Posterior Drawer
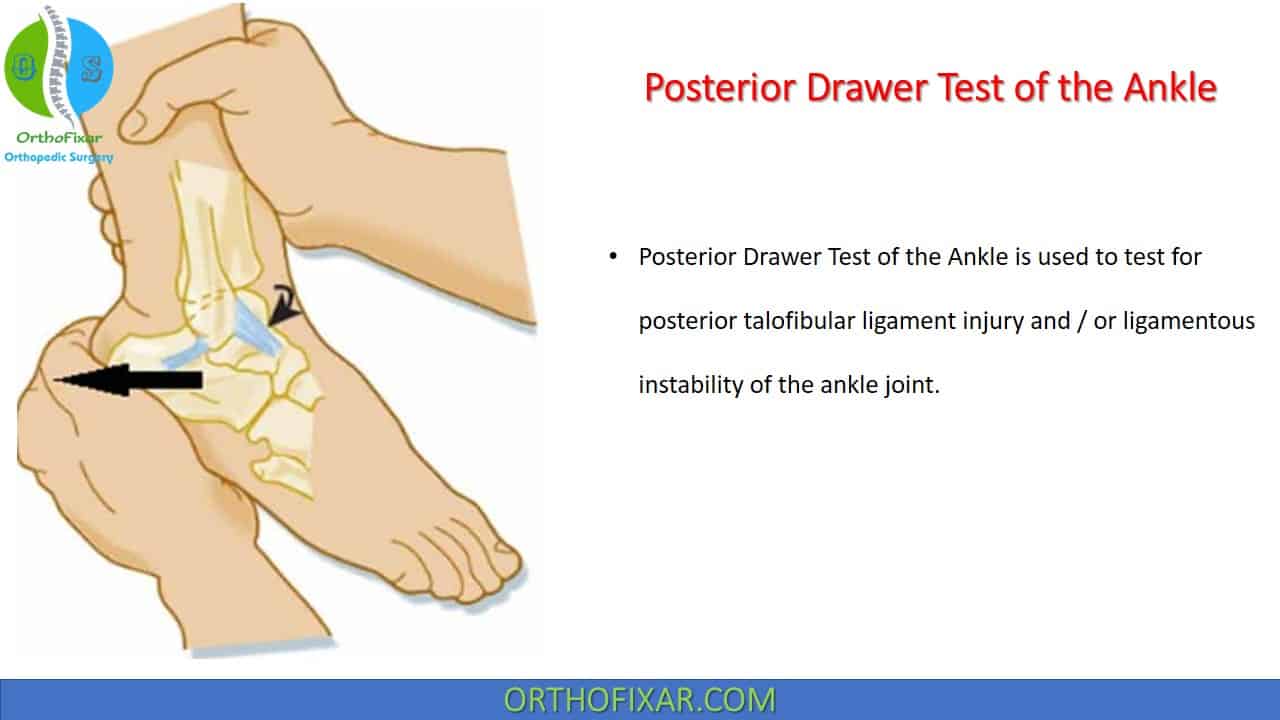
Posterior Drawer - Diagnosis can be suspected with a knee effusion and a positive dial test but mri studies are required for confirmation. Web the posterior drawer is a common orthopedic test to diagnose posterior cruciate ligament tears (pcl). Web what does a positive posterior drawer test of the knee mean? Web anatomy of the knee. Patients with knee rotatory instability will often present with joint line tenderness accompanied by swelling in the posterolateral corner of the knee. Web the posterior drawer test is used to assess the integrity of the pcl or posterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Web pcl injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e plc, acl). The patient should be supine on the examining table with knees flexed to 90°. Web posterior drawer test of the ankle is used to test for posterior talofibular ligament injury and / or ligamentous instability of the ankle joint. 75% of all hemarthroses are caused by disruption of acl.
Web the posterior drawer test and the lachman test were positive, while the front drawer test was negative, and no laxity of the collateral ligament was found. The patient, whose body mass index (bmi) was 22.5, did not have any chronic diseases, such as hypertension or coronary heart disease, nor did he have any endocrine or metabolic. Web posterior drawer test of the ankle is used to test for posterior talofibular ligament injury and / or ligamentous instability of the ankle joint. Web the posterior drawer test is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) in the knee. The examiner sits on the subject’s foot, with fingers behind the proximal tibia and thumbs on the tibial plateau. This test is performed with the patient supine, hip flexed to 45°, knee flexed to 90° and foot in a neutral position (i.e. Web the posterior drawer test evaluates the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) in the knee, crucial for diagnosing pcl sprains and knee stability. Web the posterior drawer test is used to assess the integrity of the pcl or posterior cruciate ligament of the knee. The examiner then sits on the toes of the tested extremity to help stabilize it. Web pcl injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e plc, acl).
This video clip is part of the fifa diploma in football medicine and. The posterior drawer test is considered positive if a posterior displacement of the proximal tibia, relative to the distal femur, more than 5 mm, or a “soft” end point, indicates. The patient, whose body mass index (bmi) was 22.5, did not have any chronic diseases, such as hypertension or coronary heart disease, nor did he have any endocrine or metabolic. The patient is supine and the knee to be tested is flexed to approximately 90 degrees. This ligament prevents backward displacement of the tibia or forward sliding of the femur. Web posterior cruciate ligament tear: In this grade, mobilizations are of small amplitude and of slow oscillations at the beginning of the joint range of motion. Web pcl injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e plc, acl). Web the posterior drawer test is a common orthopedic test used to evaluate tears of the posterior cruciate ligament. Limits posterior translation of tibia.
Posterior Drawer Test Of The Knee • Easy Explained OrthoFixar 2022 in
View the patient from the front, side, and back. Web the posterior drawer test is a common orthopedic test used to evaluate tears of the posterior cruciate ligament. Limits posterior translation of tibia. Web posterolateral corner (plc) injuries are traumatic knee injuries that are associated with lateral knee instability and usually present with a concomitant cruciate ligament injury (pcl >.
Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tear
Posterior drawer (at 90° flexion) with the knee at 90° of flexion, a posteriorly directed force is applied to the proximal tibia and posterior tibial. To test the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl). Web enroll in our online course: This video clip is part of the fifa diploma in football medicine and. Limits anterior translation of tibia.
How to do the Posterior Drawer Test for the Knee YouTube
This test is performed with the patient supine, hip flexed to 45°, knee flexed to 90° and foot in a neutral position (i.e. Web the posterior drawer test is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) in the knee. Read this post to learn how to do it! Web if your healthcare provider.
Knee Tests The Knee Resource
Web if your healthcare provider suspects a pcl tear, the posterior drawer test is the best test to diagnose it. Web posterior drawer test of the ankle is used to test for posterior talofibular ligament injury and / or ligamentous instability of the ankle joint. Read this post to learn how to do it! Web the posterior drawer test is.
Posterior Drawer Test Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injury Knee
Excessive valgus, varus, recurvatum, flexion contracture, and. The patient should be supine on the examining table with knees flexed to 90°. Limits posterior translation of tibia. Web posterior cruciate ligament tear: Read this post to learn how to do it!
Posterior Drawer Test Shoulder OrthoFixar 2023
How posterior drawer test of the ankle is performed? The patient, whose body mass index (bmi) was 22.5, did not have any chronic diseases, such as hypertension or coronary heart disease, nor did he have any endocrine or metabolic. Web enroll in our online course: The patient is supine and the knee to be tested is flexed to approximately 90.
Posterior Drawer Test for the Knee YouTube
Assess the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) anatomy. Ankle posterior drawer test was first described by frost and hanson in 1977. Web enroll in our online course: Web posterior cruciate ligament tear: Limits posterior translation of tibia.
Posterior drawer test for PCL YouTube
Web pcl injuries are traumatic knee injuries that may lead to posterior knee instability and often present in combination with other ipsilateral ligamentous knee injuries (i.e plc, acl). The patient, whose body mass index (bmi) was 22.5, did not have any chronic diseases, such as hypertension or coronary heart disease, nor did he have any endocrine or metabolic. View the.
Posterior Drawer Test Of The Ankle 2024
Patient lies supine with hips and knees flexed to 90°, examiner supports ankles and observes for a posterior shift of the tibia as compared to the uninvolved knee. Evaluate posterior translation, identify potential pcl injuries, and guide appropriate treatment for improved knee stability and reduced risk of instability. Similar to the previous drawer test, the test is performed in the.
PPT Joints of the Lower Limb PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Limits anterior translation of tibia. To assess the integrity of the pcl. The examiner then sits on the toes of the tested extremity to help stabilize it. Diagnosis can be suspected with a knee effusion and a positive dial test but mri studies are required for confirmation. Have the patient's affected hip and knee in a flexed position.
The Pcl Is Attached To The Posterior Intercondylar Area Of The Tibia And Passes Anteriorly, Medially, And Upward To Attach To The Lateral Side Of The Medial Femoral Condyle.
Web the posterior drawer test and the lachman test were positive, while the front drawer test was negative, and no laxity of the collateral ligament was found. To assess the integrity of the pcl. Web if your healthcare provider suspects a pcl tear, the posterior drawer test is the best test to diagnose it. Ankle posterior drawer test was first described by frost and hanson in 1977.
How Posterior Drawer Test Of The Ankle Is Performed?
Posterior drawer (at 90° flexion) with the knee at 90° of flexion, a posteriorly directed force is applied to the proximal tibia and posterior tibial. Similar to the previous drawer test, the test is performed in the supine position with the hip flexed 45° and the knee 90°, according to rubinstein et al. Have the patient's affected hip and knee in a flexed position. This ligament prevents backward displacement of the tibia or forward sliding of the femur.
Limits Anterior Translation Of Tibia.
The patient, whose body mass index (bmi) was 22.5, did not have any chronic diseases, such as hypertension or coronary heart disease, nor did he have any endocrine or metabolic. To test the integrity of the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl). Limits posterior translation of tibia. The test simply involves your practitioner inspecting and manipulating your knee to assess its movement and level of resistance.
Assess The Integrity Of The Posterior Cruciate Ligament (Pcl) Anatomy.
Web the posterior drawer test evaluates the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) in the knee, crucial for diagnosing pcl sprains and knee stability. The posterior drawer test is considered positive if a posterior displacement of the proximal tibia, relative to the distal femur, more than 5 mm, or a “soft” end point, indicates. Diagnosis can be suspected with a knee effusion and a positive dial test but mri studies are required for confirmation. Web anatomy of the knee.