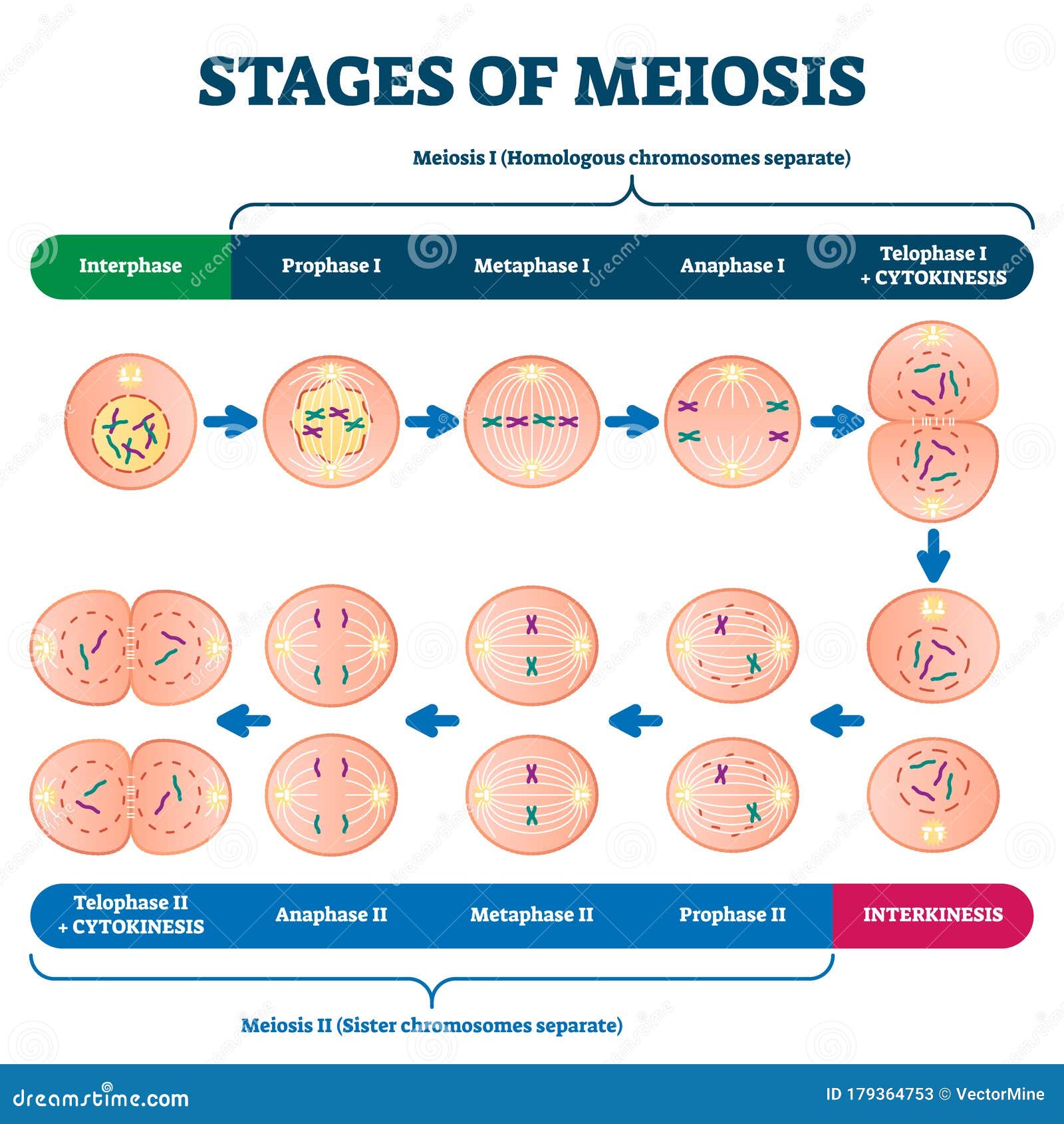
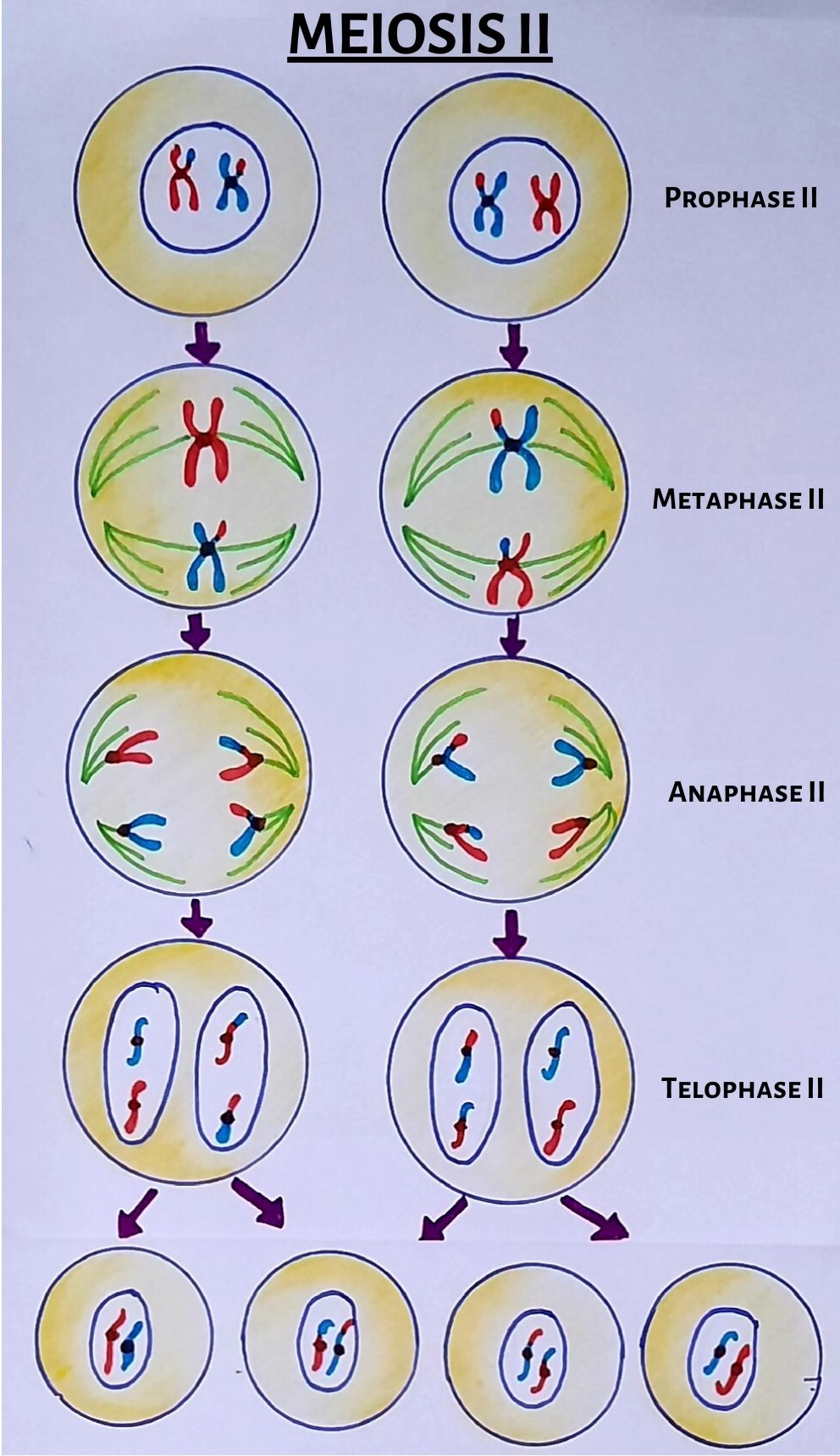
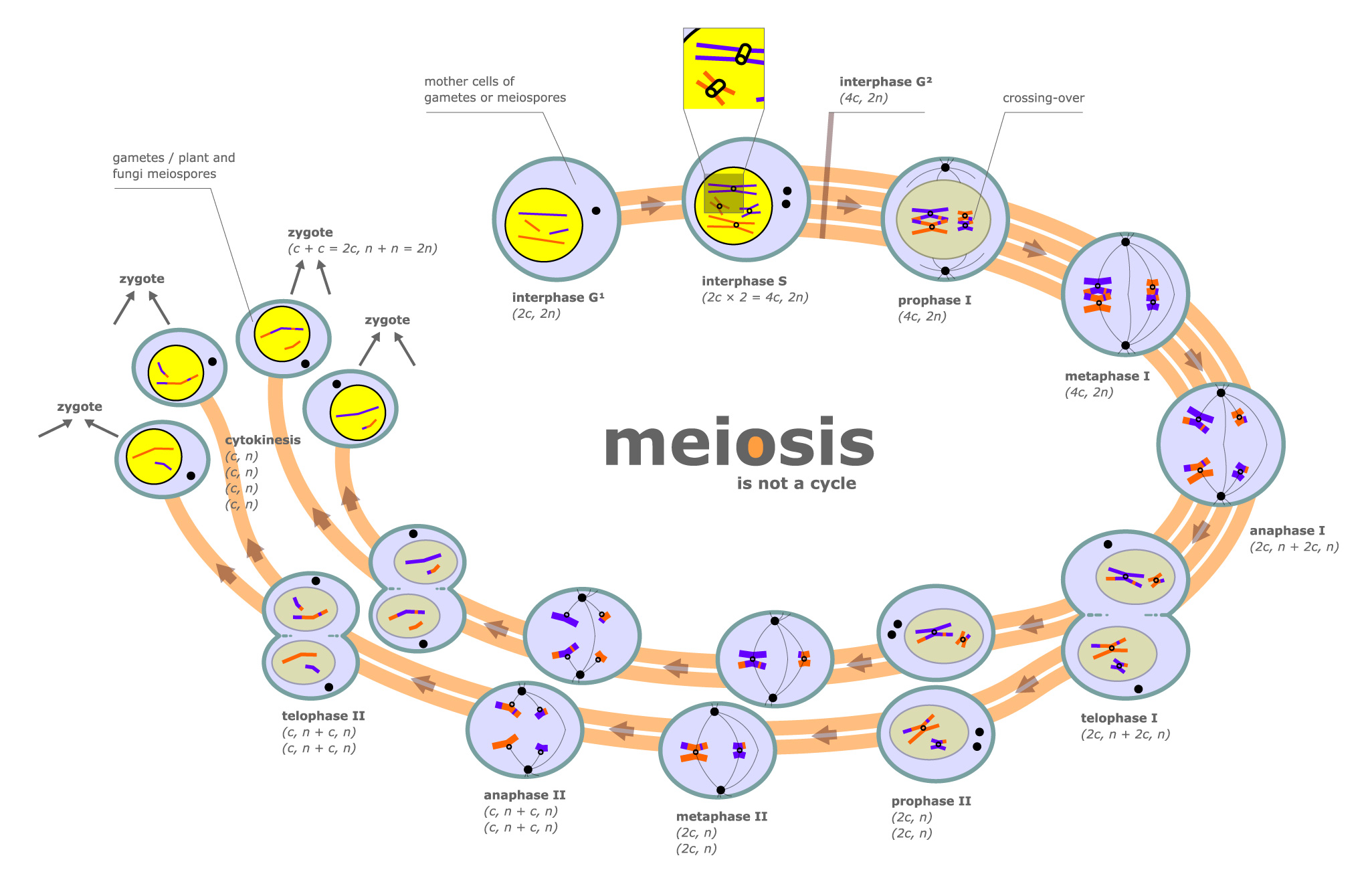
Meiosis Drawing Stages
Meiosis Drawing Stages - At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Web identify the stages of meiosis. Therefore, when meiosis is completed, each daughter cell contains only half the number (n) of chromosomes as the original cell. Spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes at the centromere. Web there are two stages or phases of meiosis: Web drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells. The process of meiosis happens in the male and female reproductive organs. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In kind means that the offspring of any organism closely resemble their parent or parents.
Spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes at the centromere. Daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell. In metaphase i, chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. Meiotic stages and their events. Web meiosis involves only one round of dna replication where each chromosome replicates to form sister chromatids. As in mitosis, the cell grows during g 1 phase, copies all of its chromosomes during s phase, and prepares for division during g 2 phase. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Web meiosis i encompasses four stages: Many organisms package these cells into gametes, such as egg and sperm. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
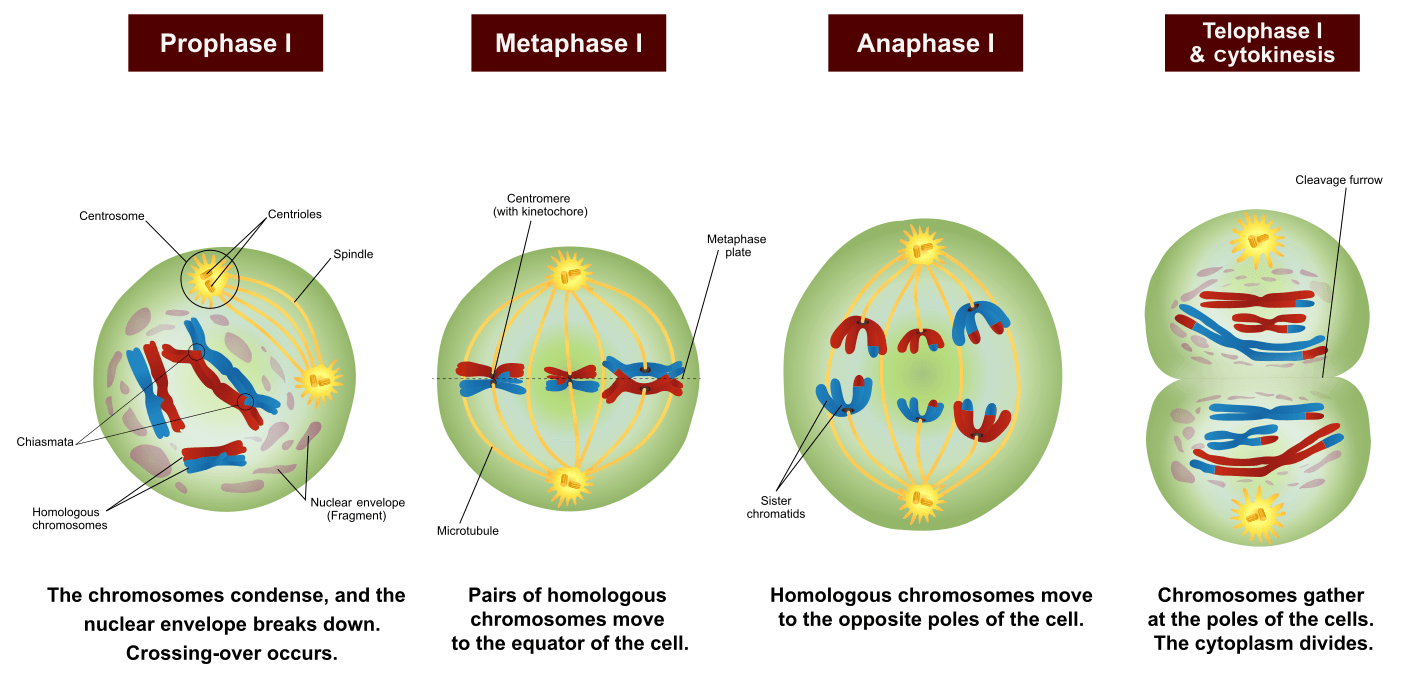
Web meiosis begins with prophase i and the contraction of the chromosomes in the nucleus of the diploid cell. As a cell divides to form gametes:. Before entering meiosis i, a cell must first go through interphase. Each pair of chromosomes—called a tetrad, or a bivalent—consists of four chromatids. You will also need to record the main events that are happening at each stage. Meiosis cell division takes place in the following stages: Prophase i is divided into five different stages: Meiosis i and meiosis ii. Homologous paternal and maternal chromosomes pair up along the midline of the cell. Describe why meiosis involves two rounds of nuclear division.
Meiosis Phases Explore the various stages of meiosis
Web there are two stages or phases of meiosis: Web meiosis involves only one round of dna replication where each chromosome replicates to form sister chromatids. Spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes at the centromere. This is the stage where genetic recombination may occur (via crossing over). Web stages/phases of meiosis.
Meiosis Definition, Stages, Function and Purpose Biology Dictionary
Many organisms package these cells into gametes, such as egg and sperm. Web meiosis occurs in eukaryotic life cycles involving sexual reproduction, consisting of the cyclical process of growth and development by mitotic cell division, production of gametes by meiosis and fertilization. The chromosomes begin to condense accompanied by the dissolution of the nuclear membrane and the disappearance of the.
Meiosis Definition, Stages, & Purpose with Diagram
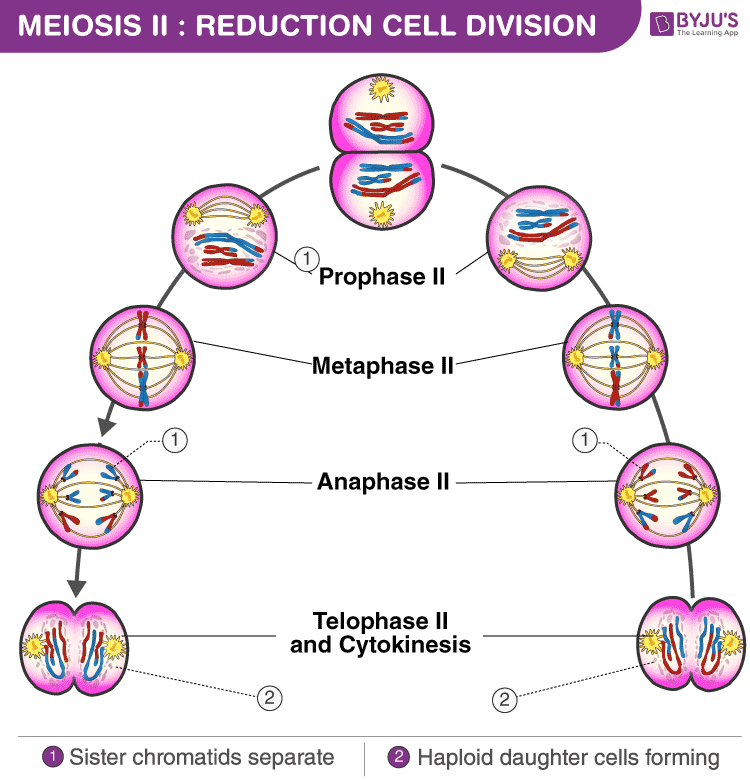
Meiotic stages and their events. Web there are six stages within each of the divisions, namely prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. Describe why meiosis involves two rounds of nuclear division. Each round of division contains a period of karyokinesis (nuclear division) and cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division). Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Meiosis Phases, Stages, Applications with Diagram
Daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell. Web there are six stages within each of the divisions, namely prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. The gametes can then meet, during reproduction, and fuse to create a new zygote. Web the diagram of meiosis along with the explanation of its different stages is given below in detail. Web.
Mitotic Cell Division What Is Mitosis? What Is Meiosis?
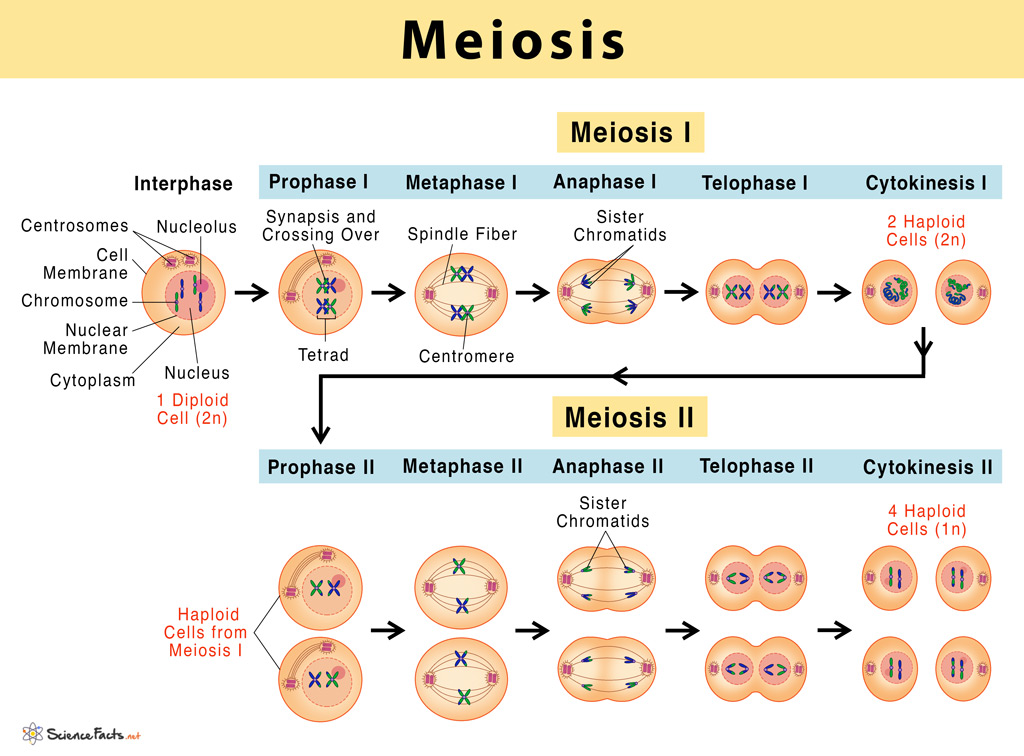
Web meiosis involves two successive stages or phases of cell division, meiosis i and meiosis ii. Web in each round of division, cells go through four stages: Web meiosis occurs in eukaryotic life cycles involving sexual reproduction, consisting of the cyclical process of growth and development by mitotic cell division, production of gametes by meiosis and fertilization. Below are drawings.
Stages of Meiosis Vector Illustration. Labeled Cell Division Process
Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i and meiosis ii. Below are drawings in the stages of meiosis. Web meiosis involves only one round of dna replication where each chromosome replicates to form sister chromatids. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. In kind means that the offspring of any.
What is meiosis? Facts
Web identify the stages of meiosis. Meiosis i and meiosis ii. This is the stage where genetic recombination may occur (via crossing over). Web meiosis begins with prophase i and the contraction of the chromosomes in the nucleus of the diploid cell. Web meiosis i encompasses four stages:
Meiosis, Stages, Meiosis vs Mitosis The Virtual Notebook
Meiosis cell division takes place in the following stages: Meiosis is composed of two rounds of cell division, namely meiosis i and meiosis ii. Web the diagram of meiosis along with the explanation of its different stages is given below in detail. Daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell. Before entering meiosis i, a cell must first go.
Meiosis Phases, Stages, Applications with Diagram
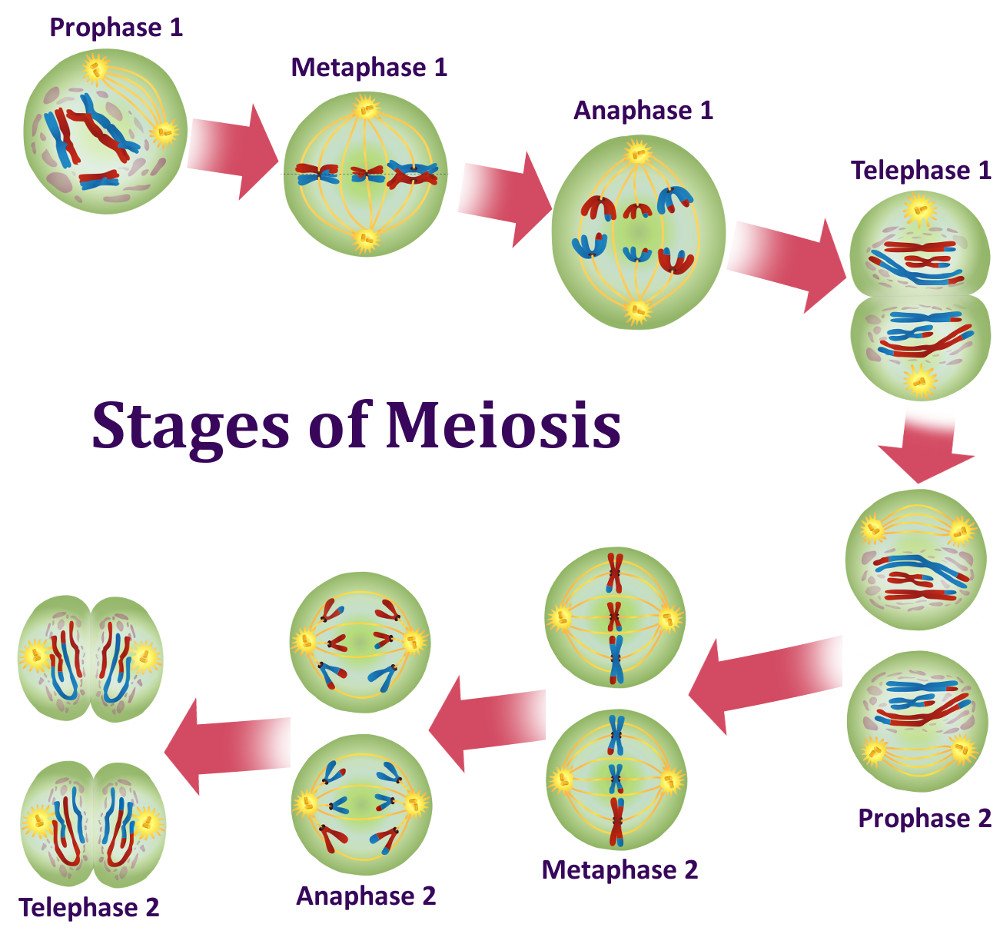
You will also need to record the main events that are happening at each stage. The process of meiosis happens in the male and female reproductive organs. Each pair of chromosomes—called a tetrad, or a bivalent—consists of four chromatids. The gametes can then meet, during reproduction, and fuse to create a new zygote. Meiosis i and meiosis ii.
FileMeiosis diagram.jpg
Web there are six stages within each of the divisions, namely prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. Therefore, when meiosis is completed, each daughter cell contains only half the number (n) of chromosomes as the original cell. In this article, we will look at the stages of meiosis and consider its significance in disease. The period prior to the.
More Than 13 Meiosis Questions Answered Correctly.
Web meiosis occurs in eukaryotic life cycles involving sexual reproduction, consisting of the cyclical process of growth and development by mitotic cell division, production of gametes by meiosis and fertilization. Web identify the stages of meiosis. In kind means that the offspring of any organism closely resemble their parent or parents. As in mitosis, the cell grows during g 1 phase, copies all of its chromosomes during s phase, and prepares for division during g 2 phase.
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, And Telophase.
Web in each round of division, cells go through four stages: The process of meiosis happens in the male and female reproductive organs. Cut these out and put them in the proper order for meiosis on the next sheet provided. Web stages/phases of meiosis.
The Chromosomes Begin To Condense Accompanied By The Dissolution Of The Nuclear Membrane And The Disappearance Of The Golgi Apparatus And Er Complex.
Web meiosis i encompasses four stages: Before entering meiosis i, a cell must first go through interphase. Web meiosis involves two successive stages or phases of cell division, meiosis i and meiosis ii. Web meiosis begins with prophase i and the contraction of the chromosomes in the nucleus of the diploid cell.
Before A Dividing Cell Enters Meiosis, It Undergoes A Period Of Growth Called Interphase.
As a cell divides to form gametes:. Each stage includes a period of nuclear division or karyokinesis and a cytoplasmic division or cytokinesis. This is the stage where genetic recombination may occur (via crossing over). Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.