Sodium Electron Configuration Long Form
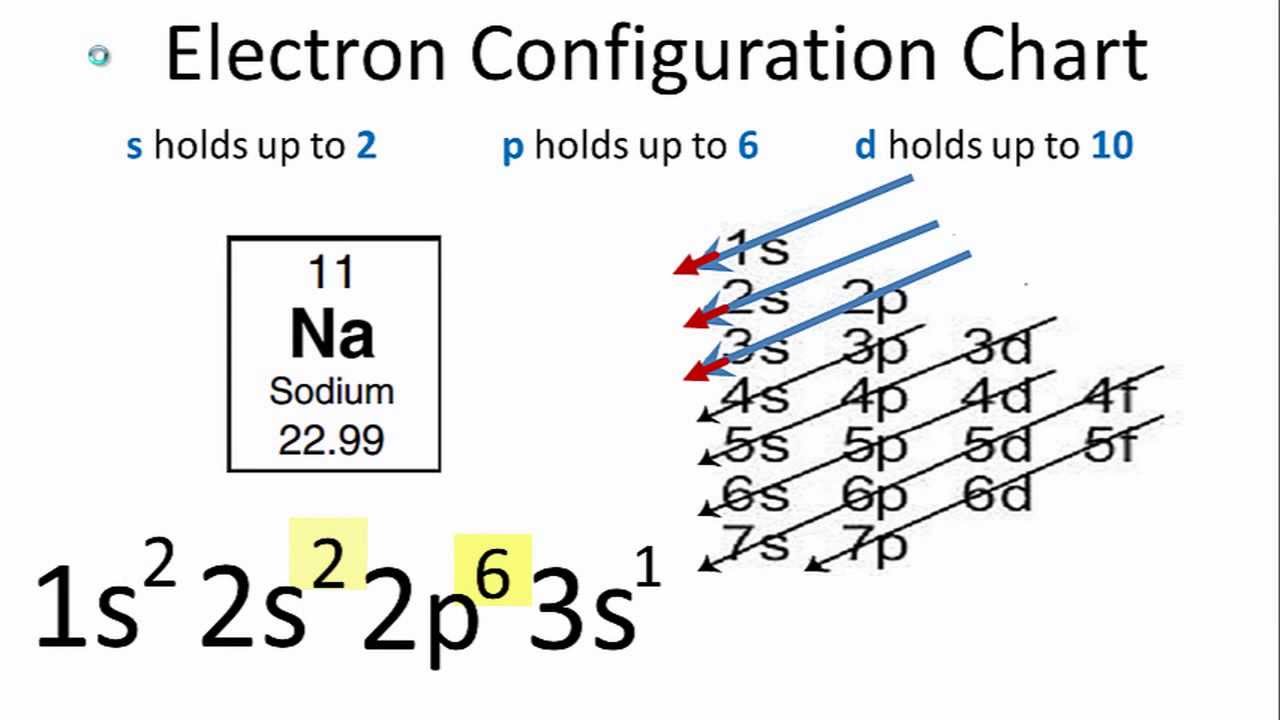
Sodium Electron Configuration Long Form - 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6: Electron configuration of sodium (na) [ne] 3s 1: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5: Sharp (s), principal (p), diffuse (d), and fundamental (f). Web this page shows the electron configurations of the neutral gaseous atoms in their ground states. Electron configuration can be done in two ways. Web electron configuration of oxygen (o) [he] 2s 2 2p 4: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. Electron configuration of fluorine (f) [he] 2s 2 2p 5:
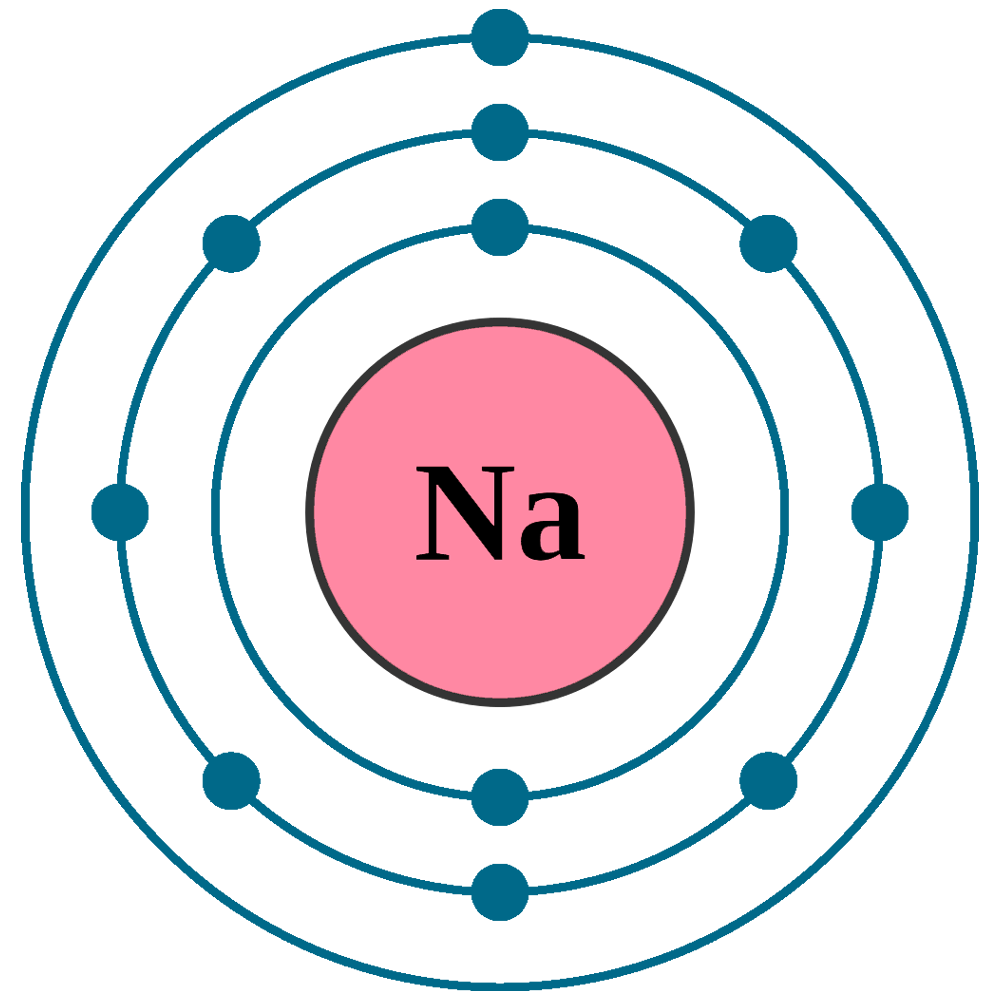
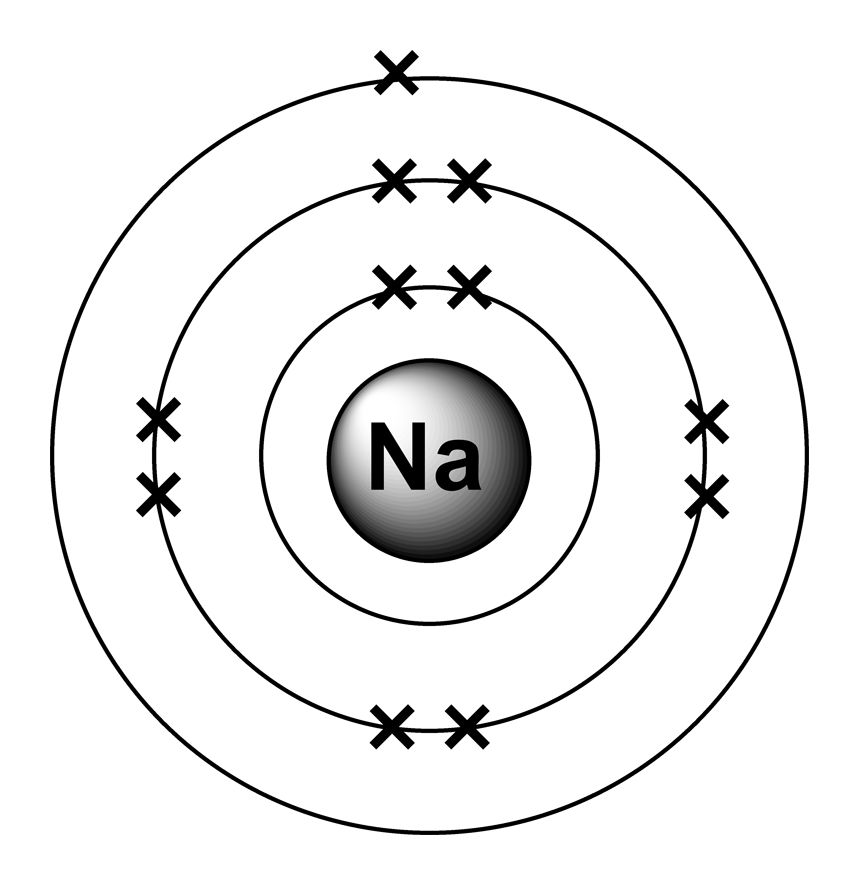
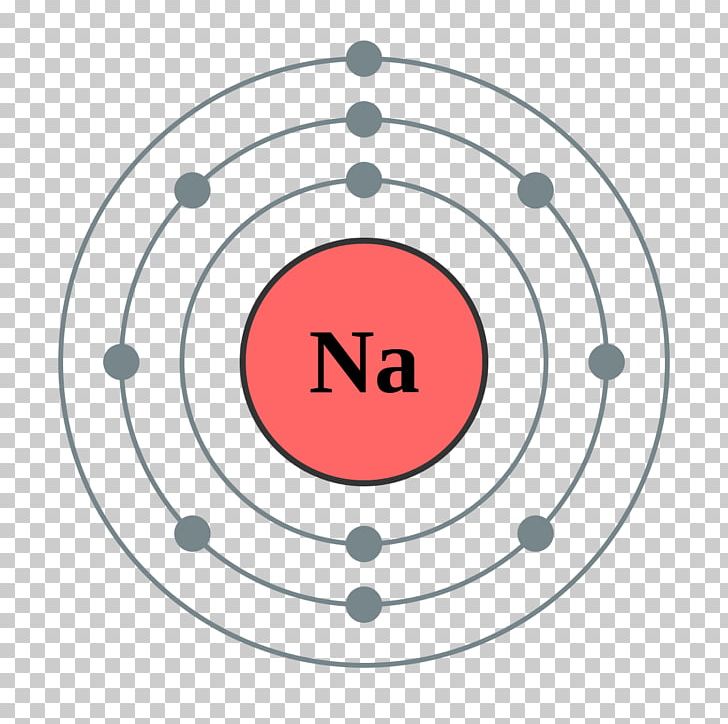
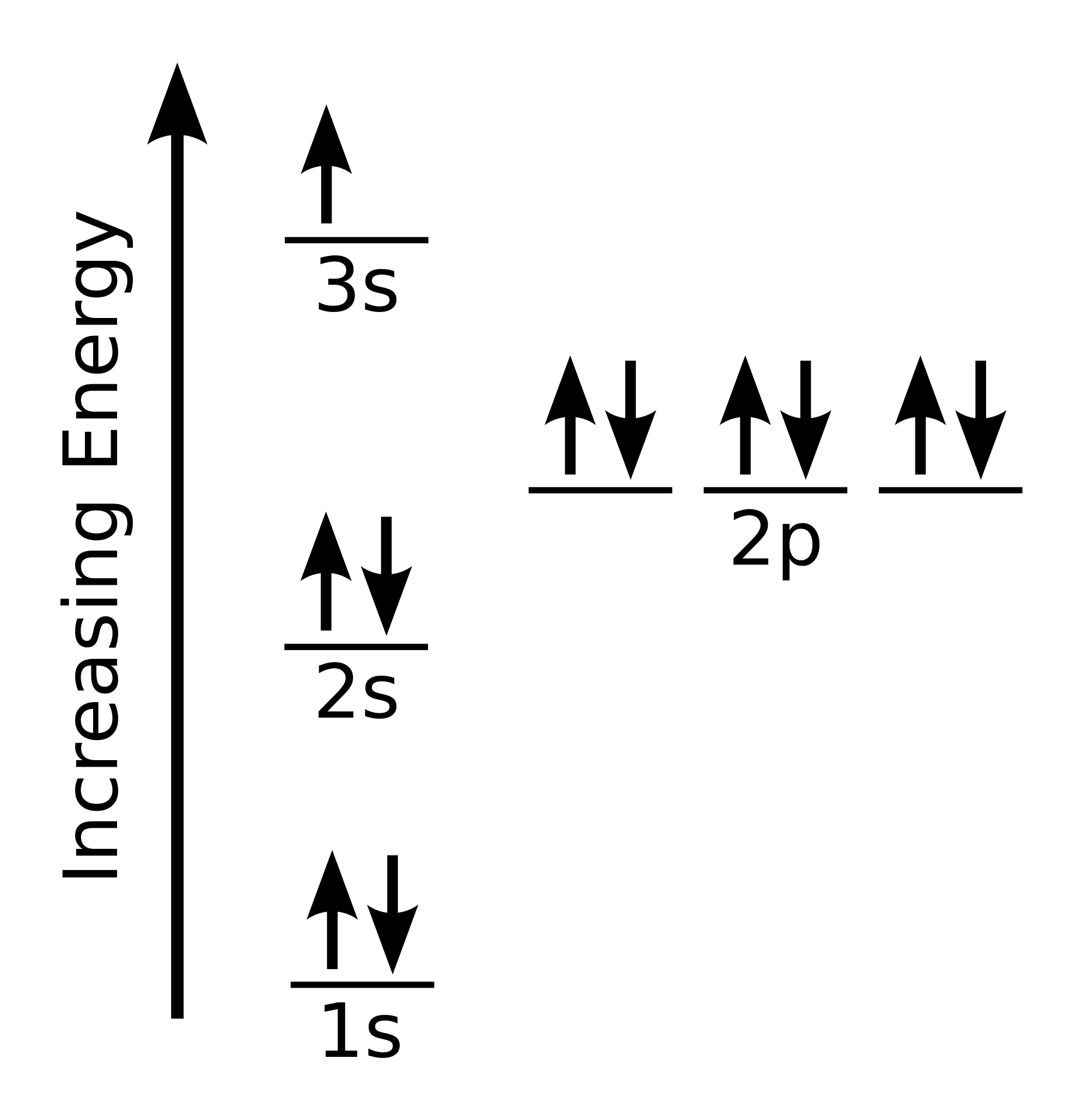
Web the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom. Web the arrangement of electrons in sodium in specific rules in different orbits and orbitals is called the electron configuration of sodium. Web the commonly used long form of the periodic table is designed to emphasize electron configurations. Electron configuration can be done in two ways. The nex six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( figure 6.25 ): Atomic number the number of protons in an atom. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1: Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for sodium go in the 2s orbital. Electron configuration of neon (ne) [he] 2s 2 2p 6:
Web long form of sodium electron configuration: These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6: Web all of the electrons in the noble gas neon (atomic number 10) are paired, and all of the orbitals in the n = 1 and the n = 2 shells are filled. In aufbau principle, the electrons are filled according to the increasing energy level of orbitals. Web the commonly used long form of the periodic table is designed to emphasize electron configurations. Atomic number the number of protons in an atom. Sharp (s), principal (p), diffuse (d), and fundamental (f). Electron configuration of sodium (na) [ne] 3s 1: The nex six electrons will go in the 2p orbital.
sodium electron configuration Newton Desk
Web electron configuration of oxygen (o) [he] 2s 2 2p 4: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4: The nex six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Web the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom. These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce:
savvychemist Ionization Energy (5) Orbitals and the Pauli Exclusion
The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. Electron configuration of fluorine (f) [he] 2s 2 2p 5: Web electron configuration of oxygen (o) [he] 2s 2 2p 4: Web the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom. For each atom the subshells.
Electron configurations
The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for sodium go in the 2s orbital. Electron configuration of fluorine (f) [he] 2s 2 2p 5: Web in writing the electron configuration for sodium the first two electrons will go in the 1s.
Electron Configuration Long Form 4 Ways To Write Electron
Web the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for sodium go in the 2s orbital. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1: Web all of the electrons in the noble gas neon (atomic number 10) are paired,.
Electron Configuration Orbital Diagram For Sodium Diagram Media
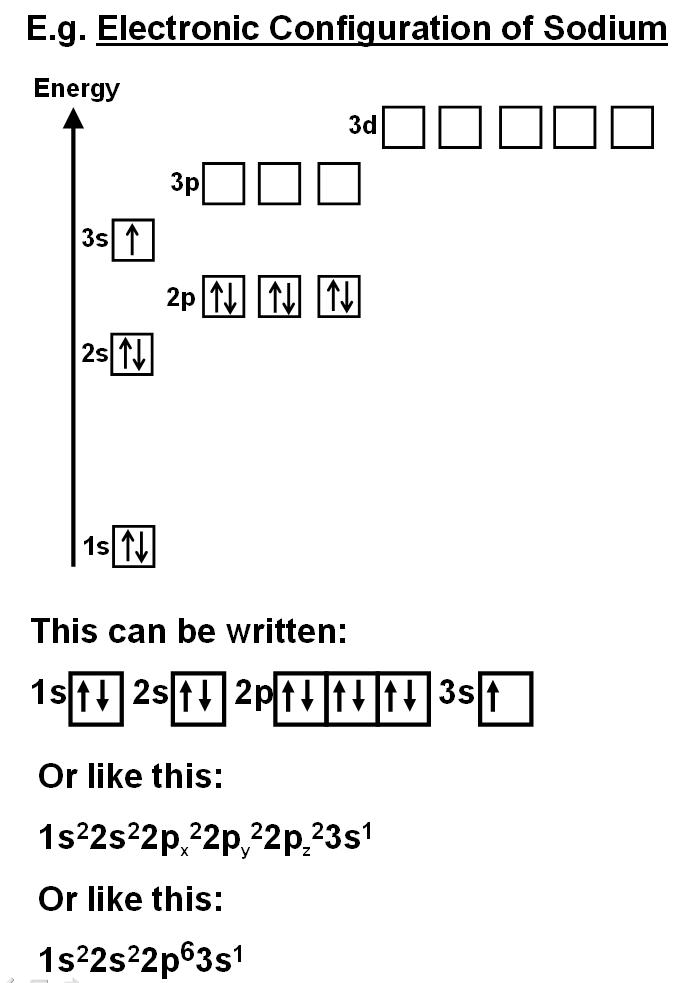
These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce: Sharp (s), principal (p), diffuse (d), and fundamental (f). The electron configuration of sodium is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 if the electron arrangement is through orbitals. We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( figure 6.25 ): Web this.
Why is there are huge energy change between the 9th and the 10th
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6: The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. Electron configuration of fluorine (f) [he] 2s 2 2p 5: Web the commonly used long form of the periodic table is designed to emphasize electron configurations.
Sodium Electron Configuration YouTube
Electron configuration can be done in two ways. For each atom the subshells are given first in concise form, then with all subshells written out, followed by the number of electrons per shell. We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( figure 6.25 ): 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1. Web.
Sodium Electron Configuration (Na) with Orbital Diagram
1s 2 2s 2 2p 4: These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce: Web the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom is called the electron configuration of the atom. Web the commonly used long form of the periodic table is designed to emphasize electron configurations. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6:
FileElectron shell 011 sodium.png Wikimedia Commons
Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for sodium go in the 2s orbital. These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1: Web the commonly used long form of the periodic table is designed to emphasize electron configurations. Web electron configuration of oxygen (o) [he] 2s.
Sodium electron configuration Stock Image C029/5024 Science Photo
Electron configuration of fluorine (f) [he] 2s 2 2p 5: The alkali metal sodium (atomic number 11) has one more electron than the neon atom. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6: The sodium atom (na) and si +3 , p +4 , s +5 , cl +6 have the same electronic configuration. Electronic configuration of sodium in short form:
Web Block Elements Are Organised Into Blocks By The Orbital Type In Which The Outer Electrons Are Found.
1s 2 2s 2 2p 6: Web this page shows the electron configurations of the neutral gaseous atoms in their ground states. Web all of the electrons in the noble gas neon (atomic number 10) are paired, and all of the orbitals in the n = 1 and the n = 2 shells are filled. The electron configuration of sodium is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 if the electron arrangement is through orbitals.
Electron Configuration Of Fluorine (F) [He] 2S 2 2P 5:
The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. Electronic configuration of sodium in short form: The electron configurations and orbital diagrams of these four elements are: Electron configuration through orbit (bohr principle)
1S 2 2S 2 2P 4:
We describe an electron configuration with a symbol that contains three pieces of information ( figure 6.25 ): Web the commonly used long form of the periodic table is designed to emphasize electron configurations. 1s 2 2s 2 2p 5: Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for sodium go in the 2s orbital.
1S 2 2S 2 2P 6 3S 1:
Electron configuration of sodium (na) [ne] 3s 1: These blocks are named for the characteristic spectra they produce: Sharp (s), principal (p), diffuse (d), and fundamental (f). 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1.