Newtons Second Law Drawing
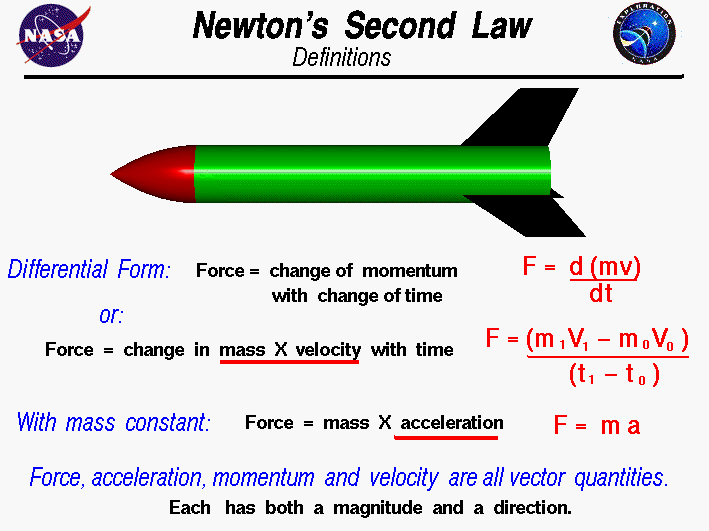
Newtons Second Law Drawing - Newton's second law tells us exactly how much an object will accelerate for a given net force. This change in momentum is in the same. All external forces acting on the car are shown. Web donald trump pledged to double down on tax cuts if he wins a second term as president, drawing a distinction with president joe biden who has called for tax hikes on businesses and the richest americans. F net = m a. Web in equation form, newton’s second law of motion is a = fnet m a = f net m, often written in the more familiar form: This type of motion is addressed by newton’s second law of motion, which states how force causes changes. The natural behavior of a body is to move in a straight line at constant speed. A = σ f m. 0 = 1 m(fg −fn) 0 = 1 m ( f g − f n) solving this for fn f n yields:
This change in momentum is in the same direction as the resultant force. An understanding of forces and their tendency to balance or not balance each other is crucial to understanding how the object will change or not change its state of motion. Web therefore, we introduce newton’s second law and then do an example problem. Newton's second law and a force analysis. Web newton's second law tells us that if the force is the same, the acceleration of two arrows together will be half the acceleration of the single arrow. The resultant force on an object is equal to its rate of change in momentum. Newton's laws of motion describe the connection between the forces that act upon an object and the manner in which the object moves. Web newton’s first law considered bodies at rest or bodies in motion at a constant velocity.the other state of motion to consider is when an object is moving with a changing velocity, which means a change in the speed and/or the direction of motion. “instead of a biden tax hike, i’ll give you a trump middle class, upper class, lower class, business class big tax cut,” trump said at a. Therefore, we can find the force as follows:
“instead of a biden tax hike, i’ll give you a trump middle class, upper class, lower class, business class big tax cut,” trump said at a. Newton's laws of motion describe the connection between the forces that act upon an object and the manner in which the object moves. An understanding of forces and their tendency to balance or not balance each other is crucial to understanding how the object will change or not change its state of motion. 0 = 1 m(fg −fn) 0 = 1 m ( f g − f n) solving this for fn f n yields: Often expressed as the equation a = fnet/m (or rearranged to fnet=m*a), the equation is probably the most important equation in all of mechanics. The law is often expressed in the form of the following two equations. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. Newton’s 2nd law relates an object’s mass, the net force on it, and its acceleration: Web newton's second law describes the affect of net force and mass upon the acceleration of an object. Newton’s second law says that the acceleration and net external force are directly proportional, and there is an inversely proportional relationship between acceleration and mass.
PPT Isaac Newton PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1953539
Web newton’s first law considered bodies at rest or bodies in motion at a constant velocity.the other state of motion to consider is when an object is moving with a changing velocity, which means a change in the speed and/or the direction of motion. This type of motion is addressed by newton’s second law of motion, which states how force.
Second Law of Motion Newtons LAWS of PHYSICS
Web in equation form, newton’s second law of motion is a = fnet m a = f net m, often written in the more familiar form: 0 = 1 m(fg −fn) 0 = 1 m ( f g − f n) solving this for fn f n yields: Web newton's second law describes the affect of net force and mass.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion Concept of a System · Physics
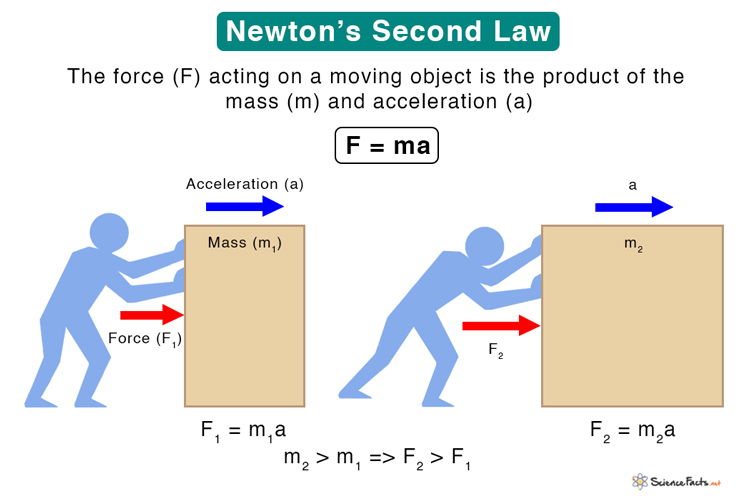
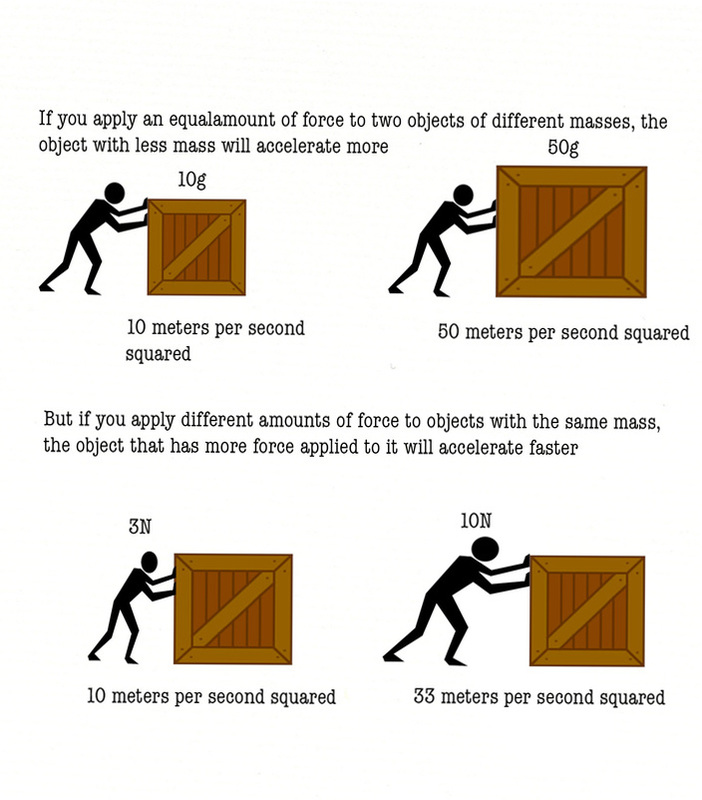
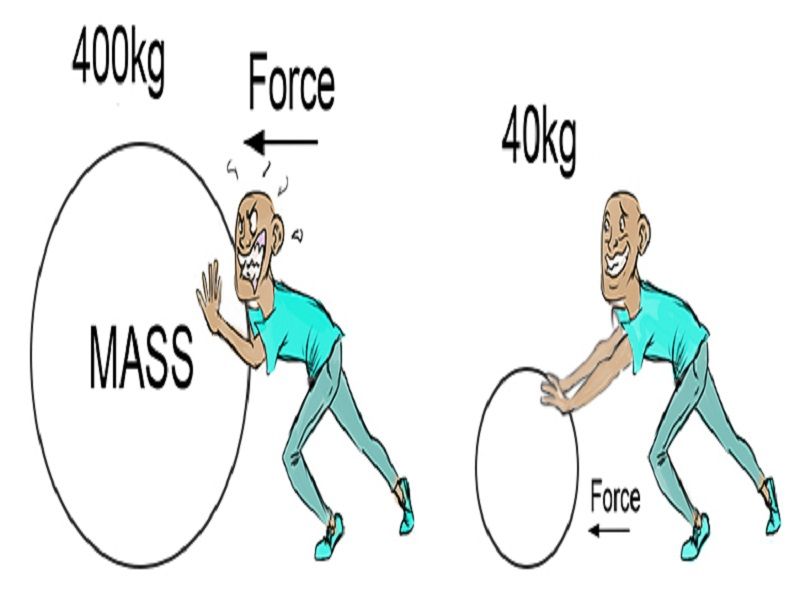
The natural behavior of a body is to move in a straight line at constant speed. For example, a large force on a tiny object gives it a huge acceleration, but a small force on a huge object gives it very little. The acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external.
Newton's Second Law of Motion
Mission nl5 involves the comparison of the relative magnitude of the individual forces that act upon an object in various physical situations. The linear acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the vector sum of all the forces acting on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass (a = f/m). Web newton’s first law considered bodies at.
10 Examples of Newton’s Second Law of Motion in Everyday Life StudiousGuy
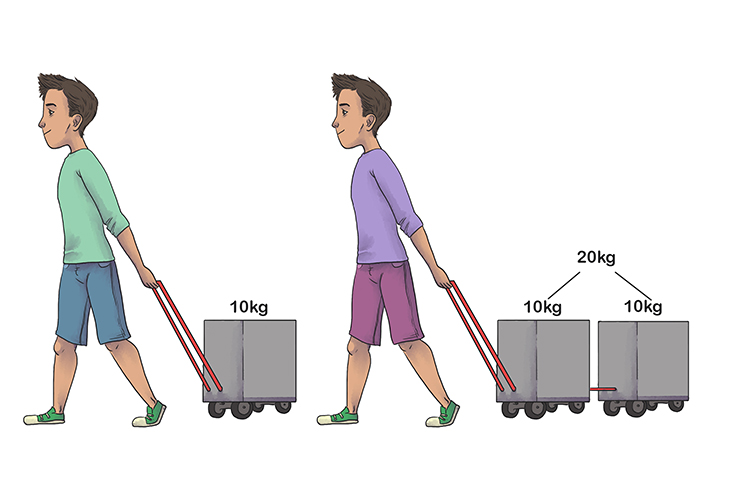
You can see that this is true by comparing the distance traveled by one arrow with that traveled. In unit 2 of the physics classroom, newton's second law was. W = mg w = m g. To be clear, a is the acceleration of the object, σ f is the net force on the object, and m is the mass.
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
Newton’s second law is closely related to his first law. Web the acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system, and inversely proportional to its mass. A body's motion preserves the status quo, but external forces can perturb this. Web quinn declined to put a timeline.
Newton’s Second Law Statement, Examples, and Equation
Web newton’s second law of motion. 0 = 1 m(fg −fn) 0 = 1 m ( f g − f n) solving this for fn f n yields: Newton’s second law is closely related to his first law. The modern understanding of newton's first law is that no inertial observer is privileged over any other. Web we know objects can.
CC Cycle 2 Week 17 How to Draw Newton's Second Law of Motion Newtons
Substituting the values, we get. A body's motion preserves the status quo, but external forces can perturb this. All external forces acting on the car are shown. Newton’s second law says that the acceleration and net external force are directly proportional, and there is an inversely proportional relationship between acceleration and mass. Newton’s 2nd law relates an object’s mass, the.
Newton's second law Examples
Web newton’s first law considered bodies at rest or bodies in motion at a constant velocity.the other state of motion to consider is when an object is moving with a changing velocity, which means a change in the speed and/or the direction of motion. Is there an analogous equation to newton’s second law, σ f → = m a →,.
Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion Physics of Basketball UWMadison
It is used to predict how an object will accelerated (magnitude and direction) in the presence of an. (a) two students push a stalled car. Newton's second law and a force analysis. Web figure 5.10 different forces exerted on the same mass produce different accelerations. The resultant force on an object is equal to its rate of change in momentum.
Newton’s Second Law Of Motion.
Body at rest remains at rest or, if in motion, remains in motion at constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force; A body's motion preserves the status quo, but external forces can perturb this. Substituting the values, we get. →a = →fnet m, where →a is the acceleration, →fnet is the net force, and m is the mass.
This Is Often Written In The More Familiar Form.
Web note that the only a in the free body diagram is horizontal. Therefore, we can find the force as follows: The law is often expressed in the form of the following two equations. Web newton’s first law considered bodies at rest or bodies in motion at a constant velocity.the other state of motion to consider is when an object is moving with a changing velocity, which means a change in the speed and/or the direction of motion.
This Type Of Motion Is Addressed By Newton’s Second Law Of Motion, Which States How Force Causes Changes.
Web newton’s second law of motion. This change in momentum is in the same direction as the resultant force. Web newton's second law describes the affect of net force and mass upon the acceleration of an object. Web newton's second law tells us that if the force is the same, the acceleration of two arrows together will be half the acceleration of the single arrow.
For Example, A Large Force On A Tiny Object Gives It A Huge Acceleration, But A Small Force On A Huge Object Gives It Very Little.
We have thus far found many counterparts to the translational terms used throughout this text, most recently, torque, the rotational analog to force. The linear acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the vector sum of all the forces acting on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass (a = f/m). Fn =fg f n = f g. Is there an analogous equation to newton’s second law, σ f → = m a →, σ f → = m a →, which involves torque and rotational.


.PNG)