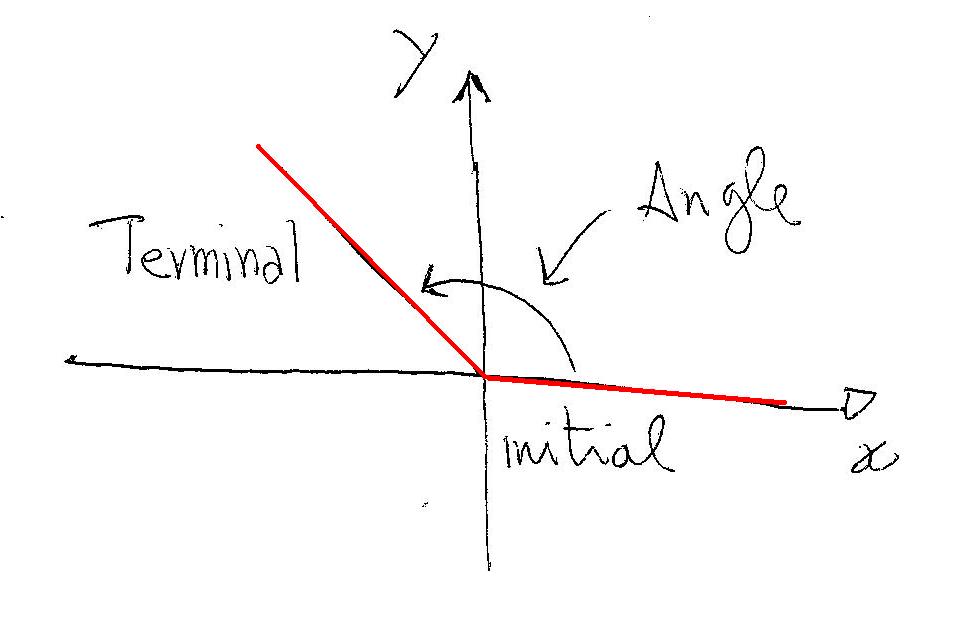
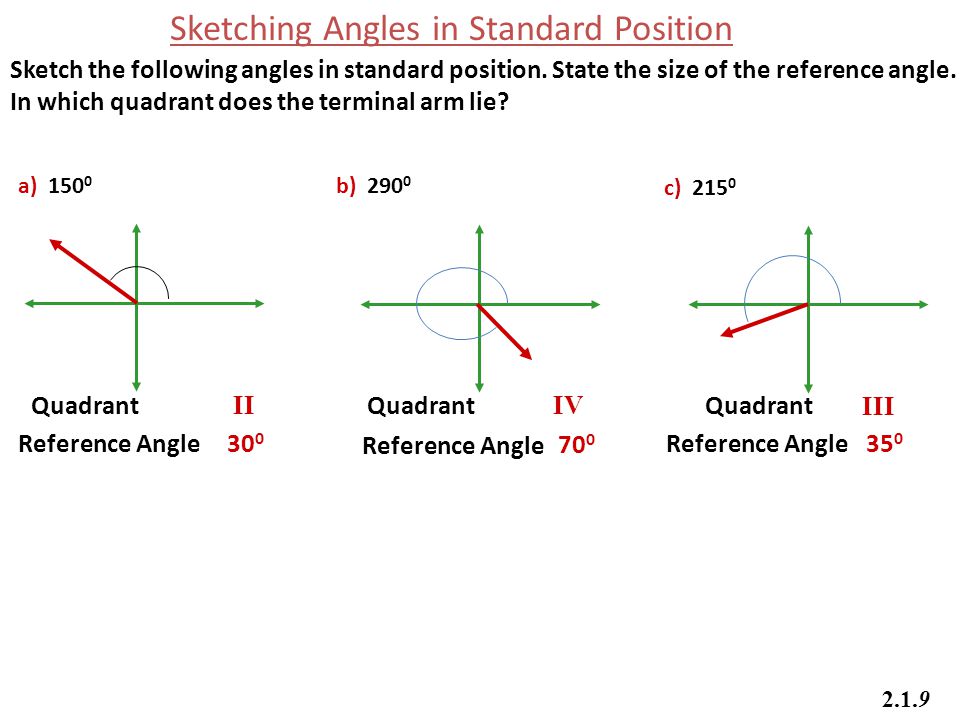
How To Draw Angle In Standard Position
How To Draw Angle In Standard Position - An angle is then measured positive for a counterclockwise rotation and negative for a clockwise rotation: Emphasis is on reference angle, principle angle and coterminal angle. Y = 0 0 ≤ x ≤ r. Try the free mathway calculator and problem solver below to practice various. Start by placing the baseline of a protractor on a cartesian plane with the vertex at the origin. We want to be consistent in how we draw these angles, and we call these decisions the standard position of an angle. Cos at + 0 2π 2 − a 2, sin at + 0 2π 2 − a 2. We do that by dividing the angle measure in degrees by 360°. Web 1 choose a point p on the terminal side. In this position, the vertex of the angle (b) is on the origin of the x and y axis.
Trace the first or initial side of the. Web given an angle measure in degrees, draw the angle in standard position. T + 1 cos at + 0 − 2π 2 + a 2, t + 1 sin at + 0 − 2π 2 + a 2. We do that by dividing the angle measure in degrees by 360°. My instructional approach emphasizes conceptual understanding of and connections between concepts and. Drawing angles using degrees in standard position. Cos at + 0 2π 2 − a 2, sin at + 0 2π 2 − a 2. Notice that the measure of the 4 2 0 ∘ angle is 3 6 0 ∘ more than the measure of the 6 0. Web learn about the concept of angle in standard position. If the terminal side of an angle lies on the axes (such as 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, 360º ), it is called a quadrantal.
Web learn how to draw an angle in standard position both in degrees and in radians in this math tutorial by mario's math tutoring. Web 1 choose a point p on the terminal side. Explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. An angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing the same endpoint. An angle is then measured positive for a counterclockwise rotation and negative for a clockwise rotation: Trace the first or initial side of the. Reduce the fraction to simplest form. We discuss what the initial r. Reduce the fraction to simplest form. We want to be consistent in how we draw these angles, and we call these decisions the standard position of an angle.
Drawing angles in standard position Trigonometry ShowMe
Reduce the fraction to simplest form. Y = tan a x r cos a ≤ x ≤ 0. Reduce the fraction to simplest form. In addition to degrees, the measure of an angle can be described in radians. Web for the following exercises, draw an angle in standard position with the given measure.30°here are all of our math playlists:functions:📕functions and.
How To Draw An Angle In Standard Position With The Given Measure All
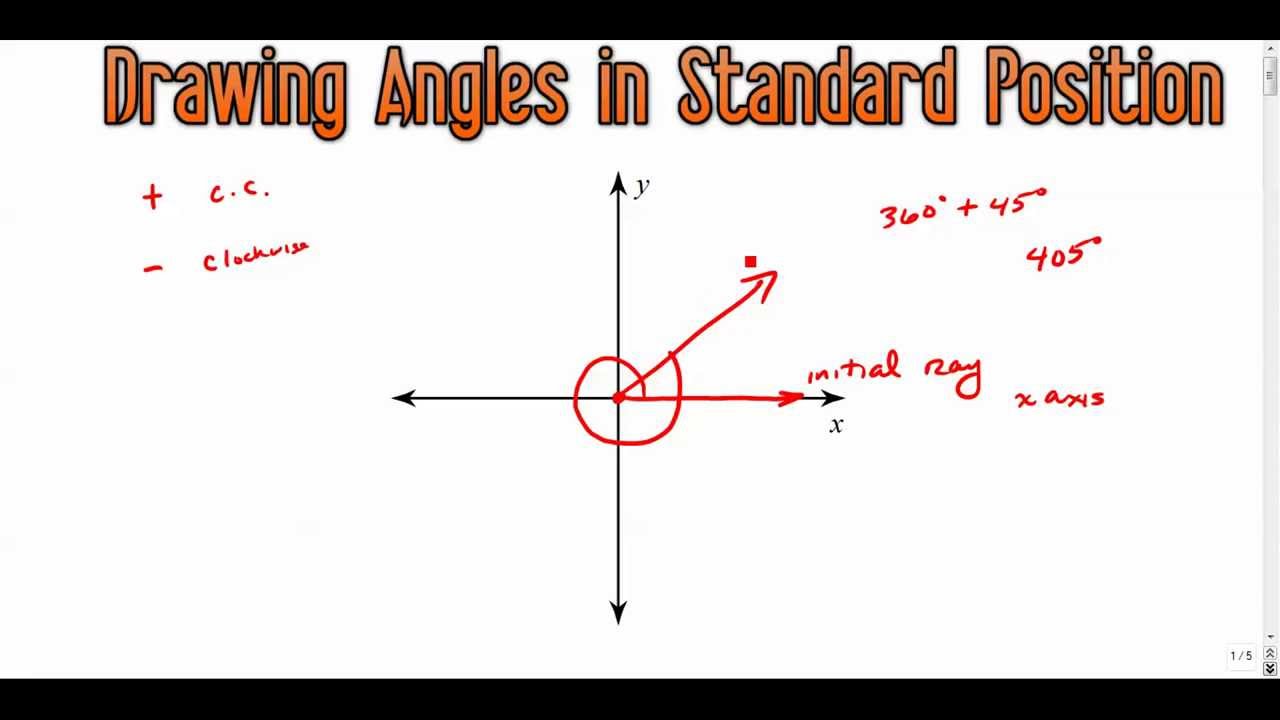
We want to be consistent in how we draw these angles, and we call these decisions the standard position of an angle. The first decision was to have the two rays intersect at the origin. An angle is then measured positive for a counterclockwise rotation and negative for a clockwise rotation: Web 1 choose a point p on the terminal.
Draw an Angle in Standard Position YouTube
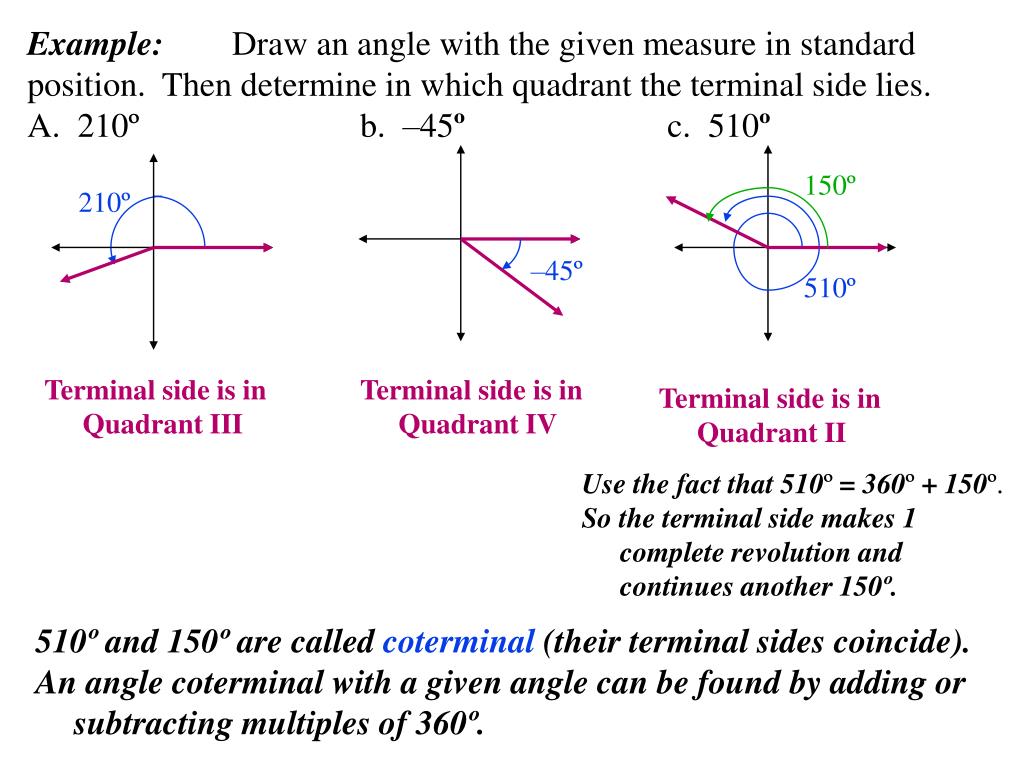
Notice that the measure of the 4 2 0 ∘ angle is 3 6 0 ∘ more than the measure of the 6 0. To place the terminal side of the angle, we must calculate the fraction of a full rotation the angle represents. My instructional approach emphasizes conceptual understanding of and connections between concepts and. Web to draw an.
Drawing Angles in Standard Position YouTube
Web for the following exercises, draw an angle in standard position with the given measure.30°here are all of our math playlists:functions:📕functions and functi. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders. We discuss what the initial r. In addition to degrees, the measure of an angle can be described in radians. This video shows how to draw angles in.
Drawing an Angle in Standard Position (degrees) YouTube
Express the angle measure as a fraction of 360°. Reduce the fraction to simplest form. Web 1 choose a point p on the terminal side. Y = tan a x r cos a ≤ x ≤ 0. Drawing angles using degrees in standard position.
How To Draw An Angle In Standard Position With The Given Measure All
The first decision was to have the two rays intersect at the origin. An angle is then measured positive for a counterclockwise rotation and negative for a clockwise rotation: Web given an angle measure in degrees, draw the angle in standard position. This video shows how to draw angles in standard position. Web the new ipad pro — the thinnest.
Angle in Standard Position Drawing & Examples How to Draw an Angle in
Web 1 choose a point p on the terminal side. Web the new ipad pro — the thinnest apple product ever — features a stunningly thin and light design, taking portability to a whole new level. Web learn how to draw an angle in radians in standard position in this video math tutorial by mario's math tutoring. If the terminal.
How do you draw angles of rotation in standard position? Socratic
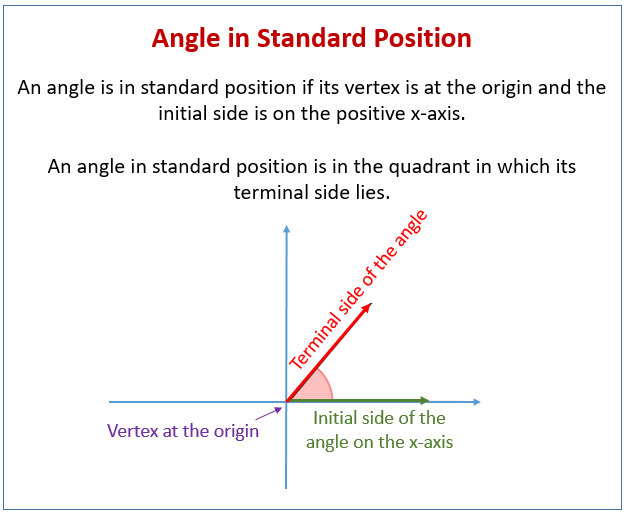
An angle is then measured positive for a counterclockwise rotation and negative for a clockwise rotation: Trace the first or initial side of the. To convert between degrees and radians, use the proportion \(\frac{θ}{180}=\frac. An angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing the same endpoint. In this position, the vertex of the angle (b) is on the origin.
Sketch The Angle In Standard Position at Explore
Web for the following exercises, draw an angle in standard position with the given measure.30°here are all of our math playlists:functions:📕functions and functi. In addition to degrees, the measure of an angle can be described in radians. My instructional approach emphasizes conceptual understanding of and connections between concepts and. Drawing angles using degrees in standard position. Web to draw an.
Express The Angle Measure As A Fraction Of[Latex]\,\Text{360°}.[/Latex] Reduce The Fraction To Simplest Form.
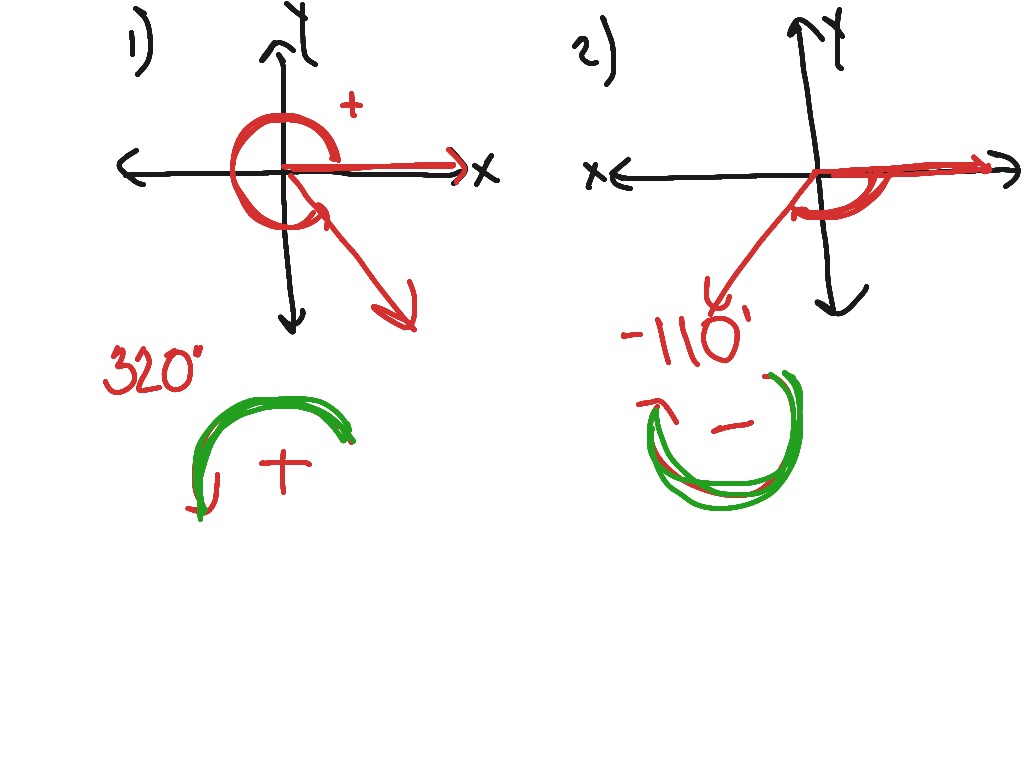
Web learn how to draw an angle in standard position both in degrees and in radians in this math tutorial by mario's math tutoring. For example, to draw a 90° angle, we calculate that. Web to draw an angle in standard position, follow these steps: Web this consists of drawing two rays which intersect, conventionally at the origin, to form an angle that has a measure between 0∘ and 360∘.
In Trigonometry An Angle Is Usually Drawn In What Is Called The Standard Position As Shown Below.
T + 1 cos at + 0 − 2π 2 + a 2, t + 1 sin at + 0 − 2π 2 + a 2. Web for the following exercises, draw an angle in standard position with the given measure.30°here are all of our math playlists:functions:📕functions and functi. Web given an angle measure in degrees, draw the angle in standard position. To place the terminal side of the angle, we must calculate the fraction of a full rotation the angle represents.
Web Learn About The Concept Of Angle In Standard Position.
In other words, the angles have the same terminal side. Reduce the fraction to simplest form. All angles in this video are measured in degrees. In this position, the vertex of the angle (b) is on the origin of the x and y axis.
Y = Tan A X R Cos A ≤ X ≤ 0.
Cos at + 0 2π 2 − a 2, sin at + 0 2π 2 − a 2. An angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing the same endpoint. If the terminal side of an angle lies on the axes (such as 0º, 90º, 180º, 270º, 360º ), it is called a quadrantal. This video shows how to draw angles in standard position.