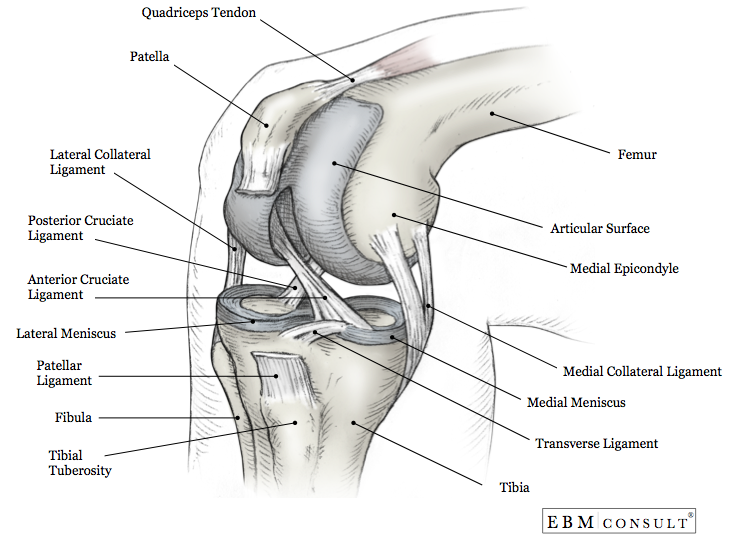
Posterior Drawer Sign
Posterior Drawer Sign - Web knee injuries are usually physically examined. Web an anterior drawer test can be one part of those knee examinations. Web according to the available evidence, the sag sign is best test for ruling out a pcl injury when negative, while the quadriceps active test is the best test for ruling in a pcl injury when positive. (1994) the posterior drawer test has a sensitivity of 89% and a specificity. Web the posterior drawer test is a common orthopedic test to assess for posterior cruciate ligament tears. The patient is asked to isometrically contract the hamstrings while the clinician stabilizes the foot. Test accuracy / reliability / evidence: Web gravity “sag” sign near extension, active reduction “quad activation” of posterior tibial subluxation, and posterior drawer tests. Web citation, doi, disclosures and article data. Whereas excessive posterior displacement of the tibia may indicate injury of the posterior cruciate ligament.
The test simply involves your practitioner. The examiner should place his/her hands along the sides of the affected knee, while palpating the. Web posterior drawer sign (pcl) this video outlines the posterior drawer test/sign for pcl pathology. Web 🎓free online courses: Web this video demonstrates the posterior sag sign and posterior drawer test in a patient with a pcl tear. Web posterior sag sign. The anterior tibial translocation sign or anterior drawer sign (a.k.a. Web for more knee examination video tutorials, visit the amboss library: Whereas excessive posterior displacement of the tibia may indicate injury of the posterior cruciate ligament. Then, with the palms placed on either side of the proximal tibia, a posterior force is applied.
With the patient lying supine, the hip bent at 45 degrees and the knee bent at 90 degrees, the examiner sits on the patient’s foot to stabilize the limb. Web this video demonstrates the posterior sag sign and posterior drawer test in a patient with a pcl tear. Web gravity “sag” sign near extension, active reduction “quad activation” of posterior tibial subluxation, and posterior drawer tests. The test simply involves your practitioner. A torn pcl allows the free tibia to. Budoff and nirschl agree that the posterior drawer is the best test to determine pcl integrity, but conclude that grading is the most important as this will determine the course of treatment. These tests evaluate for posterior collateral ligament. Web an anterior drawer test can be one part of those knee examinations. Web enroll in our online course: These physical tests are often enough to find out if there’s an injury.
Posterior Drawer Test, PCL Injury Tests —
Like the anterior drawer test, the test is conducted in supine lying position with the hip flexed to 45° and the knee flexed to 90°. Posterior drawer (at 90° flexion) with the knee at 90° of flexion, a posteriorly directed force is applied to the proximal tibia and posterior tibial translation is quantified. Budoff and nirschl agree that the posterior.
Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
Some older studies note a lower sensitivity (accuracy) level for detecting acl injuries — as low as 61 percent. To assess the integrity of the pcl. The pcl is attached to the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia and passes anteriorly, medially, and upward to attach to the lateral side of the medial femoral condyle. Anterior translation of tibia) is.
PPT Joints of the Lower Limb PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Have the patient's affected hip and knee in a flexed position. Web this video demonstrates the posterior sag sign and posterior drawer test in a patient with a pcl tear. The test simply involves your practitioner. Test accuracy / reliability / evidence: Web according to the available evidence, the sag sign is best test for ruling out a pcl injury.
Posterior Drawer Test for the Knee YouTube
Then, with the palms placed on either side of the proximal tibia, a posterior force is applied. Like the anterior drawer test, the test is conducted in supine lying position with the hip flexed to 45° and the knee flexed to 90°. Healthcare provider often perform a posterior drawer test to assess the function of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl)—one.
Physical Exam Posterior Drawer Test
The patient is asked to isometrically contract the hamstrings while the clinician stabilizes the foot. This study reported that in subacute/chronic acl ruptures (more than 2 weeks before examination), the sensitivity is 40.9% and the specificity is 98.4%. The most common causes of pcl tears are due to dashboard. Posterior drawer test sensitivity and specificity sensitivity = 0.90 specificity =.
Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament YouTube
Don't be confused by the resting position and the leg. Like the anterior drawer test, the test is conducted in supine lying position with the hip flexed to 45° and the knee flexed to 90°. Healthcare provider often perform a posterior drawer test to assess the function of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl)—one of the four ligaments of the knee..
Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injury Knee
This ligament prevents backward displacement of the tibia or forward sliding of the femur. If your healthcare provider suspects a pcl tear, the posterior drawer test is the best test to diagnose it. Anterior translation of tibia) is seen in cases of complete rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament and refers to anterior translocation (anterior tibial subluxation) of the tibia.
Special Test Category Ankle & Foot Examination OrthoFixar
The most common causes of pcl tears are due to dashboard. Web the drawer test is used in the initial clinical assessment of suspected rupture of the cruciate ligaments in the knee. Budoff and nirschl agree that the posterior drawer is the best test to determine pcl integrity, but conclude that grading is the most important as this will determine.
Posterior Drawer Test Of The Knee • Easy Explained OrthoFixar 2022 in
Then, with the palms placed on either side of the proximal tibia, a posterior force is applied. The anterior tibial translocation sign or anterior drawer sign (a.k.a. With the patient lying supine, the hip bent at 45 degrees and the knee bent at 90 degrees, the examiner sits on the patient’s foot to stabilize the limb. Posterior drawer (at 90°.
PPT Physical Examination PowerPoint Presentation ID214946
(1994) the posterior drawer test has a sensitivity of 89% and a specificity. This ligament prevents backward displacement of the tibia or forward sliding of the femur. Then, with the palms placed on either side of the proximal tibia, a posterior force is applied. Web an anterior drawer test can be one part of those knee examinations. Like the anterior.
With The Patient Lying Supine, The Hip Bent At 45 Degrees And The Knee Bent At 90 Degrees, The Examiner Sits On The Patient’s Foot To Stabilize The Limb.
The examiner should be seated on the patient's foot of the involved limb. Healthcare provider often perform a posterior drawer test to assess the function of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl)—one of the four ligaments of the knee. Web posterior sag sign. Don't be confused by the resting position and the leg.
Web Katz And Fingeroth [1] Reported That The Knee Anterior Draw Test In Acute Acl Ruptures (Within 2 Weeks Of Examination) Has A Sensitivity Of 22.2% And A Specificity Of >95%.
Web an anterior drawer test can be one part of those knee examinations. Have the patient's affected hip and knee in a flexed position. Web functional posterior drawer test 2. Have the patient flex the hip and knees to 90°, feet.
Posterior Drawer Test Sensitivity And Specificity Sensitivity = 0.90 Specificity = 0.99 +Lr = 90
The posterior drawer test is the most frequently evaluated test but determining the value of the test is difficult. Test accuracy / reliability / evidence: Web 🎓free online courses: In addition to the tiered rack itself, the organizer comes with 28 empty spice jars, 386 labels and a.
Web The Drawer Test Is Used In The Initial Clinical Assessment Of Suspected Rupture Of The Cruciate Ligaments In The Knee.
The patient is asked to isometrically contract the hamstrings while the clinician stabilizes the foot. To assess the integrity of the pcl. This ligament prevents backward displacement of the tibia or forward sliding of the femur. (1994) the posterior drawer test has a sensitivity of 89% and a specificity.