Thylakoid Drawing
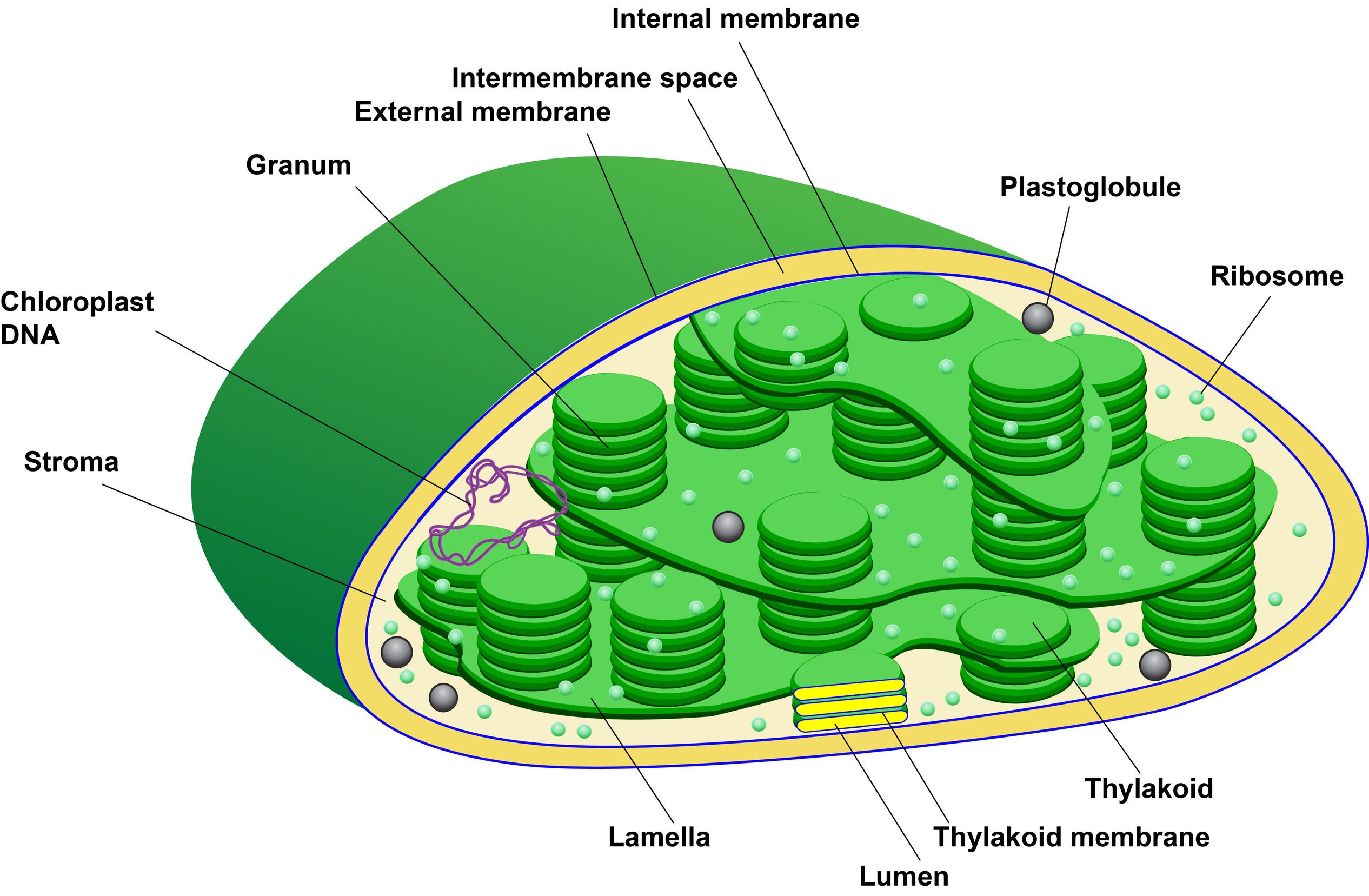
Thylakoid Drawing - Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lume. Electron carrier molecules are usually arranged in electron transport chains (etcs). What is the function of thylakoid membrane in plants? The energy storage molecule atp and the reduced electron carrier nadph. The thylakoid membrane contains the chlorophyll pigment that makes plants look green. Wikimedia commons has media related to chloroplasts. There, water (h 2 o) is oxidized, and oxygen (o 2) is released. Author chelsie wheeler view bio. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Web a chloroplast consists of thylakoid membranes surrounded by stroma.
They consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Electron carrier molecules are usually arranged in electron transport chains (etcs). In plants, the light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of organelles called chloroplasts. It is the site that contains the chlorophyll used to absorb light and use it. Web author steven aiken view bio. It is the site of photosynthesis, a process where light energy is converted into chemical energy, fueling the organism’s activities. The structure of the thylakoid helps in accomplishing this role. Emmanuel boutet schematic of a chloroplast: Also, see where thylakoids are found.
Clegg mt, gaut bs, learn gh, morton br (july 1994). The structure of the thylakoid helps in accomplishing this role. Web april 8, 2022 by joseph foster. Thylakoid lumen (inside of thylakoid); The thylakoid membrane function in a cell is the site that captures sunlight that is needed for photosynthesis. In plants, the light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of organelles called chloroplasts. Web schematic drawing of thylakoid stacks within plant chloroplasts. Web the chloroplast is involved in both stages of photosynthesis. Electron carrier molecules are usually arranged in electron transport chains (etcs). Also, see where thylakoids are found.
Thylakoids; Grana; Thylakoid Membrane
Embedded in the thylakoid membrane are molecules of chlorophyll, a pigment (a molecule that absorbs light) through which the entire process of photosynthesis begins. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lume. The light reactions take place in the thylakoid. How thylakoid membranes are generated to form a metabolically active membrane network and how thylakoid membranes orchestrate the.
Thylakoid Easy science, Science student, Science education
Web © 2024 google llc. Web author steven aiken view bio. Also, see where thylakoids are found. The light reactions take place in the thylakoid. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen.
What is the function of Thylakoid?
Web updated on october 03, 2019. Emmanuel boutet schematic of a chloroplast: What is the function of thylakoid membrane in plants? Instructor kristin klucevsek view bio. Web author steven aiken view bio.
Schematic representation of derived types of thylakoid arrangement
There, water (h 2 o) is oxidized, and oxygen (o 2) is released. Embedded in the thylakoid membrane are molecules of chlorophyll, a pigment (a molecule that absorbs light) through which the entire process of photosynthesis begins. Cellular processes for building and altering this membrane network are therefore essential for life on earth. Learn about photosynthesis's light reaction in the.
Thylakoid biology Britannica
The thylakoid membranes contain molecules of the green pigment chlorophyll. The structure of the thylakoid helps in accomplishing this role. Web a chloroplast consists of thylakoid membranes surrounded by stroma. Learn about chloroplast structure and some of the important components of chloroplasts including chlorophyll,. It is the site of photosynthesis, a process where light energy is converted into chemical energy,.
Plastids Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram
In plants, the light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of organelles called chloroplasts. Web © 2024 google llc. Web april 8, 2022 by joseph foster. Web chloroplasts play a key role in the process of photosynthesis. Clegg mt, gaut bs, learn gh, morton br (july 1994).
Thylakoid membrane bound chloroplast compartments structure outline
Web chloroplasts play a key role in the process of photosynthesis. They consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. A chloroplast is a type of organelle known as a plastid, predominantly found in plant cells and algae. Embedded in the thylakoid membrane are molecules of chlorophyll, a pigment (a molecule that absorbs light) through which the entire process.
What Is A Thylakoid Laurie Media
Web chloroplasts play a key role in the process of photosynthesis. Web thylakoids (dark green) inside a chloroplast. They consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. The structure of the thylakoid helps in accomplishing this role. Web a chloroplast consists of thylakoid membranes surrounded by stroma.
Structure of Chloroplast Granum. Thylakoid Stock Illustration
They consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Web april 8, 2022 by joseph foster. Web a chloroplast consists of thylakoid membranes surrounded by stroma. Learn the definition of a thylakoid and see what thylakoids do. There, water (h 2 o) is oxidized, and oxygen (o 2) is released.
Photosynthesis · Microbiology
Embedded in the thylakoid membrane are molecules of chlorophyll, a pigment (a molecule that absorbs light) through which the entire process of photosynthesis begins. Web author steven aiken view bio. How thylakoid membranes are generated to form a metabolically active membrane network and how thylakoid membranes orchestrate the insertion and localization of protein complexes for efficient electron flux remain elusive..
It Is The Site Of.
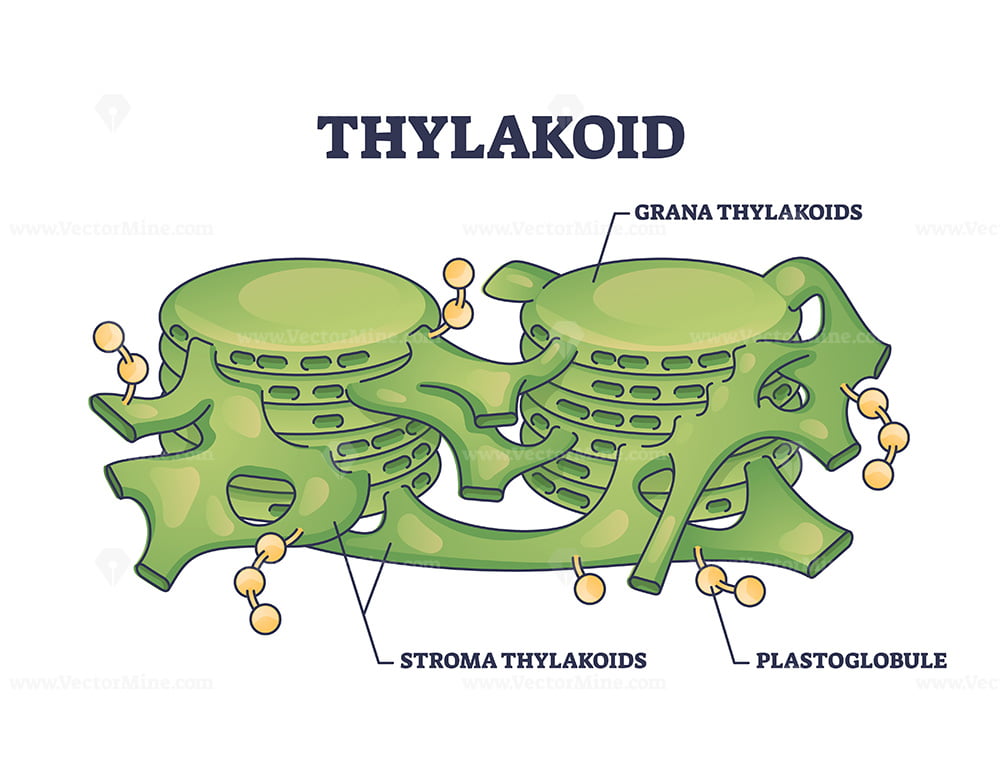
Learn the definition of a thylakoid and see what thylakoids do. The energy storage molecule atp and the reduced electron carrier nadph. Thylakoids found in chloroplasts are normally stacks of disks that are refered to as grana or granum. A chloroplast is a type of organelle known as a plastid, predominantly found in plant cells and algae.
The Thylakoid Membranes Contain Molecules Of The Green Pigment Chlorophyll.
Wikimedia commons has media related to chloroplasts. Electron carrier molecules are usually arranged in electron transport chains (etcs). Web the chloroplast is involved in both stages of photosynthesis. Author chelsie wheeler view bio.
Learn About Photosynthesis's Light Reaction In The Grana And Thylakoid Membrane And Dark Reaction In The Stroma.
Also, see where thylakoids are found. It is the site that contains the chlorophyll used to absorb light and use it. Web updated on october 03, 2019. Web thylakoids (dark green) inside a chloroplast.
Web Chloroplasts Play A Key Role In The Process Of Photosynthesis.
There, water (h 2 o) is oxidized, and oxygen (o 2) is released. The thylakoid membrane contains the chlorophyll pigment that makes plants look green. Embedded in the thylakoid membrane are molecules of chlorophyll, a pigment (a molecule that absorbs light) through which the entire process of photosynthesis begins. Web schematic drawing of thylakoid stacks within plant chloroplasts.