How To Draw Nucleic Acids
How To Draw Nucleic Acids - Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Identify, in general terms, the enzymatic hydrolysis products of nucleosides. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show how the nucleotide units are joined together. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. There are 2 main types of. Web outline the relationship between nucleic acids, nucleotides and nucleosides. It is this linear sequence of nucleotides that make up the primary structure of dna or rna. We discuss the components of each, and the differences between the two. Web dssr (dissecting the spatial structure of rna) is an integrated software tool for the analysis/annotation, model building, and schematic visualization of 3d nucleic acid structures (see the figures below and the video overview ). Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information.
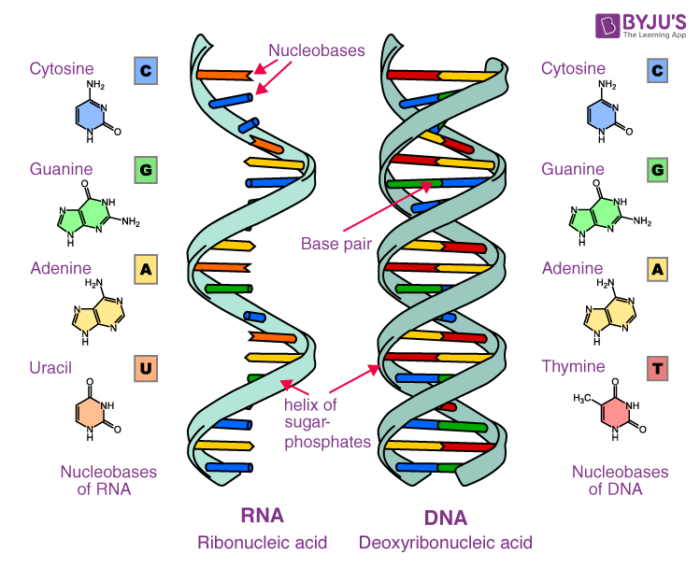
Web a type of rna called messenger rna or mrna reads dna and makes a copy of it, through a process called transcription. They are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Identify, in general terms, the enzymatic hydrolysis products of nucleosides. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Mrna carries this copy from the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where transfer rna or trna helps to match amino acids to the code, ultimately forming proteins through a process called translation. Nucleic acids are macromolecules made up of monomers called nucleotides. Web please support the channelmy videos are funded by people like you. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) and ribonucleic acid ( rna ).
Web outline the relationship between nucleic acids, nucleotides and nucleosides. Primary structure consists of a linear sequence of nucleotides that are linked together by phosphodiester bond. Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. Dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and rna stands for ribonucleic acid. Web introduction to nucleic acids. They are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Web 2d nucleic acid structure drawing programs can be roughly separated into two categories: Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides | high school biology | khan academy Mrna carries this copy from the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where transfer rna or trna helps to match amino acids to the code, ultimately forming proteins through a process called translation.
Nucleic Acids Function, Examples, and Monomers
Dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and rna stands for ribonucleic acid. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides | high school biology | khan academy Web dssr (dissecting the spatial structure of rna) is an integrated software tool for the analysis/annotation, model building, and schematic visualization of 3d nucleic acid structures (see the figures below and the video overview )..
Basic Structure Of Nucleic Acid
Nucleic acids are macromolecules made up of monomers called nucleotides. Indicate the nitrogen atom by which a given purine or pyrimidine base attaches to the sugar component in nucleotides and nucleosides. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. Web dssr (dissecting the spatial structure of rna) is.
Nucleic acid definition, nucleic acid structure, function & types
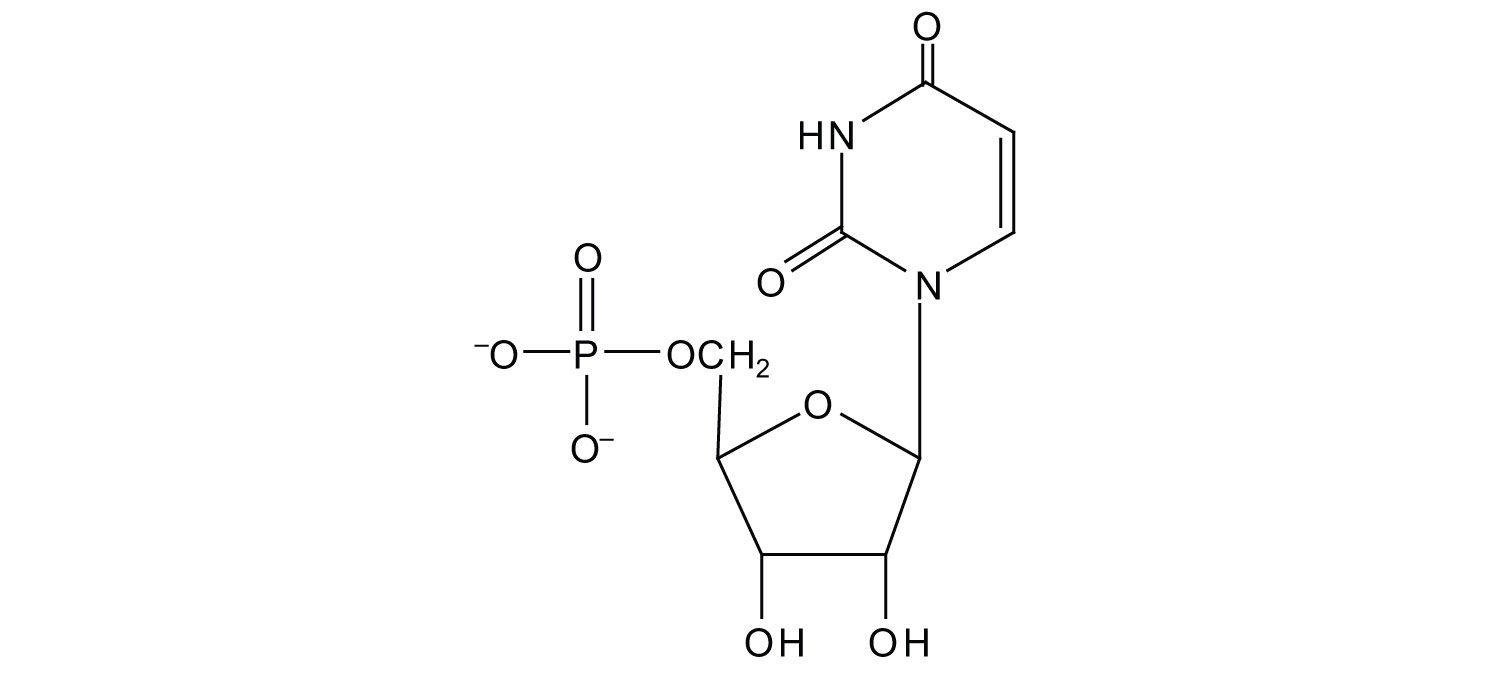
Explain the structural difference between the sugar components of dna and rna. Here, we’ll just take a quick look at nucleic acids from the macromolecule perspective. There are 2 main types of. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and rna stands for ribonucleic acid.
Nucleic Acids Jack's AP Biology Journal
The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) and ribonucleic acid ( rna ). Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides | high school biology | khan academy Web a type of.
Molecular structure of nucleic acids Science online
Primary structure consists of a linear sequence of nucleotides that are linked together by phosphodiester bond. Identify, in general terms, the enzymatic hydrolysis products of nucleosides. Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) and ribonucleic acid ( rna ). Here, we’ll just take a.
Nucleic Acids
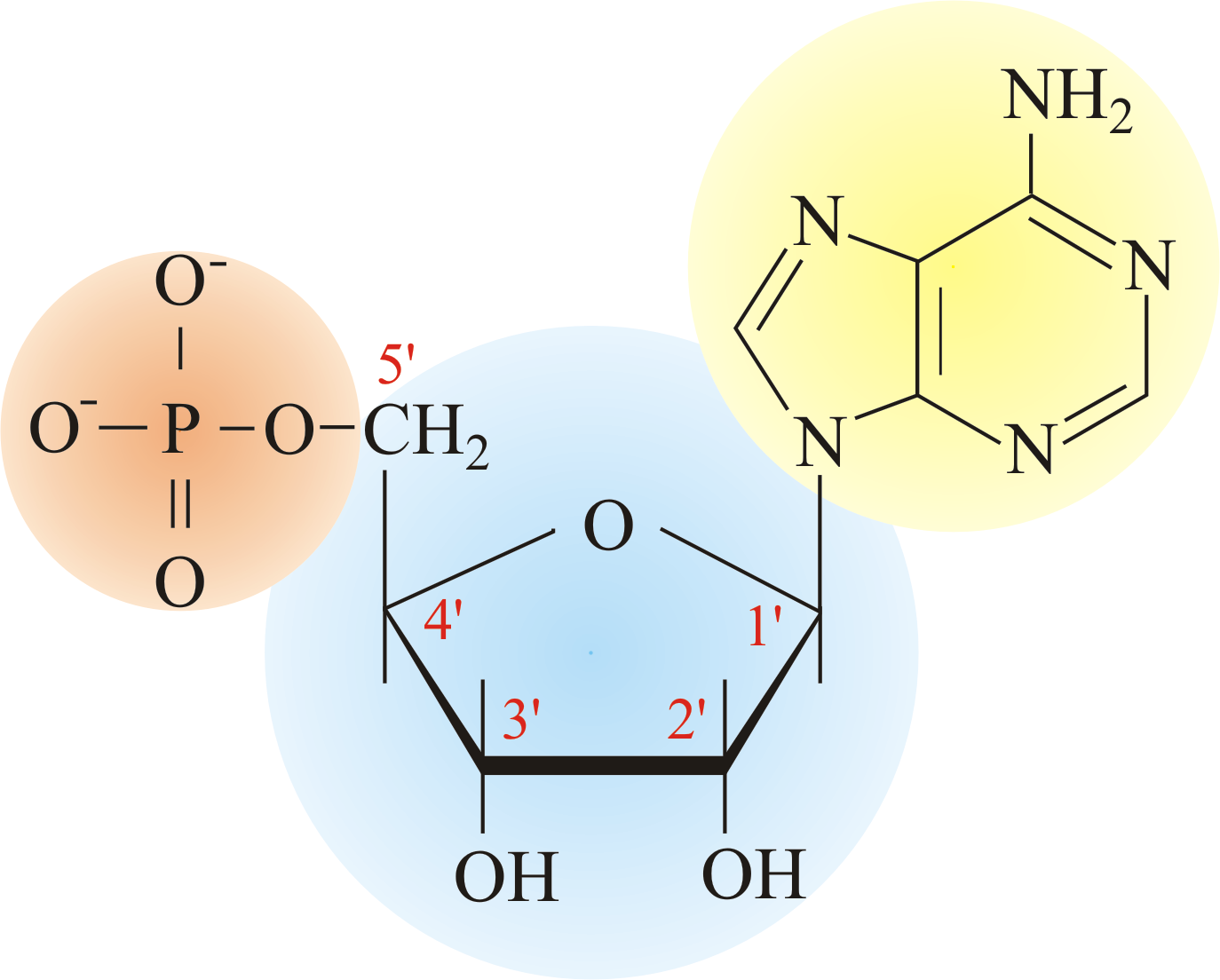
See below the above structure is a color (magenta)nucleotide. Explain the structural difference between the sugar components of dna and rna. Web introduction to nucleic acids. There are 2 main types of. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing.
DNA/RNA Structure How to Draw Nucleic Acids YouTube
Web moof's medical biochemistry video course: Web introduction to nucleic acids and nucleotides | high school biology | khan academy Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. 5.1 nucleotides and the phosphodiester bond. Primary structure consists of a linear sequence of nucleotides that are linked together by phosphodiester bond.
Describe the Roles of Nucleic Acids Dna and Rna
Nucleic acids are macromolecules made up of monomers called nucleotides. See below the above structure is a color (magenta)nucleotide. Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information. Describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show how the nucleotide units are joined together.
Nucleic acid Definition, Function, Structure, & Types Britannica
Web please support the channelmy videos are funded by people like you. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. Web describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. Nucleotides consist of 3 components: Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life.
Nucleic Acids Types, Structure, Function & Definition
The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) and ribonucleic acid ( rna ). Dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and rna stands for ribonucleic acid. If you enjoy them, please help me make more: The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid.
Web Introduction To Nucleic Acids And Nucleotides.
Web a type of rna called messenger rna or mrna reads dna and makes a copy of it, through a process called transcription. It is this linear sequence of nucleotides that make up the primary structure of dna or rna. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) and ribonucleic acid ( rna ). Indicate the nitrogen atom by which a given purine or pyrimidine base attaches to the sugar component in nucleotides and nucleosides.
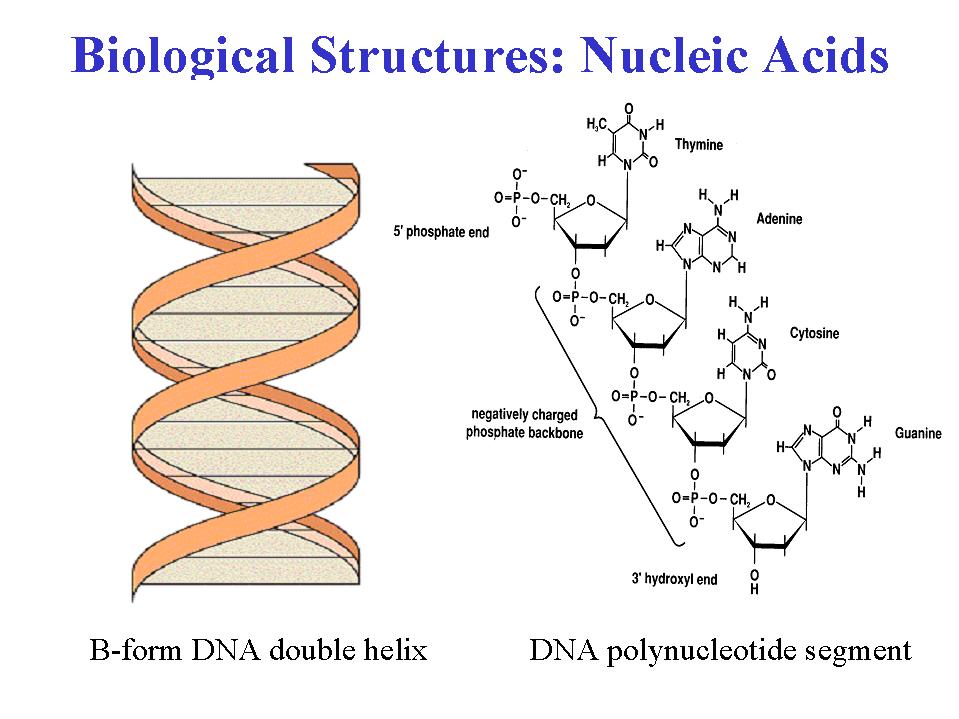
Describe The Secondary Structure Of Dna And The Importance Of Complementary Base Pairing.
The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Web moof's medical biochemistry video course: The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Dna stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and rna stands for ribonucleic acid.
Web Please Support The Channelmy Videos Are Funded By People Like You.
Web dssr (dissecting the spatial structure of rna) is an integrated software tool for the analysis/annotation, model building, and schematic visualization of 3d nucleic acid structures (see the figures below and the video overview ). Web this biochemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into nucleic acids such as dna and rna. Web describe the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Web 2d nucleic acid structure drawing programs can be roughly separated into two categories:
Sketch A Section Of Nucleic Acid To Show How The Nucleotide Units Are Joined Together.
Primary structure consists of a linear sequence of nucleotides that are linked together by phosphodiester bond. Explain the structural difference between the sugar components of dna and rna. Web introduction to nucleic acids. Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)