How To Draw Homeostasis
How To Draw Homeostasis - The body maintains homeostasis for many factors. Describe the factors affecting homeostasis. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Medical equipment used to check homeostasis (sabine bracker, istockphoto) biology , health. If unsuccessful, disaster or death ensues. Homeostasis is maintained at many levels, not just the level of. To distinguish negative feedback from positive feedback. Introduction to homeostasis and regulation. In a similar vein, no one organ system of the body acts alone; It functions from the tiny level of individual cells to affecting the whole body at once.
It provides monitoring, response, and regulation of all systems in the human body and other organisms. Armandoh.org/shopalthough the environment around an organism changes, the organism maintains relatively stable internal conditions. When used as an adjective, it. Recognise negative and positive feedback, giving one physiologic example of each mechanism. This stimulus is “heard” by a specific sensor. Web homeostasis is the tendency to resist change in order to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment. Web homeostasis describes the dynamic balance of the body’s internal environment and the effort to maintain a constant, stable inside. To identify and example of two organ systems working together to maintain homeostasis. How does this align with my curriculum? Introduction to homeostasis and regulation.
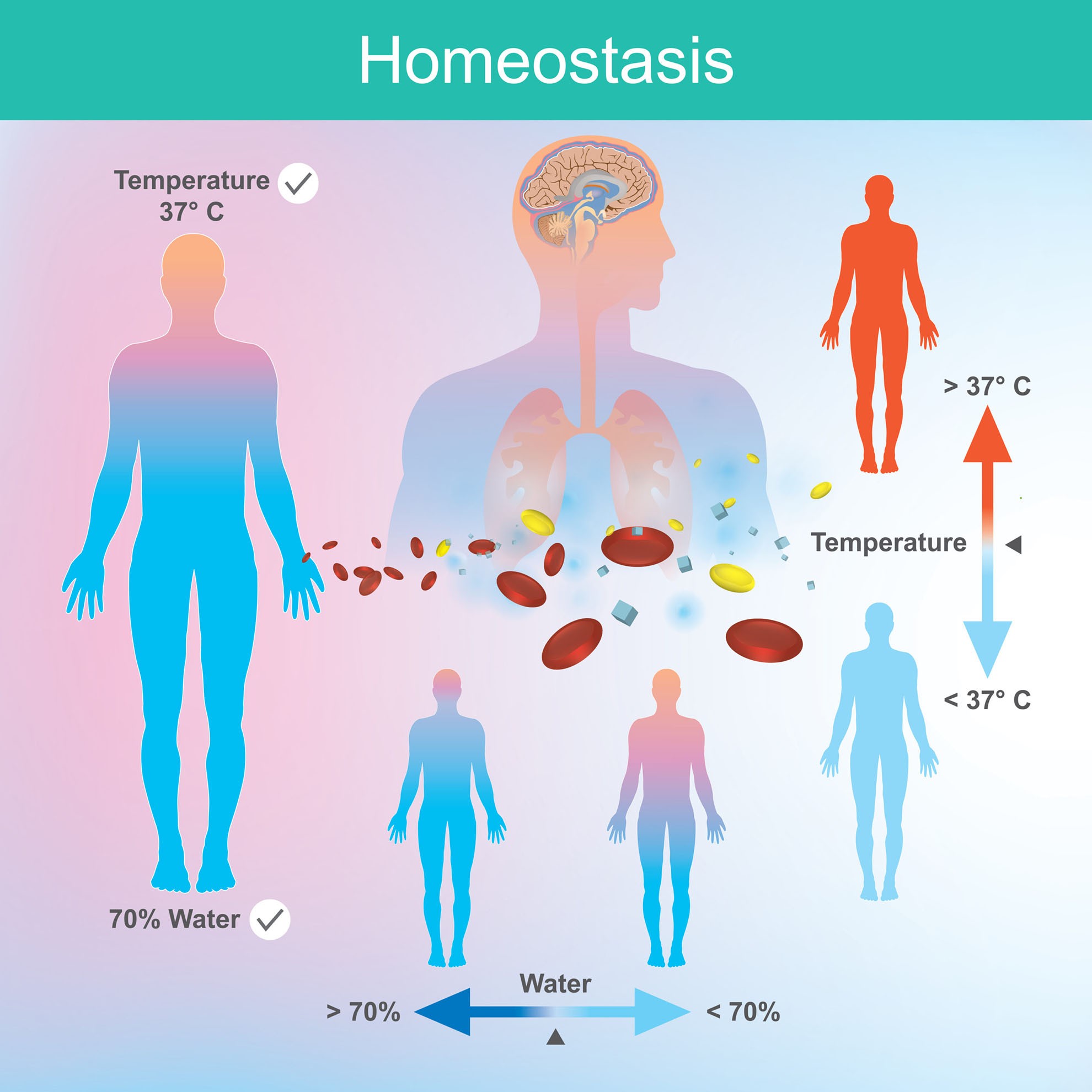
It provides monitoring, response, and regulation of all systems in the human body and other organisms. Medical equipment used to check homeostasis (sabine bracker, istockphoto) biology , health. Web jim davis and emily cobb. If unsuccessful, disaster or death ensues. Setpoint, variable, receptor (sensor), effector (target), and control (integrating) center. These processes take place mostly without our conscious awareness. Learn about homeostasis and how the body regulates temperature, blood pressure,. To identify the process by which body systems are kept within certain limits. The word homeostasis derives from greek, with home meaning “similar,” and stasis, meaning “stable.”. Regulation of body temperature cannot occur without the cooperation of the integumentary system, nervous system, musculoskeletal system, and cardiovascular system at a minimum.
Homeostasis examples and meaning in biology Jotscroll
In a similar vein, no one organ system of the body acts alone; Learn about homeostasis and how the body regulates temperature, blood pressure,. Your body has set points for a variety of states—including temperature, weight, sleep, thirst, and hunger. To identify the process by which body systems are kept within certain limits. Explain how negative feedback controls body temperature.
Homeostasis as biological state with temperature regulation outline
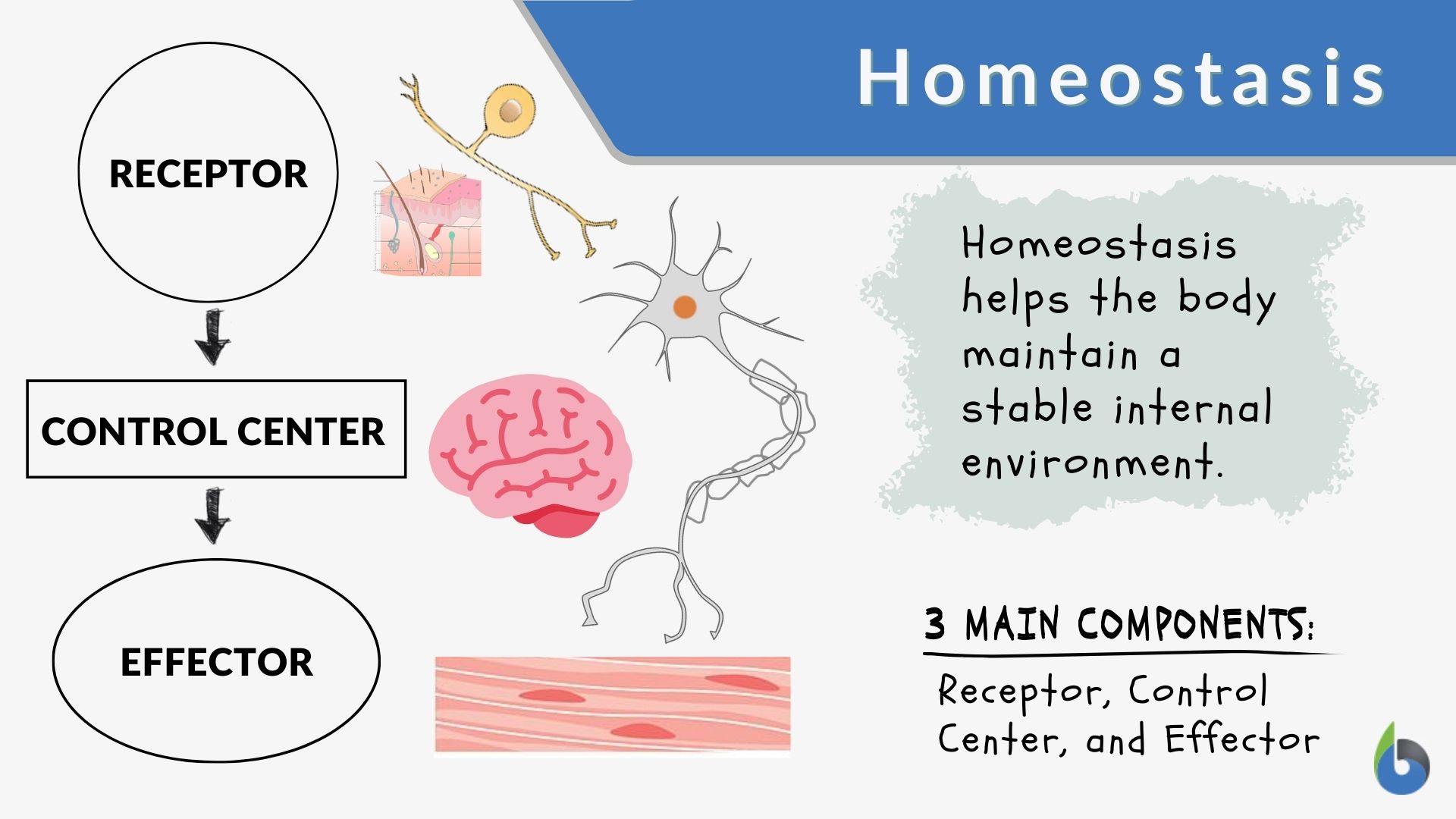
Web of all the body systems, the nervous system is the major control system of homeostasis. Web homeostasis is the tendency to resist change in order to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment. Homeostasis is maintained at many levels, not just the level of. A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates. Some of.
[Life Process Class 10] Why is Homeostasis important? Biology
Homeostasis is not the same as chemical or physical equilibrium. Medical equipment used to check homeostasis (sabine bracker, istockphoto) biology , health. This video gives examples of negative feedback (. Discuss positive and negative feedback mechanisms used in homeostasis. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point.
Homeostasis
Web homeostasis is the tendency of biological systems to maintain relatively constant conditions in the internal environment while continuously interacting with and adjusting to changes originating within or outside the system. A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates. From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a.
Biology homeostasis science vector illustration infographic 20561283
Web homeostasis is the tendency of biological systems to maintain relatively constant conditions in the internal environment while continuously interacting with and adjusting to changes originating within or outside the system. The constant equilibrium created by homeostasis is vital. Web homeostasis refers to an organism's ability to regulate various physiological processes to keep internal states steady and balanced. For example,.
what is the process of homeostasis
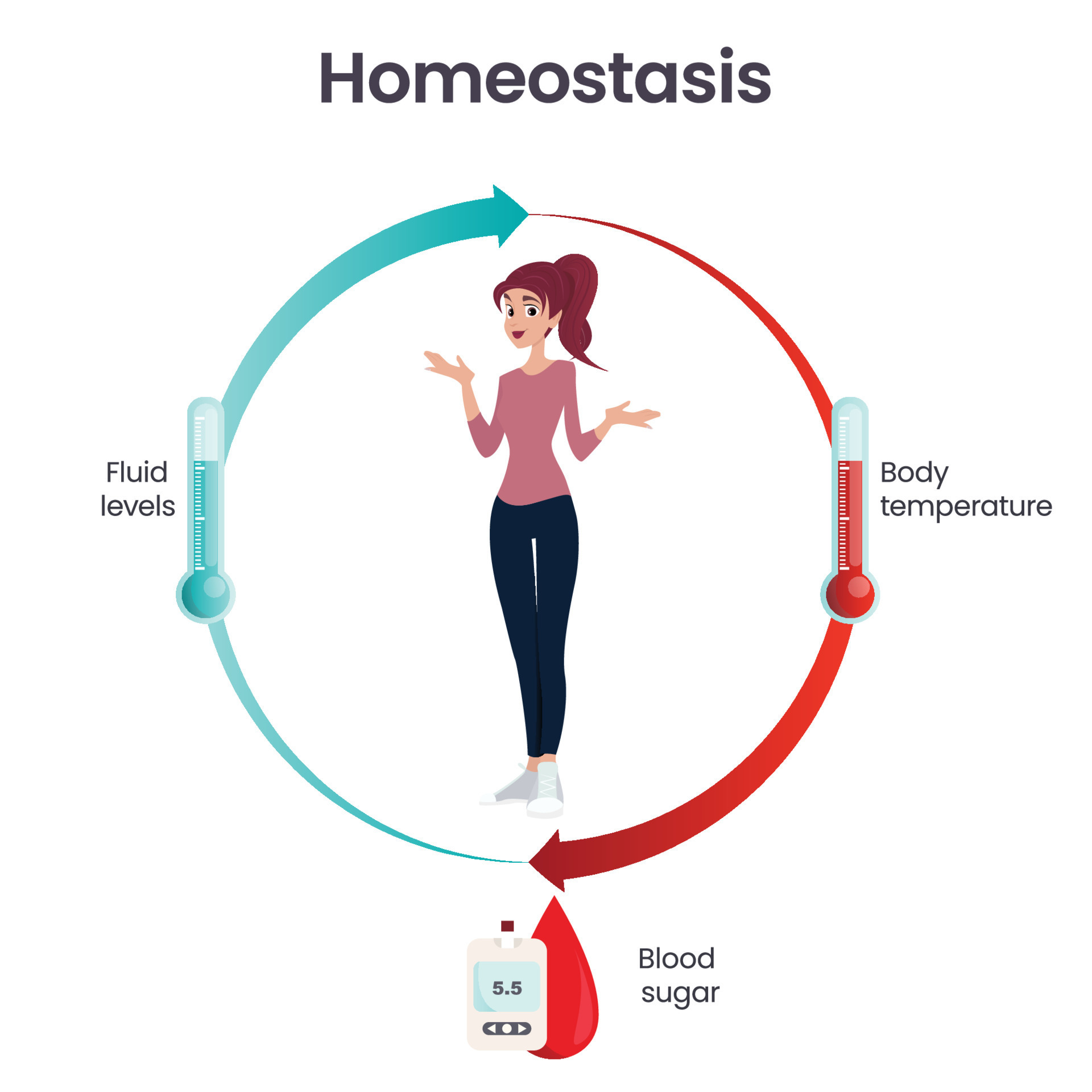
From body temperature to blood pressure to levels of certain nutrients, each physiological condition has a particular set point. Explain how negative feedback controls body temperature. Web of all the body systems, the nervous system is the major control system of homeostasis. Homeostasis is a physiological process that keeps the internal environment of a living organism stable and balanced. Describe.
Maintaining Homeostasis Bruin Blog
If unsuccessful, disaster or death ensues. If homeostasis is successful, life continues; A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates. Add milk to the coffee and eventually, when equilibrium is achieved, there will. Define the setpoint and normal range for physiological measures.
Homeostasis Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
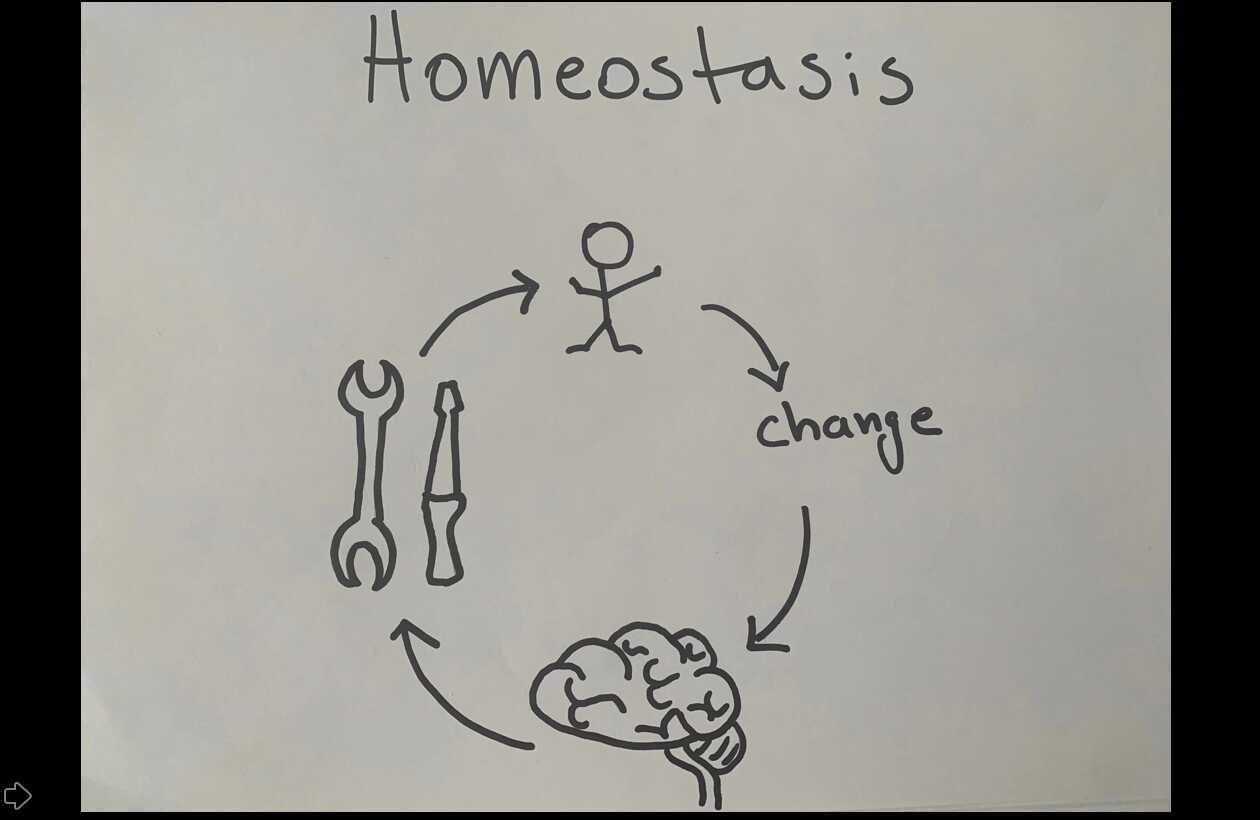
Homeostasis typically involves negative feedback loops that counteract changes of various properties from. Web maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. Web maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. This stimulus is “heard” by a specific sensor. Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions.
Homeostasis Definition, Importance & Examples Lesson
In a similar vein, no one organ system of the body acts alone; Web explore homeostasis with the amoeba sisters and learn how homeostasis relates to feedback in the human body. Regulation of body temperature cannot occur without the cooperation of the integumentary system, nervous system, musculoskeletal system, and cardiovascular system at a minimum. Define the following terms as they.
49+ Homeostasis Picture Biology Home
How does this align with my curriculum? Your body has set points for a variety of states—including temperature, weight, sleep, thirst, and hunger. If homeostasis is successful, life continues; The constant equilibrium created by homeostasis is vital. When used as an adjective, it.
Web Homeostasis Refers To An Organism's Ability To Regulate Various Physiological Processes To Keep Internal States Steady And Balanced.
The word homeostasis derives from greek, with home meaning “similar,” and stasis, meaning “stable.”. Web buy images here: Such equilibrium occurs when no net change is occurring: It functions from the tiny level of individual cells to affecting the whole body at once.
From Body Temperature To Blood Pressure To Levels Of Certain Nutrients, Each Physiological Condition Has A Particular Set Point.
Homeostasis is a physiological process that keeps the internal environment of a living organism stable and balanced. How does this align with my curriculum? Web homeostasis is the tendency to resist change in order to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment. Web of all the body systems, the nervous system is the major control system of homeostasis.
This Process Involves Various Biological Mechanisms That Detect Changes, Trigger Responses, And Restore Balance.
Follow along as we guide you through the process of drawing different body types and poses. Define the setpoint and normal range for physiological measures. Web maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions. Maintaining homeostasis requires that the body continuously monitor its internal conditions.
Recognise Negative And Positive Feedback, Giving One Physiologic Example Of Each Mechanism.
Identify and define the four interacting components that maintain homeostasis in feedback loops. Homeostasis is not the same as chemical or physical equilibrium. Describe thermoregulation of endothermic and ectothermic animals. Describe the factors affecting homeostasis.

![[Life Process Class 10] Why is Homeostasis important? Biology](https://d77da31580fbc8944c00-52b01ccbcfe56047120eec75d9cb2cbd.ssl.cf6.rackcdn.com/e8414069-a51e-419b-a17c-de6cb8aeabb1/homeostasis----teachoo.jpg)