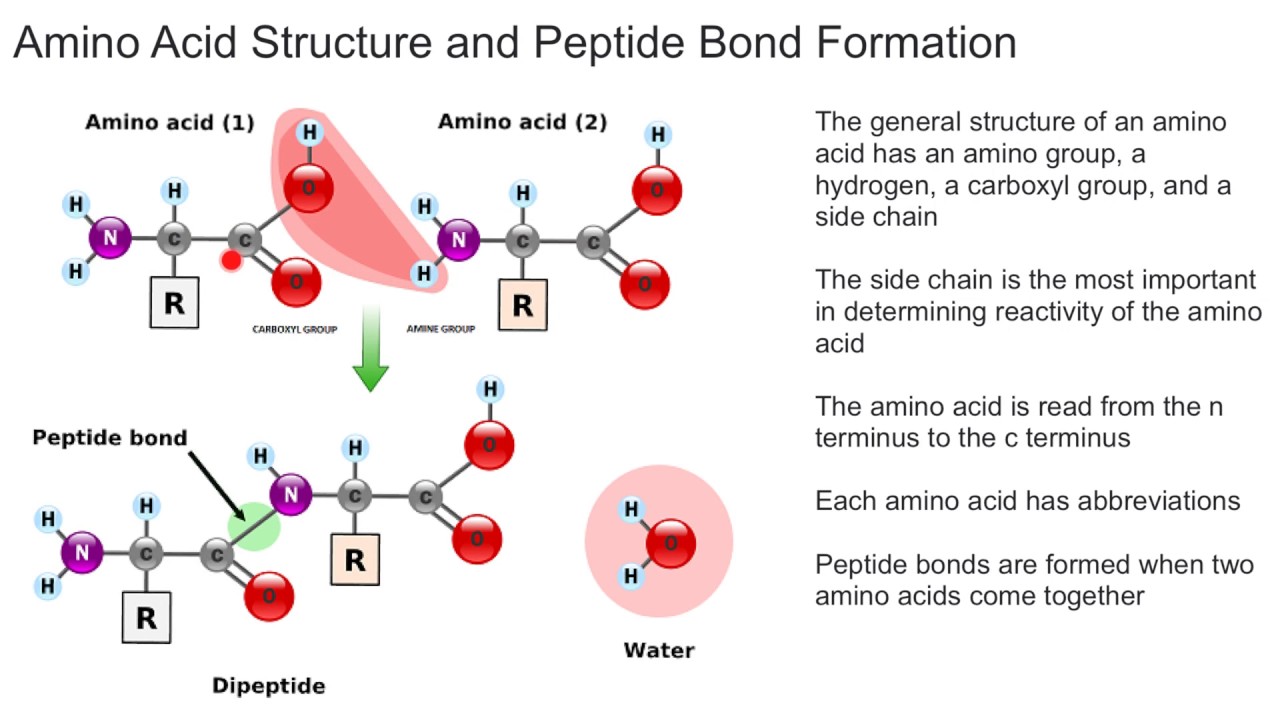
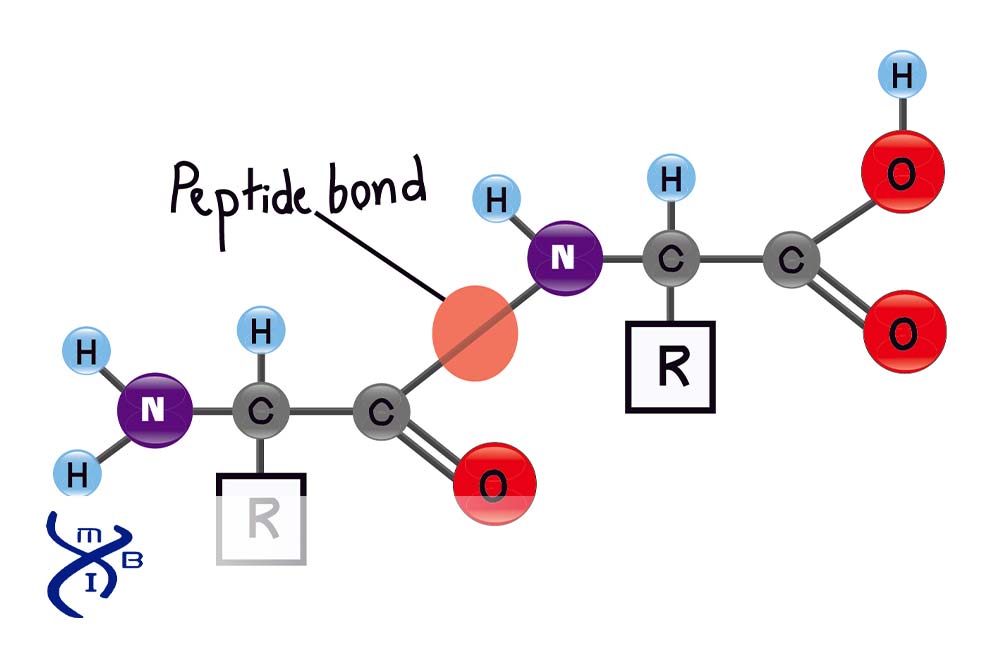
How To Draw A Peptide Bond
How To Draw A Peptide Bond - Web a peptide bond is a covalent bond formed between two amino acids. During protein synthesis, the carboxyl group of the amino acid at the end of the growing polypeptide chain chain reacts with the amino group of an incoming amino acid, releasing a molecule of water. A tool that draws peptide primary structure and calculates theoretical peptide properties. To connect amino acids together, a. Amino acids undergo condensation to form a molecule called a dipeptide. This tool allows to construct peptide sequence and calculate molecular weight and molecular formula. Proteins are used in many roles including structural support, catalyzing important reactions, and recognizing molecules in the environment. Web the configuration of the peptide bond is central to the sort of secondary structure the protein backbone can adopt. Note that the product molecule still has a reactive amino group on the left and a reactive carboxyl group on the right. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now:
Web an amide bond joining two amino acid units is called a peptide bond. The process can continue until thousands of units have joined, resulting in large proteins. Web the configuration of the peptide bond is central to the sort of secondary structure the protein backbone can adopt. Web these chains contain two or more amino acids (forming amino acid polymers) that are coupled by a peptide bond. Web each bond forms in a dehydration synthesis (condensation) reaction. Peptides differ from proteins by amount of amino acid residues the molecule contains. The resulting molecule is called a dipeptide. A peptide bond is the amide bond that occurs between the amine nitrogen of one amino acid and the carboxyl carbon of another amino acid. The amine end (n terminal) of an amino acid is always on the left, while the acid end (c terminal) is on the right. Web the primary structure of peptides or proteins is the sequence of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
A peptide bond is the amide bond that occurs between the amine nitrogen of one amino acid and the carboxyl carbon of another amino acid. Amino acids undergo condensation to form a molecule called a dipeptide. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. During protein synthesis, the carboxyl group of the amino acid at the end of the growing polypeptide chain chain reacts with the amino group of an incoming amino acid, releasing a molecule of water. Web peptide bond formation mechanism. By convention, the amide bond in the peptides should be made in the order that the amino acids are written. Web peptide bond formation or amide synthesis. The amine end (n terminal) of an amino acid is always on the left, while the acid end (c terminal) is on the right. When you draw out the peptide bond, you describe. Furthermore, peptide bonds can be broken down through hydrolysis.
What are the 6 Major Chemical Bonds or Interactions In Proteins?
Furthermore, peptide bonds can be broken down through hydrolysis. Web peptide bonds are the vital links that connect amino acids to form polypeptide chains, which fold into functional proteins. The resulting bond between amino acids is a peptide bond Web peptide bond formation or amide synthesis. Web amino acids are the monomers of proteins.
How to draw amino acids and peptide bonds to make a protein YouTube
When you draw out the peptide bond, you describe. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: Web peptide sequence builder. Web best shampoo for fine hair overall: Living organisms use peptide bonds to form long chains of amino acids, known as proteins.
Biochemistry Glossary Peptide Bond Formation Draw It to Know It
The resulting molecule is called a dipeptide. Web experience an ultimate bond repair with our olive oil & peptide shampoo, conditioner and hair mask.reverses hair damage in just 1 wash**based on consumer stu. Web the linear sequence of amino acids within a protein is considered the primary structure of the protein. Web the configuration of the peptide bond is central.
Amino Acid Structure and Peptide Bond Formation YouTube
Web the linear sequence of amino acids within a protein is considered the primary structure of the protein. Amino acids undergo condensation to form a molecule called a dipeptide. Web best shampoo for fine hair overall: It is easy to understand by imagining a normal helix and converting a trans peptide bond into its cis form. To connect amino acids.
What Is A Peptide Bond Simple Definition And How To Identify It?
The process can continue until thousands of units have joined, resulting in large proteins. Leaving the order the same, connect the amino acids to one another by forming peptide bonds. Identify the structures of each of the three given amino acids and draw them in the same order as given in the name. The amine end (n terminal) of an.
Drawing Formation of a Peptide Bond YouTube
For a tripeptide (three amino acids), there are 2 peptide bonds. Web peptide bond formation mechanism. Web a dipeptide would have two amino acids. Amino acid oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation, & photophosphorylation. A peptide bond is the amide bond that occurs between the amine nitrogen of one amino acid and the carboxyl carbon of another amino acid.
Biochemistry Glossary Peptide Bonds Draw It to Know It
Web a tool that draws peptide primary structure and calculates theoretical peptide properties. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Web a peptide bond is a covalent bond formed between two amino acids. Proteins are built from a set of only twenty amino acids, each of which has a unique side. By convention, the amide bond in the peptides.
IBDP BIOLOGY TOPIC 2.4 SKILL 1 DRAWING MOLECULAR DIAGRAMS TO SHOW THE
When you draw out the peptide bond, you describe. Web hedge funds draw pension money to riskiest corner of a $1.3 trillion credit market. Web a peptide bond is a covalent chemical bond formed by linking the carboxyl group of one free amino acid molecule to the amino group of another. Web the linear sequence of amino acids within a.
Peptide Bond Definition, Formation, Structure, Examples
Web the configuration of the peptide bond is central to the sort of secondary structure the protein backbone can adopt. Web to connect amino acids together, a peptide bond (also called an amide bond) has to be formed. For a tripeptide (three amino acids), there are 2 peptide bonds. Note that the product molecule still has a reactive amino group.
Peptide Bond Definition, Structure, Mechanism, and Examples
The resulting molecule is called a dipeptide. An r group (which is how each amino acid differs and why amino acid properties. This page was last updated: Proteins are used in many roles including structural support, catalyzing important reactions, and recognizing molecules in the environment. It is easy to understand by imagining a normal helix and converting a trans peptide.
Note That The Product Molecule Still Has A Reactive Amino Group On The Left And A Reactive Carboxyl Group On The Right.
The resulting bond between amino acids is a peptide bond Best shampoo for fine, thin hair: Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. To connect amino acids together, a.
Amino Acids Undergo Condensation To Form A Molecule Called A Dipeptide.
A peptide bond is the amide bond that occurs between the amine nitrogen of one amino acid and the carboxyl carbon of another amino acid. Web the primary structure of peptides or proteins is the sequence of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. A peptide bond is therefore the basis of. Web the linear sequence of amino acids within a protein is considered the primary structure of the protein.
Continue This Pattern Over And Over Until You Reach The Desired Length Of Your Peptide Chain (Pictures 2 And 3)
It is easy to understand by imagining a normal helix and converting a trans peptide bond into its cis form. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. The result is that the hydrogen bond network stabilising the helix is broken (see fig. Web to connect amino acids together, a peptide bond (also called an amide bond) has to be formed.
The Formation Of Peptides Is Nothing More Than The Application Of The Amide Synthesis Reaction.
These can react with additional amino acids to lengthen the peptide. Peptides differ from proteins by amount of amino acid residues the molecule contains. Furthermore, peptide bonds can be broken down through hydrolysis. Web a tool that draws peptide primary structure and calculates theoretical peptide properties.