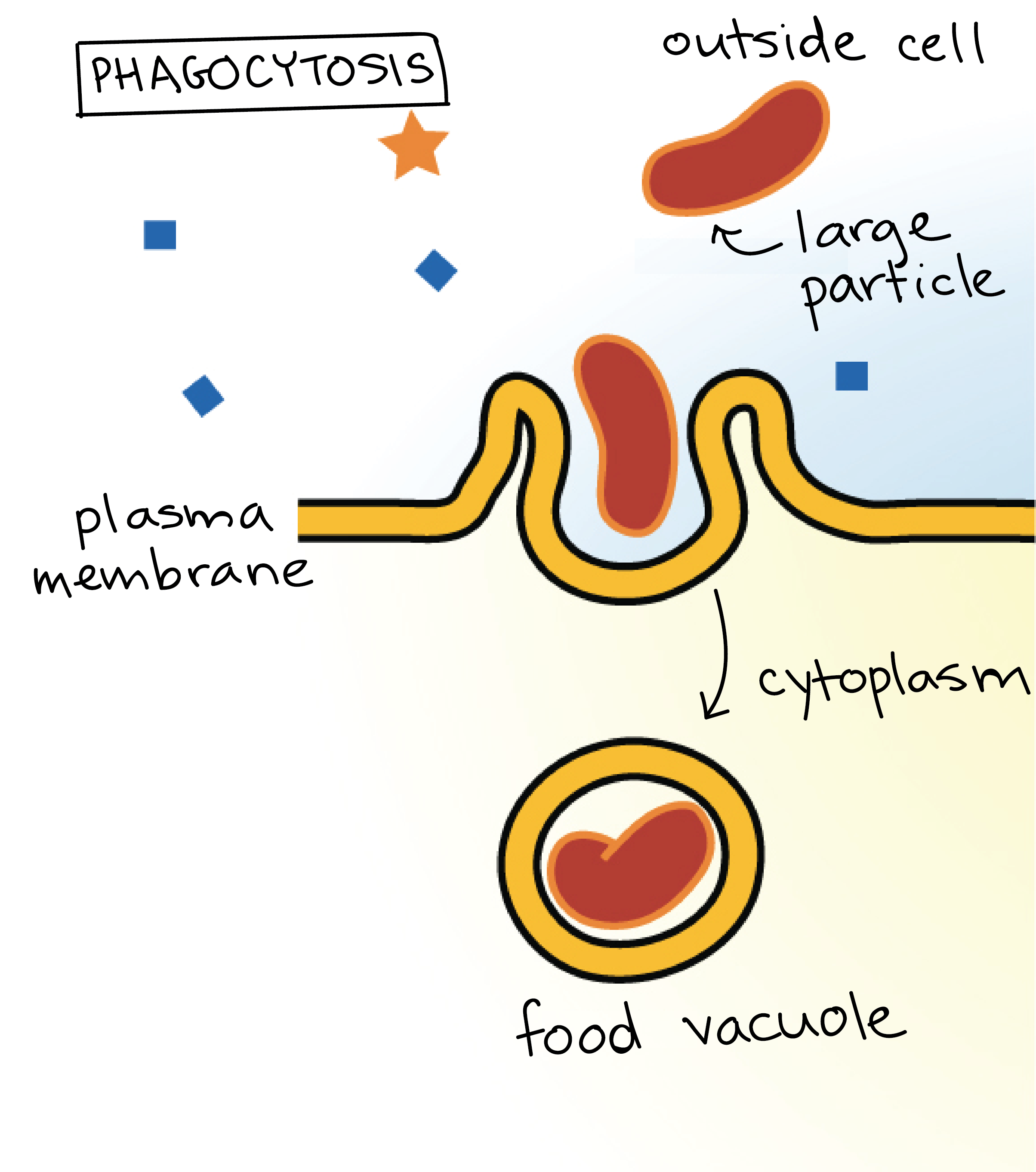
The transport of the substance is mediated by the vesicles that eliminate the cell debris and release specific proteins, enzymes, hormones etc., outside the cell. Web exocytosis is a general term used to denote vesicle fusion at the plasma membrane, and it is the final step in the secretory pathway that typically begins in the endoplasmic reticulum (er), passes through the golgi apparatus, and ends at the outside of the cell. Exocytosis is the natural process of transporting molecules from within a cell to the outside space. Web tufts university & harvard. It is a type of active transport mechanism that makes the use of atp. Phagocytosis targets large structures (e.g.,. Following exocytosis, endocytosis is initiated to retrieve exocytosed vesicles within seconds to minutes. Exocytosis occurs via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Thus it is a form of bulk transport. The electron micrograph in figure 3.25.1 shows a guinea pig phagocyte ingesting polystyrene beads.
Can transport soluble proteins or plasma. In this process, the vesicles containing the fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. Web exocytosis is an important process of plant and animal cells as it performs the opposite function of endocytosis. Exocytosis is important for the transport. Web exocytosis is the process by which a large amount of molecules are released; See exocytosis stock video clips. University of reading) for help with figure 1and for drawing the diagrams in. Exocytosis is a form of bulk transport during which large numbers of molecules are transported out of the cell. This illustration is included in the following illustration toolkit. Web what is exocytosis.
A Definition of Exocytosis With Steps and Examples
Following exocytosis, endocytosis is initiated to retrieve exocytosed vesicles within seconds to minutes. Web exocytosis is a general term used to denote vesicle fusion at the plasma membrane, and it is the final step in the secretory pathway that typically begins in the endoplasmic reticulum (er), passes through the golgi apparatus, and ends at the outside of the cell. These.
File0310 Exocytosis.jpg Wikimedia Commons
Web exocytosis is used continuously by plant and animal cells to excrete waste from the cells. Web exocytosis is a general term used to denote vesicle fusion at the plasma membrane, and it is the final step in the secretory pathway that typically begins in the endoplasmic reticulum (er), passes through the golgi apparatus, and ends at the outside of.
Exocytosis Cell Membrane
Also called default pathway as it does not require a signal for cargo to enter this pathway. Exocytosis is a form of bulk transport during which large numbers of molecules are transported out of the cell. New users enjoy 60% off. In this process, the vesicles containing the fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer fuse with the plasma membrane to.
A Definition of Exocytosis With Steps and Examples
Exocytosis is the natural process of transporting molecules from within a cell to the outside space. University of reading) for help with figure 1and for drawing the diagrams in. Web what is exocytosis. This illustration is included in the following illustration toolkit. These vesicles then travel to the cell surface membrane.
B for Biology Cell Membrane Protector of the Cell
The term ‘exocytosis’ was proposed by de duve in 1963. Following exocytosis, endocytosis is initiated to retrieve exocytosed vesicles within seconds to minutes. Web exocytosis is a general term used to denote vesicle fusion at the plasma membrane, and it is the final step in the secretory pathway that typically begins in the endoplasmic reticulum (er), passes through the golgi.
Exocytosis Definition, Functions with Examples, & Diagram
Web exocytosis 1) proteins synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and trafficked to the golgi apparatus 2) from the golgi, the proteins are sorted and can follow different paths: Web introduction to exocytosis!watch the next lesson: Exocytosis illustration figure drawing diagram image. Exocytosis occurs via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Following exocytosis, endocytosis is initiated to retrieve.
A Definition of Exocytosis With Steps and Examples
The term ‘exocytosis’ was proposed by de duve in 1963. Web exocytosis is a general term used to denote vesicle fusion at the plasma membrane, and it is the final step in the secretory pathway that typically begins in the endoplasmic reticulum (er), passes through the golgi apparatus, and ends at the outside of the cell. It explains the difference.
Exocytosis Process Diagram
These processes allow larger molecules that cannot diffuse through the lipid bilayer to cross the membrane. Web exocytosis is the secretion of large molecules like digestive enzymes and peptide or polypeptide hormones, each of which must exit the cell to the extracellular fluid or circulation. These vesicles then travel to the cell surface membrane. Web endocytosis and exocytosis are the.
Exocytosis Stock Illustrations 59 Exocytosis Stock Illustrations
Web exocytosis is the process by which a large amount of molecules are released; The vesicles fuse with the cell. Web exocytosis is the process by which materials are removed from, or transported out of, cells (the reverse of endocytosis) the substances to be released (such as enzymes, hormones or cell wall building materials) are packaged into secretory vesicles formed.
Exocytosis process explanation as proteins release mechanism outline
In this process, the vesicles containing the fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. The transport of the substance is mediated by the vesicles that eliminate the cell debris and release specific proteins, enzymes, hormones etc., outside the cell. Web exocytosis is used continuously by plant and animal cells.
Web Exocytosis Is Used Continuously By Plant And Animal Cells To Excrete Waste From The Cells.
The drawings in figure 7.14 are. Why choose our illustrations for your presentations and publications? Exocytosis is a form of bulk transport during which large numbers of molecules are transported out of the cell. Endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane.the membrane folds over the substance and it becomes completely enclosed by the membrane.
The Electron Micrograph In Figure 3.25.1 Shows A Guinea Pig Phagocyte Ingesting Polystyrene Beads.
Exocytosis is the reverse of endocytosis and that is just as well. Web introduction to exocytosis!watch the next lesson: Web endocytosis and exocytosis are the names given to the active, bulk transport of products across the cell membrane. These processes allow larger molecules that cannot diffuse through the lipid bilayer to cross the membrane.
Exocytosis Occurs Via Secretory Portals At The Cell Plasma Membrane Called Porosomes.
Following exocytosis, endocytosis is initiated to retrieve exocytosed vesicles within seconds to minutes. It is a type of active transport mechanism that makes the use of atp. University of reading) for help with figure 1and for drawing the diagrams in. In this process, the vesicles containing the fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell.
The Vesicles Fuse With The Cell.
Endocytosis is a mechanism for internalizing large extracellular molecules (e.g., proteins), insoluble particles, or even microorganisms. Web this biology video tutorial provides a basic introduction into cell transport. See exocytosis stock video clips. Exocytosis is important for the transport.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_process-5ae370b4a9d4f900373c9b48.jpg)

/exocytosis_2-5ae36dab04d1cf003cef3c48.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis-582df6965f9b58d5b183203f.jpg)