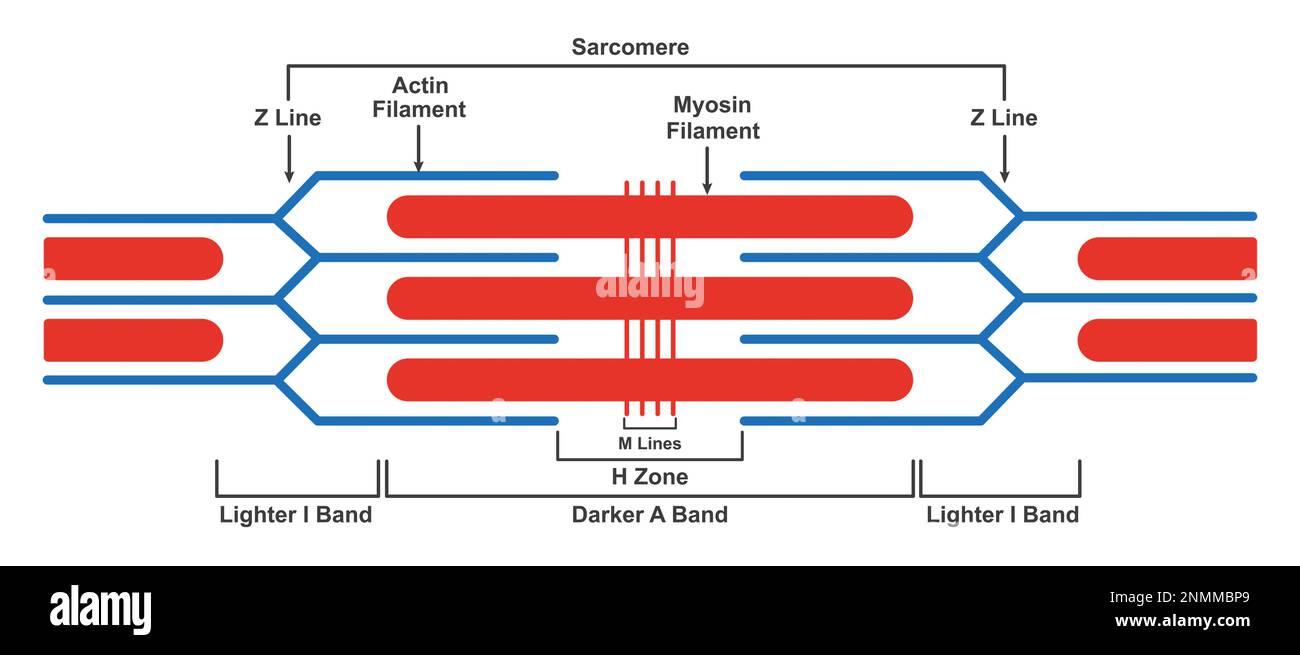
Sarcomere Drawing
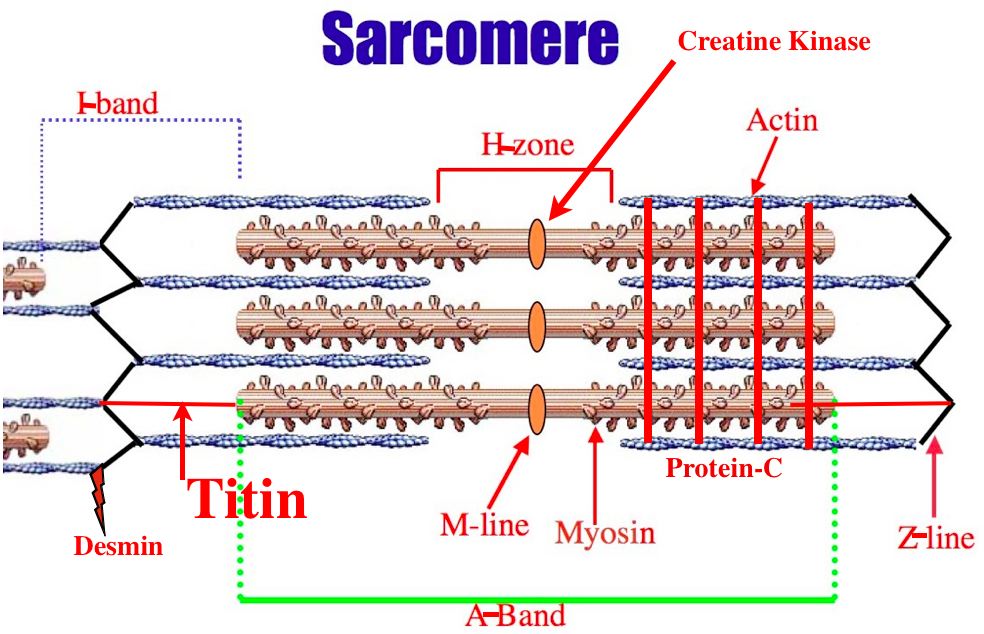
Sarcomere Drawing - These layers cover muscle subunits, individual muscle cells, and myofibrils respectively. The structure of the sarcomere is traditionally. The left side (peach color) of the sarcomere represents a half sarcomere found in vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. In addition to myosin and actin, several other proteins, such as tropomyosin,. Each sarcomere is about 2.5 micrometers in length. Web sarcomeres are contractile units of skeletal muscle that divide into “i” and “a” bands, “m” and “z” lines, and the “h” zone. The sarcomere fundamentally consists of two main myofilaments: Web a labeled sarcomere diagram is an essential tool for understanding the structure of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscle is the muscle type that initiates all of our voluntary. Web the sarcomere fundamentally consists of two main myofilaments:
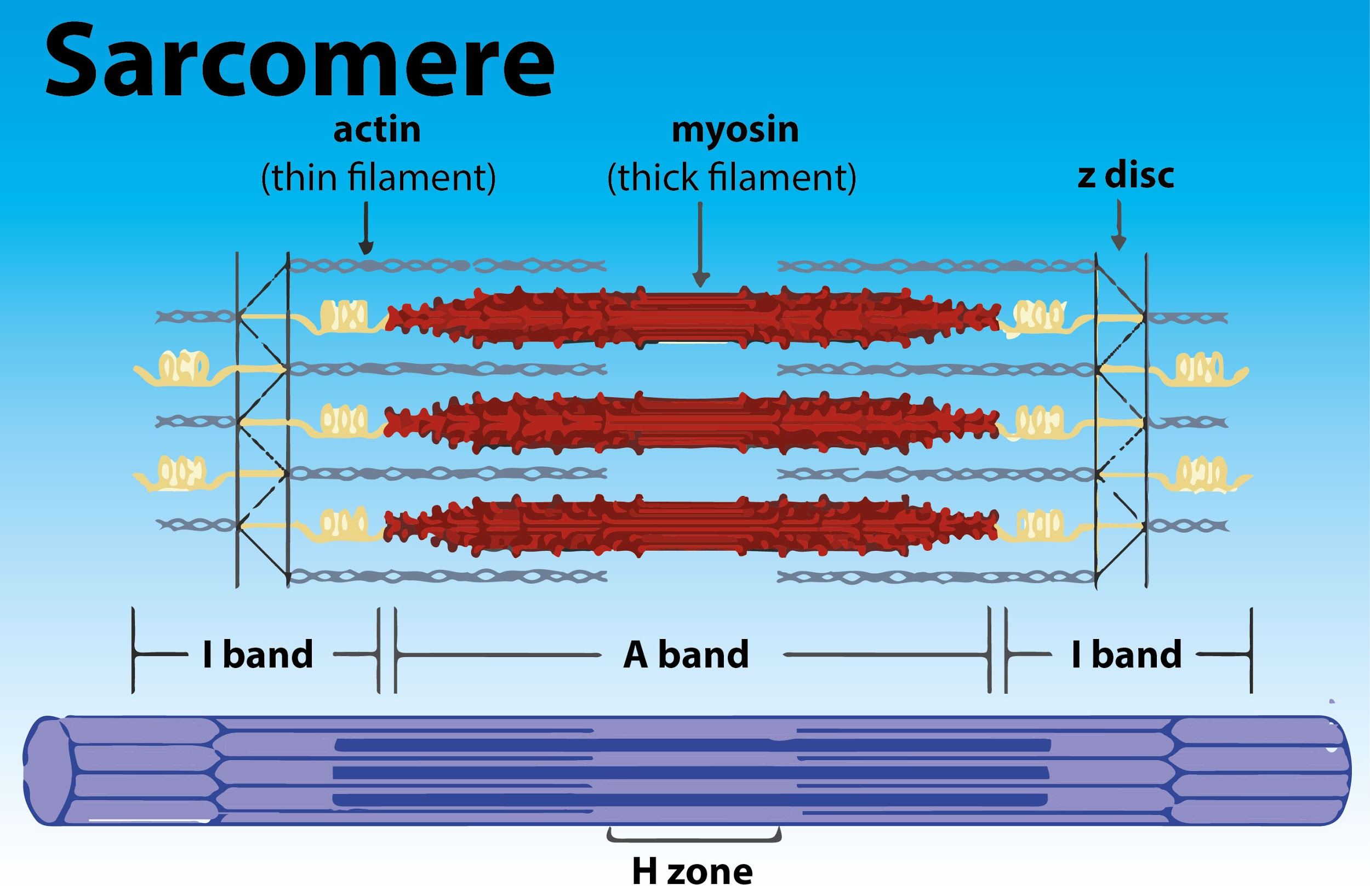
Web a sarcomere is a microscopic segment repeating in a myofibril. Anatomical is said to be the term of microanatomy. These filaments interact by sliding past each other in response to stimulus. Actin and the z discs are shown in red. Web sarcomeres are contractile units of skeletal muscle that divide into “i” and “a” bands, “m” and “z” lines, and the “h” zone. The different letters in this diagram show us the different regions of the sarcomere. Sarcomeres are the basic units of muscle contraction and are responsible for the muscle’s ability to generate force. It also allows us to understand the visible bands seen in the images of muscle tissue in micrographs; Due to the striated nature of both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle is observed by microscope slides. This is a distinguishing unit in some types of muscle tissue.
It is represented as a thin, dark line in. Web a sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of a myocyte (muscle fibre). The left side (peach color) of the sarcomere represents a half sarcomere found in vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Web sarcomeres are contractile units of skeletal muscle that divide into “i” and “a” bands, “m” and “z” lines, and the “h” zone. The thick filament is composed of the myosin protein, whereas, the thin filament is made. Each sarcomere is about 2.5 micrometers in length. Web the sarcomere fundamentally consists of two main myofilaments: The sarcomere is the basic unit function with muscle fiber cells. Mainly of actin and myosin proteins. This means it is the most basic unit that makes up our skeletal muscle.
Definition, Structure, Diagram, and Functions
The left side (peach color) of the sarcomere represents a half sarcomere found in vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Web a sarcomere (greek σάρξ sarx flesh, μέρος meros part) is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. The right side (pink color) of the sarcomere reflects a half sarcomere in. Web the sarcomere fundamentally consists of two main myofilaments: The widely.
Web a sarcomere (greek σάρξ sarx flesh, μέρος meros part) is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. These filaments interact by sliding past each other in response to stimulus. The sarcomere is the basic unit function with muscle fiber cells. Due to the striated nature of both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle is observed by microscope slides. A.
[Solved] 12. Draw and label the parts of a Course Hero
In addition to myosin and actin, several other proteins, such as tropomyosin,. The left side (peach color) of the sarcomere represents a half sarcomere found in vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Web actin and the z discs are shown in red. So, let’s go through each one by one to find out which is labeling the i band. The sarcomere is the.
muscular biology scheme vector illustration VectorMine
Note that the nebulin molecules are part of and extend the entrie length of the thin filaments. The myosin filaments are the thick filaments and should be represented as being thicker than the actin filaments; Web an accurate drawing of the sarcomere is a good way to demonstrate the relative movement of the muscle fibres during muscle contraction; This is.
Diagram Of A
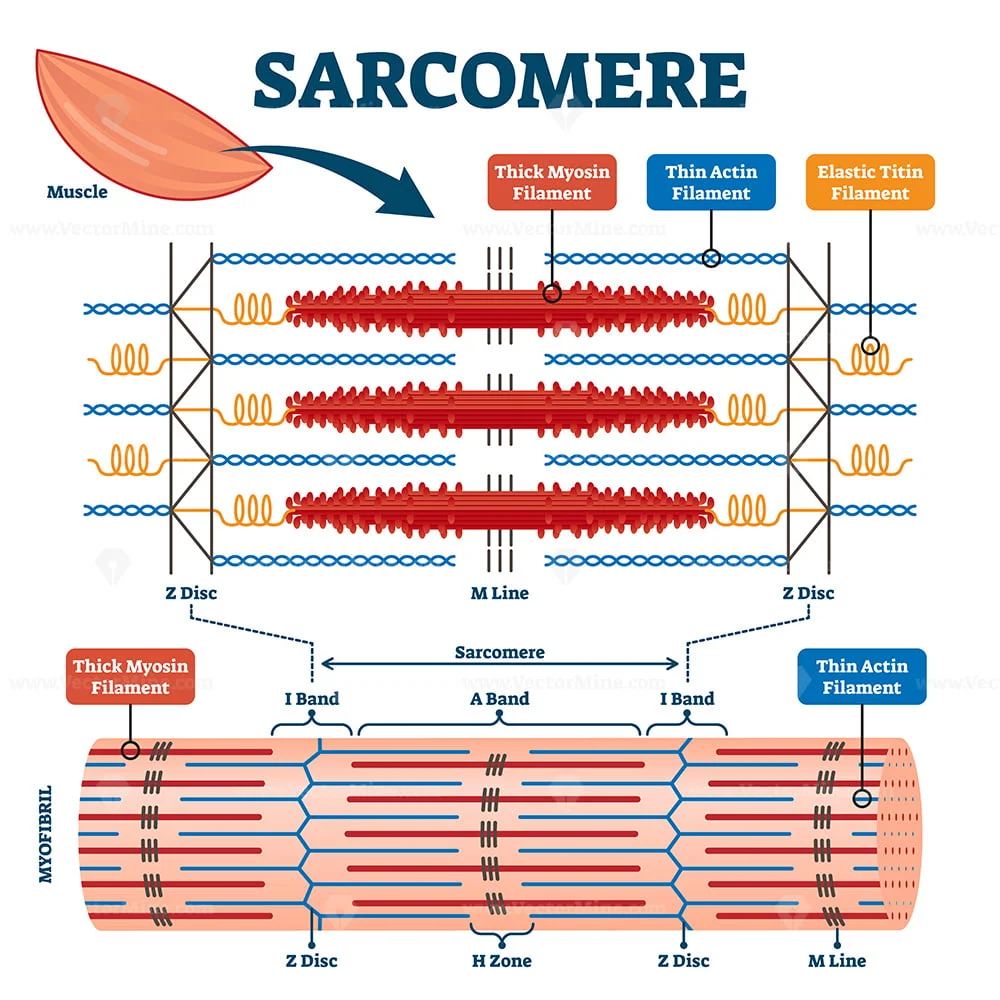
Web a sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of a myocyte (muscle fibre). Web the sarcomere is the main contractile unit of muscle fiber in the skeletal muscle.each sarcomere is composed of protein filaments (myofilaments) that include mainly the thick filaments called myosin, and thin filaments called actin.the bundles of myofilaments are called myofibrils. This means it is the most.
Diagram Diagram Quizlet
Web muscles work on a macro level, starting with tendons that attach muscles to bones. This means it is the most basic unit that makes up our skeletal muscle. Each sarcomere is about 2.5 micrometers in length. Note that the nebulin molecules are part of and extend the entrie length of the thin filaments. The different letters in this diagram.
Schematic of structure. are the functional units
Web a labeled sarcomere diagram is an essential tool for understanding the structure of a muscle cell. Due to the striated nature of both skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle is observed by microscope slides. It also allows us to understand the visible bands seen in the images of muscle tissue in micrographs; In addition to myosin and actin, several other.
Definition, Structure, Diagram, and Functions
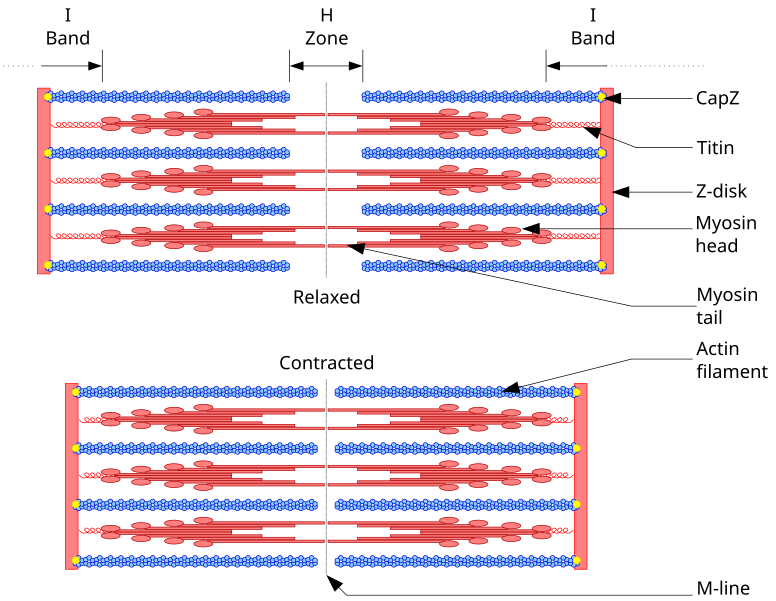
It also allows us to understand the visible bands seen in the images of muscle tissue in micrographs; Web (a) the basic organization of a sarcomere subregion, showing the centralized location of myosin (a band). The sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of skeletal muscle. A person standing between two bookcases (z bands) pulls them in via. These filaments interact.
Draw the diagram of a of skeletal muscle showing different
A sarcomere is composed of two main protein filaments (thin actin and thick myosin filaments) which are the active structures responsible for muscular contraction. It also allows us to understand the visible bands seen in the images of muscle tissue in micrographs; Web the contractile unit of skeletal muscles. Web the sarcomere fundamentally consists of two main myofilaments: Each sarcomere.
structure, illustration Stock Photo Alamy
A sarcomere is composed of two main protein filaments (thin actin and thick myosin filaments) which are the active structures responsible for muscular contraction. (b) a conceptual diagram representing the connectivity of molecules within a sarcomere. Sarcomeres are the basic contractile units of striated muscle cells. Having a clear visual representation of a sarcomere can greatly aid in understanding its.
Web A Sarcomere (Greek Σάρξ Sarx Flesh, Μέρος Meros Part) Is The Smallest Functional Unit Of Striated Muscle Tissue.
These filaments interact by sliding past each other in response to stimulus. Thick filaments are organized bundles of myosin, while thin filaments are made of actin along. Having a clear visual representation of a sarcomere can greatly aid in understanding its complex structure and functions. Sarcomeres are the basic units of muscle contraction and are responsible for the muscle’s ability to generate force.
(B) A Conceptual Diagram Representing The Connectivity Of Molecules Within A Sarcomere.
Definition, structure, diagram, and functions. Web the contractile unit of skeletal muscles. In addition to myosin and actin, several other proteins, such as tropomyosin,. Web when drawing a diagram of a sarcomere it is important to remember the following conventions:
Skeletal Muscle Is The Muscle Type That Initiates All Of Our Voluntary.
(b) a conceptual diagram representing the. Anatomical is said to be the term of microanatomy. The sarcomere is the basic contractile unit of skeletal muscle. The actin and myosin filaments overlap in certain places creating several bands and zones.
It Is Made Up Of Multiple Myosin And Actin Filaments Oriented In Parallel.
Sarcomeres are the basic contractile units of striated muscle cells. Web a sarcomere is a microscopic segment repeating in a myofibril. Web muscles work on a macro level, starting with tendons that attach muscles to bones. The neuromuscular junction another specialization of the skeletal muscle is the site where a motor neuron’s terminal meets the muscle fiber—called the neuromuscular junction (nmj).