Hypotonic Drawing
Hypotonic Drawing - Web what are iv fluids? If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, there will be a net flow of water out of the cell, and the cell will lose volume. Web what is a hypotonic solution? Three terms—hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic—are used to relate the osmolarity of a cell to the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid that contains the cells. Although some effects can be seen, the rigid cell wall can hide the magnitude of what is going on inside. Web a hypotonic solution is a dilute solution that has a salt concentration lower than that of the cell. Web hypotonic is a description of the solute content of one solution in relation to another solution. This biology video tutorial provides a basic introduction into hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic. This video covers a recap of the foundation of passive tran. What is a hypotonic solution?
A hypotonic solution example is distilled water. It is used in biology to help scientist describe cells. In the case of iv solutions, we are specifically comparing them to blood. Web to reduce edema (swelling), they might use a hypertonic iv solution to draw excess water out of your bloodstream and into your cells. The term hypotonic has two parts: Depending on the amount of water that. Web a hypotonic solution is a dilute solution that has a salt concentration lower than that of the cell. The effects of isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic extracellular environments on plant and animal cells is the same. A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute than. Web what is a hypotonic solution?
0.45% sodium chloride (0.45% nacl) 0.33% sodium. In a hypotonic situation, the extracellular fluid has lower osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell, and water enters the cell. A hypotonic solution example is distilled water. The words hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic are most often used when comparing chemical solutions while discussing osmosis. Web a hypotonic solution is a dilute solution that has a salt concentration lower than that of the cell. Web there are three classifications of tonicity that one solution can have relative to another: Three terms—hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic—are used to relate the osmolarity of a cell to the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid that contains the cells. Web to reduce edema (swelling), they might use a hypertonic iv solution to draw excess water out of your bloodstream and into your cells. In nursing, we are almost always comparing things to the human body. Web what are iv fluids?
Diagram showing hypotonic solution 1235100 Vector Art at Vecteezy
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute than. The solute is the substance present in. This video covers a recap of the foundation of passive tran. The term hypotonic has two parts: The prefix means or in latin.
Types of solutionshypertonic hypotonic and isotonic explained YouTube
Nursing considerations for isotonic iv solutions. Web the organic chemistry tutor. It is used in biology to help scientist describe cells. We already know what “tonic” means, and “hypo” refers to something that is “less or under”. In the case of iv solutions, we are specifically comparing them to blood.
Plant Cell in Hypotonic Solution
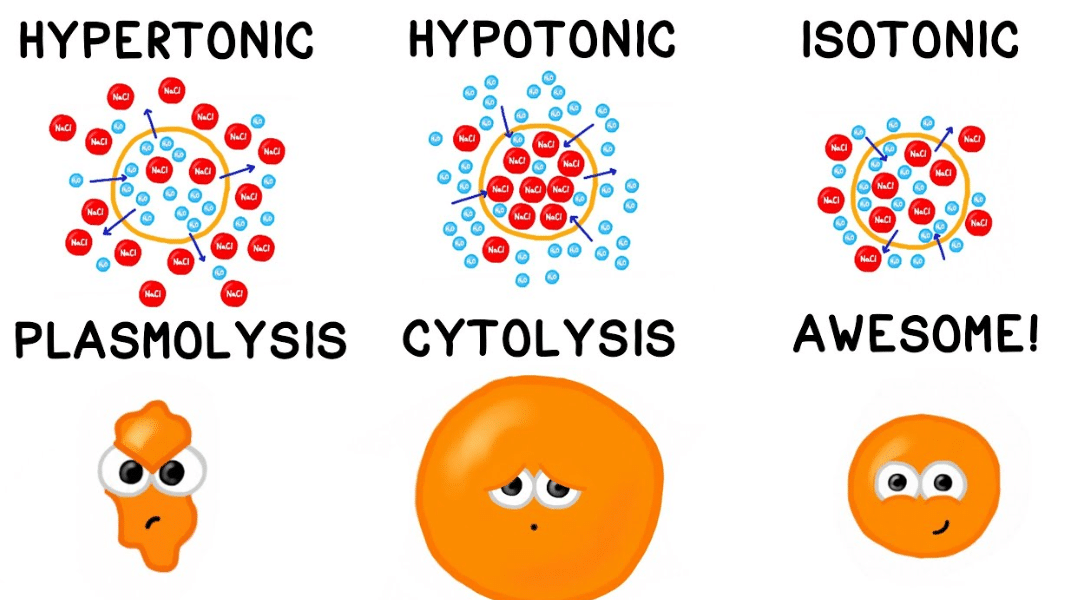
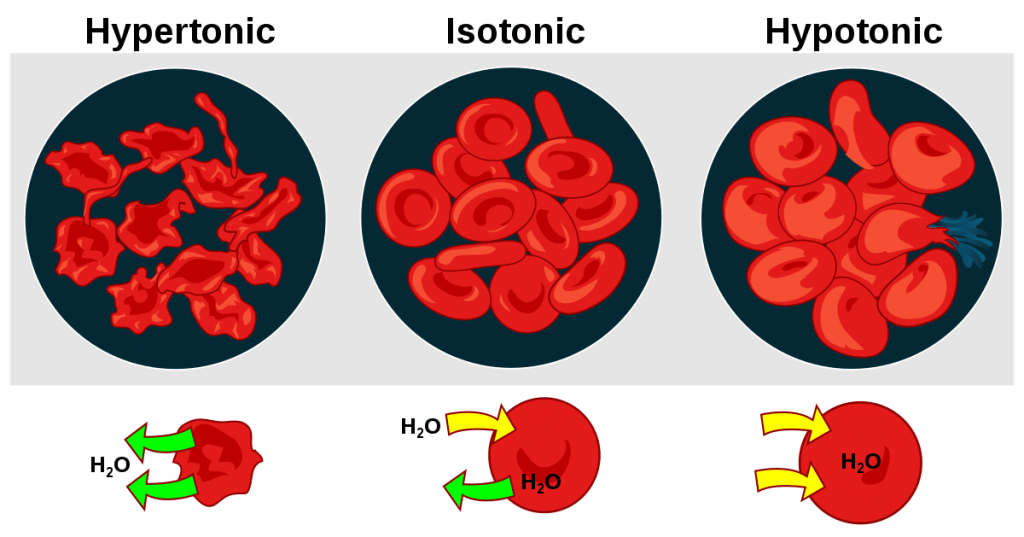
This video covers a recap of the foundation of passive tran. A hypotonic solution example is distilled water. Since the solvent will travel towards the area that has the higher solute concentration, the cell will gain water through osmosis and will, therefore, swell up (hemolysis). However, due to the cell walls of plants, the visible effects differ. 0.45% sodium chloride.
Hypotonic, Isotonic, Hypertonic Solution Effect On Cells Nursing School
Web to reduce edema (swelling), they might use a hypertonic iv solution to draw excess water out of your bloodstream and into your cells. Osmosis is a passive transport process during which water moves from areas where solutes are less concentrated to areas where they are more concentrated. Next, we’ll take a closer look at hypotonic fluids. Three terms—hypotonic, isotonic,.
Biology diagram show effect of isotonic, hypertonic and hypotonic
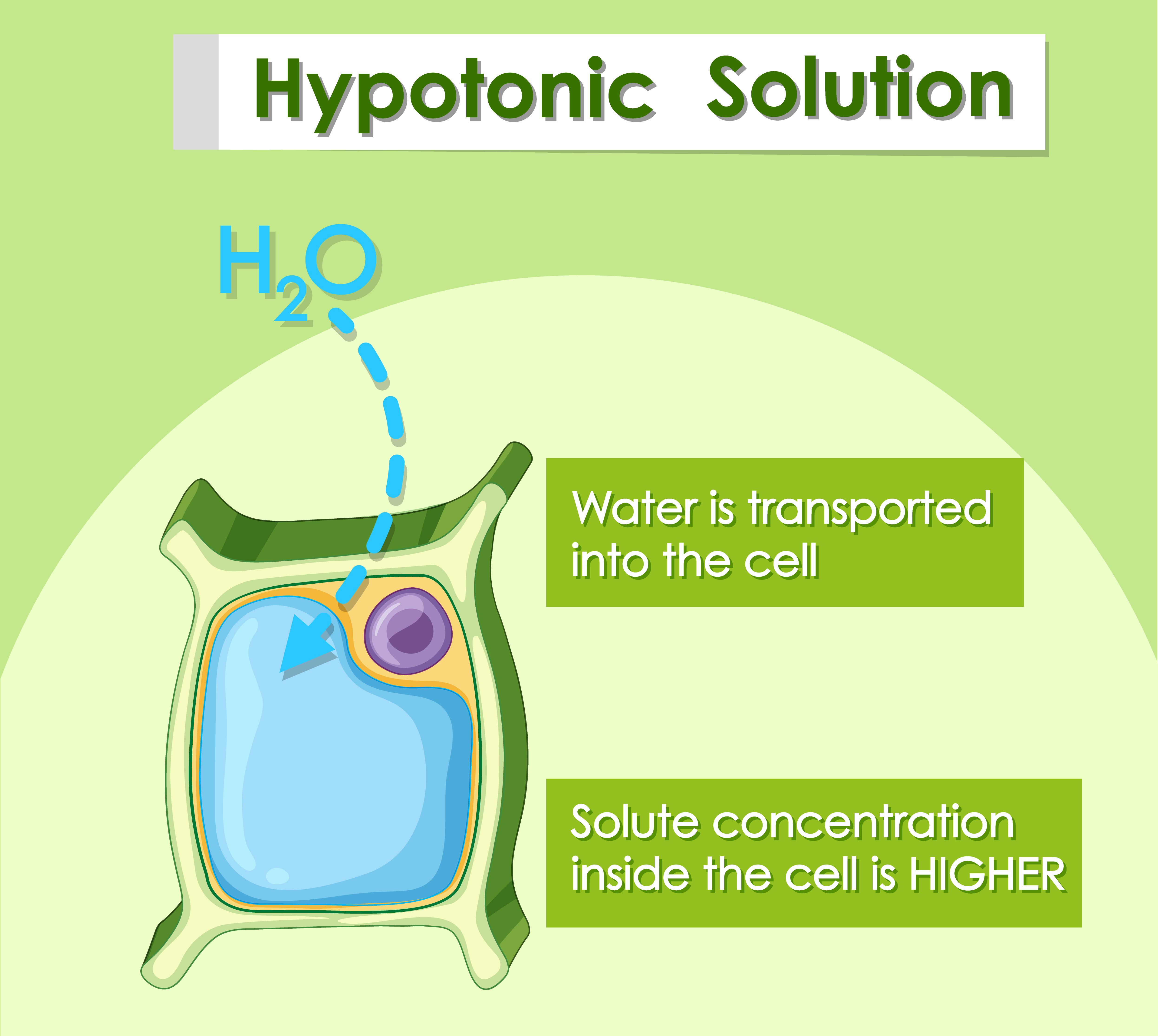
Web hypotonic is a description of the solute content of one solution in relation to another solution. Under these conditions, the osmotic pressure gradient forces water into the cell. Web a hypotonic solution is a dilute solution that has a salt concentration lower than that of the cell. 0.45% sodium chloride (0.45% nacl) 0.33% sodium. Next, we’ll take a closer.
What Is A Hypotonic Solution Get Education
Science > high school biology > energy and transport > osmosis and tonicity review. Three terms—hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic—are used to relate the osmolarity of a cell to the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid that contains the cells. In this case, water will move into the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to swell. Web hypotonic is a description of.
What Is A Hypotonic Definition And Hypotonic Solution? Best Examples
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute than. This video covers a recap of the foundation of passive tran. The effects of isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic extracellular environments on plant and animal cells is the same. Hypo means “less/under/beneath,” and tonic means “stretching or concentration of a solution.” a solution with a lower solute concentration or lower osmotic.
Hypotonic Solution Definition, Diagram & Examples Video & Lesson
Web in a hypotonic solution, the solute concentration is lower than inside the cell. College of the redwoods via asccc open educational resources initiative. 99k views 4 years ago biology. Since the solvent will travel towards the area that has the higher solute concentration, the cell will gain water through osmosis and will, therefore, swell up (hemolysis). Science > high.
What is hypotonic solution? examples and types Isbiology
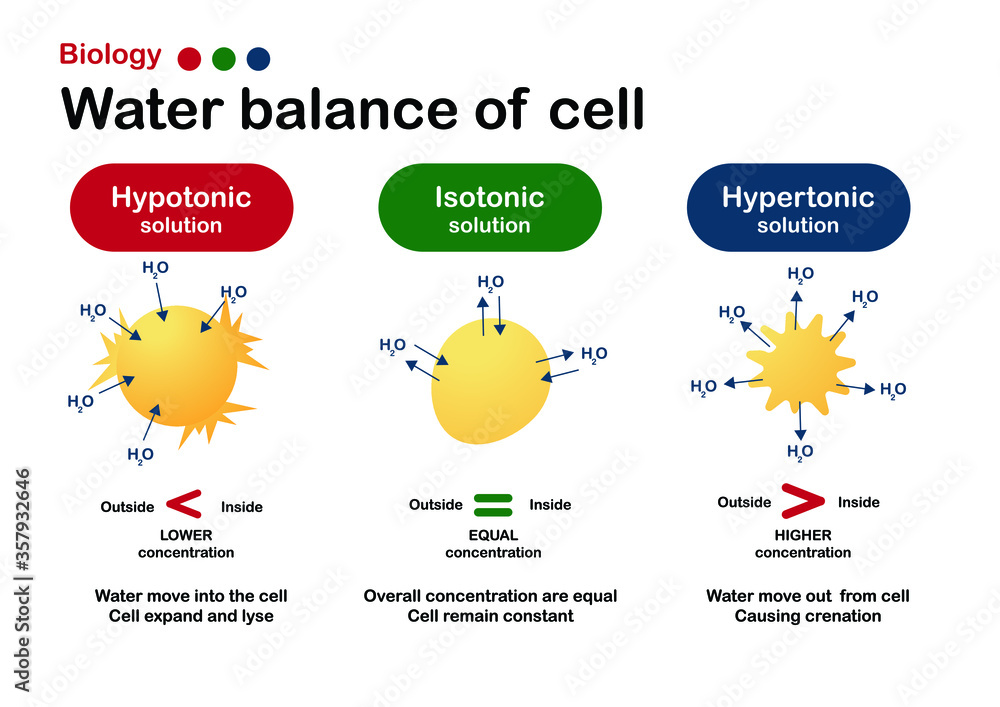
Isoosmotic and isotonic refer to solutions that have the same solute concentration as. The words hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic are most often used when comparing chemical solutions while discussing osmosis. Web in this video we discuss the three types of osmotic solutions: In a hypotonic situation, the extracellular fluid has lower osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell, and water.
What is hypotonic solution? examples and types Isbiology
0.45% sodium chloride (0.45% nacl) 0.33% sodium. Three terms—hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic—are used to relate the osmolarity of a cell to the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid that contains the cells. Hypo means “less/under/beneath,” and tonic means “stretching or concentration of a solution.” a solution with a lower solute concentration or lower osmotic pressure across a semipermeable membrane is called.
0.45% Sodium Chloride (0.45% Nacl) 0.33% Sodium.
In the case of iv solutions, we are specifically comparing them to blood. Depending on the amount of water that. The effects of isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic extracellular environments on plant and animal cells is the same. Web a hypotonic solution is a dilute solution that has a salt concentration lower than that of the cell.
Nursing Considerations For Isotonic Iv Solutions.
A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute than. Since the solvent will travel towards the area that has the higher solute concentration, the cell will gain water through osmosis and will, therefore, swell up (hemolysis). The prefix means or in latin. Isoosmotic and isotonic refer to solutions that have the same solute concentration as.
A Hypotonic Solution Is A Solution With A Lower Concentration Of Solutes Than Another Solution.
Web what are iv fluids? Once again, we can break down the name to work out the definition of these kinds of fluids. Cells in a hypotonic solution. Solutions are mixtures composed of a solute and a solvent.
However, Due To The Cell Walls Of Plants, The Visible Effects Differ.
A hypotonic solution example is distilled water. Next, we’ll take a closer look at hypotonic fluids. Osmosis is a passive transport process during which water moves from areas where solutes are less concentrated to areas where they are more concentrated. It is used in biology to help scientist describe cells.