Reduced Row Echelon Form Examples
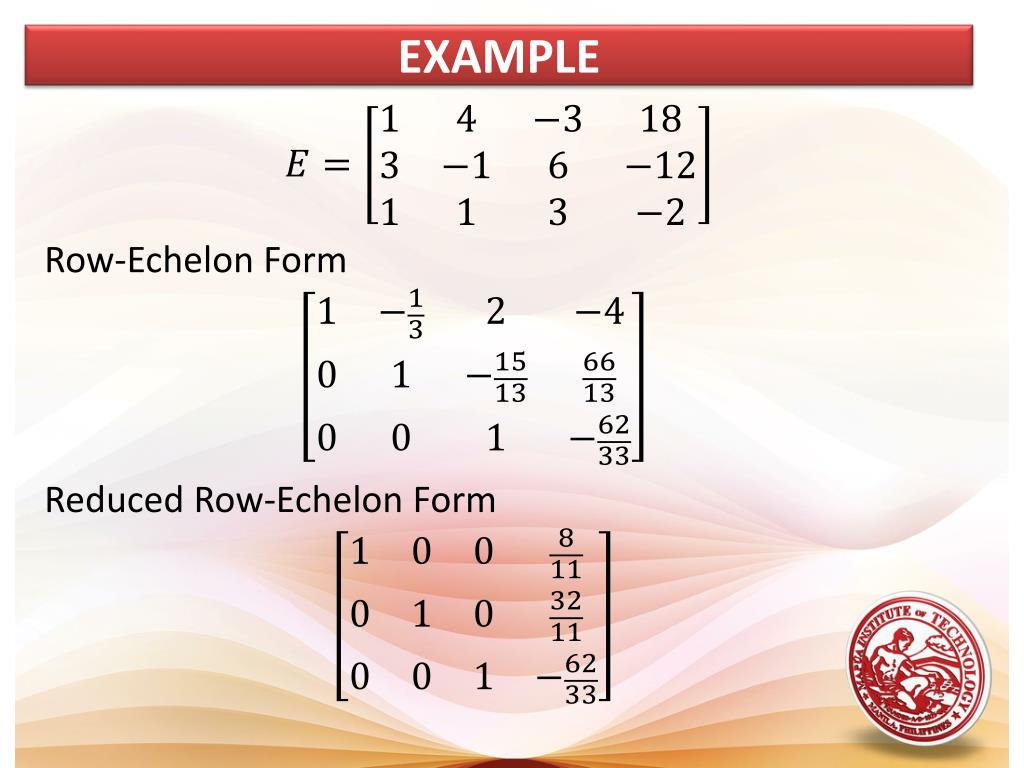
Reduced Row Echelon Form Examples - ( − 3 2 − 1 − 1 6 − 6 7 − 7 3 − 4 4 − 6) → ( − 3 2 − 1 − 1 0 − 2 5 −. We will use scilab notation on a matrix afor these elementary row operations. Example of matrix in reduced echelon form Web any matrix can be transformed to reduced row echelon form, using a technique called gaussian elimination. Consider the matrix a given by. The reduced row echelon form of the matrix tells us that the only solution is (x, y, z) = (1, − 2, 3). Then, the two systems do not have exactly the same solutions. Web reduced row echelon form is how a matrix will look when it is used to solve a system of linear equations. The matrix satisfies conditions for a row echelon form. These two forms will help you see the structure of what a matrix represents.
Example of matrix in reduced echelon form this matrix is in reduced echelon form due to the next two reasons: The reduced row echelon form of the matrix tells us that the only solution is (x, y, z) = (1, − 2, 3). Web subsection 1.2.3 the row reduction algorithm theorem. Web reduced row echelon form. Web any matrix can be transformed to reduced row echelon form, using a technique called gaussian elimination. R = rref (a,tol) specifies a pivot tolerance that the algorithm uses to determine negligible columns. Then, the two systems do not have exactly the same solutions. Many properties of matrices may be easily deduced from their row echelon form, such as the rank and the kernel. We can illustrate this by solving again our first example. In scilab, row 3 of a matrix ais given by a(3;:) and column 2 is given by a(:;2).
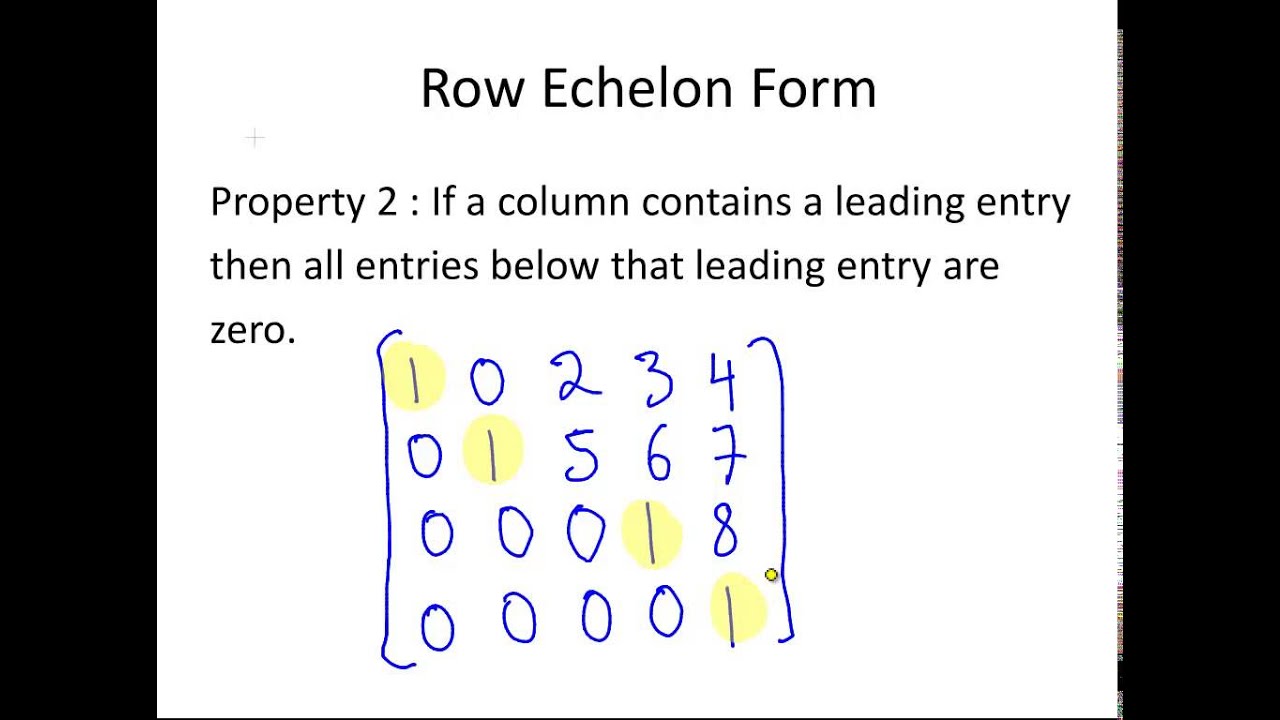
Nonzero rows appear above the zero rows. Web reduced row echelon form is how a matrix will look when it is used to solve a system of linear equations. And matrices, the convention is, just like vectors, you make them nice and bold, but use capital letters, instead of lowercase letters. R = rref (a,tol) specifies a pivot tolerance that the algorithm uses to determine negligible columns. Web using mathematical induction, the author provides a simple proof that the reduced row echelon form of a matrix is unique. [r,p] = rref (a) also returns the nonzero pivots p. Example #1 solving a system using linear combinations and rref; The leading entry in each nonzero row is 1. We can illustrate this by solving again our first example. Web subsection 1.2.3 the row reduction algorithm theorem.
Row Echelon Form of a Matrix YouTube
The leading entry in each nonzero row is 1. Web reduced row echelon form. What is a pivot position and a pivot column? The matrix satisfies conditions for a row echelon form. Web subsection 1.2.3 the row reduction algorithm theorem.
Uniqueness of Reduced Row Echelon Form YouTube
What is a pivot position and a pivot column? Every matrix is row equivalent to one and only one matrix in reduced row echelon form. Web reduced row echelon form. Many properties of matrices may be easily deduced from their row echelon form, such as the rank and the kernel. Web reduced row echelon form is how a matrix will.
Row Echelon (REF) vs. Reduced Row Echelon Form (RREF) TI 84 Calculator
If we call this augmented matrix, matrix a, then i want to get it into the reduced row echelon form of matrix a. Example #2 solving a system using ref; A matrix is in reduced row echelon form (rref) if the three conditions in de nition 1 hold and in addition, we have 4. The leading entry in each nonzero.
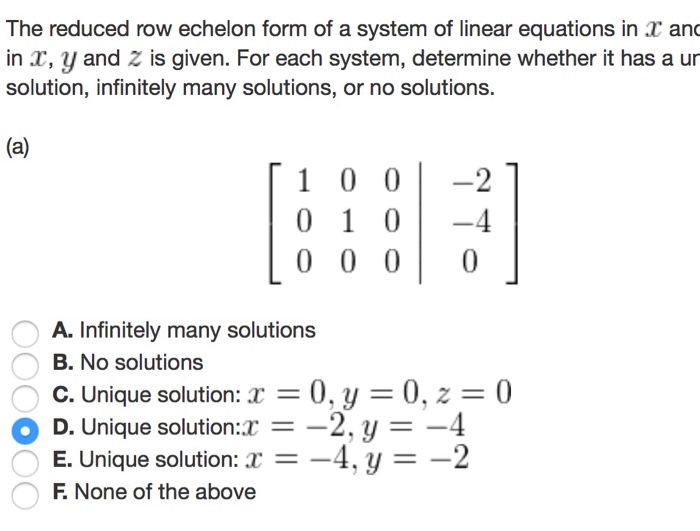
Solved The Reduced Row Echelon Form Of A System Of Linear...
Each leading 1 is the only nonzero entry in its column. Steps and rules for performing the row reduction algorithm; From the above, the homogeneous system has a solution that can be read as or in vector form as. Then, the two systems do not have exactly the same solutions. An echelon matrix (respectively, reduced echelon matrix) is one that.
PPT ROWECHELON FORM AND REDUCED ROWECHELON FORM PowerPoint
Example #2 solving a system using ref; [r,p] = rref (a) also returns the nonzero pivots p. Many properties of matrices may be easily deduced from their row echelon form, such as the rank and the kernel. From the above, the homogeneous system has a solution that can be read as or in vector form as. Nonzero rows appear above.
Linear Algebra Example Problems Reduced Row Echelon Form YouTube
From the above, the homogeneous system has a solution that can be read as or in vector form as. In scilab, row 3 of a matrix ais given by a(3;:) and column 2 is given by a(:;2). Each leading 1 is the only nonzero entry in its column. These two forms will help you see the structure of what a.
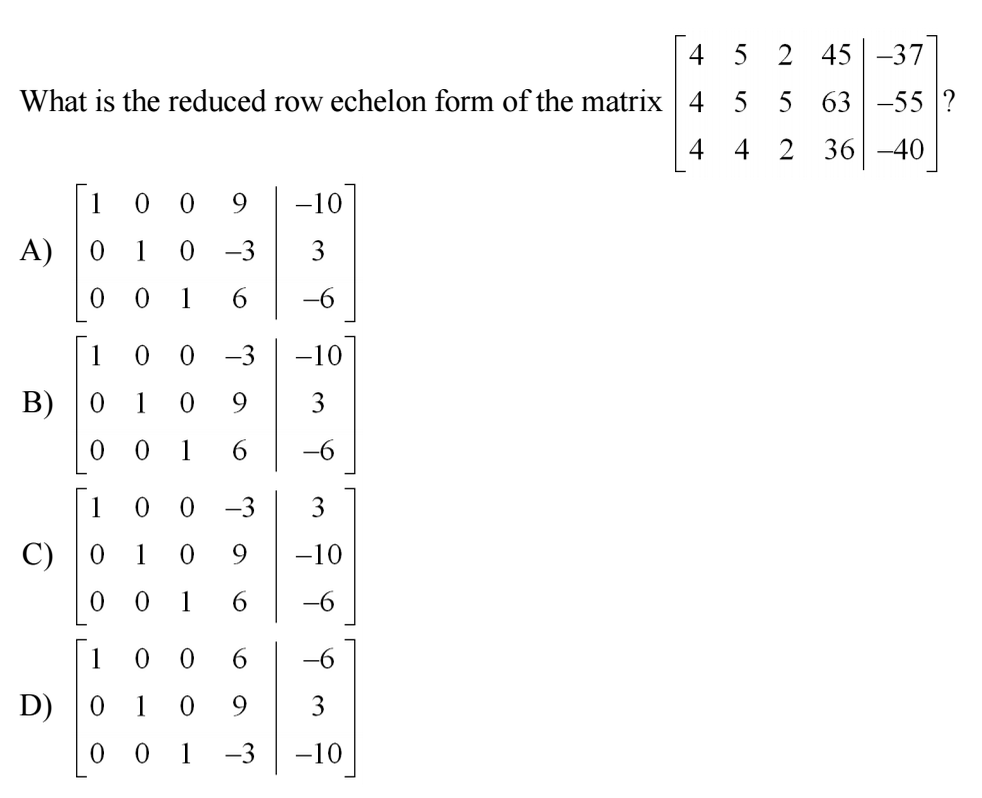
Solved What is the reduced row echelon form of the matrix
The reduced row echelon form of the matrix tells us that the only solution is (x, y, z) = (1, − 2, 3). Left most nonzero entry) of a row is in [r,p] = rref (a) also returns the nonzero pivots p. What is a pivot position and a pivot column? Example of matrix in reduced echelon form this matrix.
7.3.4 Reduced Row Echelon Form YouTube
Animated slideshow of the row reduction in this example. Web understanding row echelon form and reduced row echelon form; Web reduced row echelon form. Beginning with the same augmented matrix, we have. [r,p] = rref (a) also returns the nonzero pivots p.
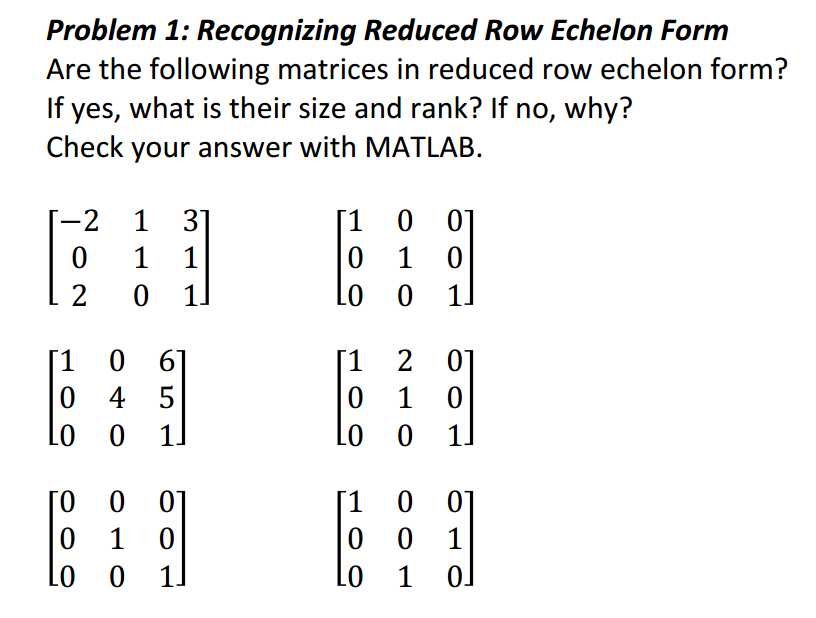
Solved Are The Following Matrices In Reduced Row Echelon
Web introduction many of the problems you will solve in linear algebra require that a matrix be converted into one of two forms, the row echelon form ( ref) and its stricter variant the reduced row echelon form ( rref). Web instead of gaussian elimination and back substitution, a system of equations can be solved by bringing a matrix to.
linear algebra Understanding the definition of row echelon form from
Example 4 is the next matrix in echelon form or reduced echelon form? What is a pivot position and a pivot column? This is particularly useful for solving systems of linear equations. We will use scilab notation on a matrix afor these elementary row operations. Web reduced echelon form or reduced row echelon form:
Every Matrix Is Row Equivalent To One And Only One Matrix In Reduced Row Echelon Form.
If we call this augmented matrix, matrix a, then i want to get it into the reduced row echelon form of matrix a. And matrices, the convention is, just like vectors, you make them nice and bold, but use capital letters, instead of lowercase letters. Web subsection 1.2.3 the row reduction algorithm theorem. Web reduced row echelon form.
R = Rref (A,Tol) Specifies A Pivot Tolerance That The Algorithm Uses To Determine Negligible Columns.
We will use scilab notation on a matrix afor these elementary row operations. Web reduced row echelon form is how a matrix will look when it is used to solve a system of linear equations. Example of matrix in reduced echelon form this matrix is in reduced echelon form due to the next two reasons: ( − 3 2 − 1 − 1 6 − 6 7 − 7 3 − 4 4 − 6) → ( − 3 2 − 1 − 1 0 − 2 5 −.
Web Using Mathematical Induction, The Author Provides A Simple Proof That The Reduced Row Echelon Form Of A Matrix Is Unique.
Example 1 the following matrix is in echelon form. This is particularly useful for solving systems of linear equations. In any nonzero row, the rst nonzero entry is a one (called the leading one). Example of matrix in reduced echelon form
The Matrix Satisfies Conditions For A Row Echelon Form.
In scilab, row 3 of a matrix ais given by a(3;:) and column 2 is given by a(:;2). Example the matrix is in reduced row echelon form. Example #2 solving a system using ref; The reduced row echelon form of the matrix tells us that the only solution is (x, y, z) = (1, − 2, 3).