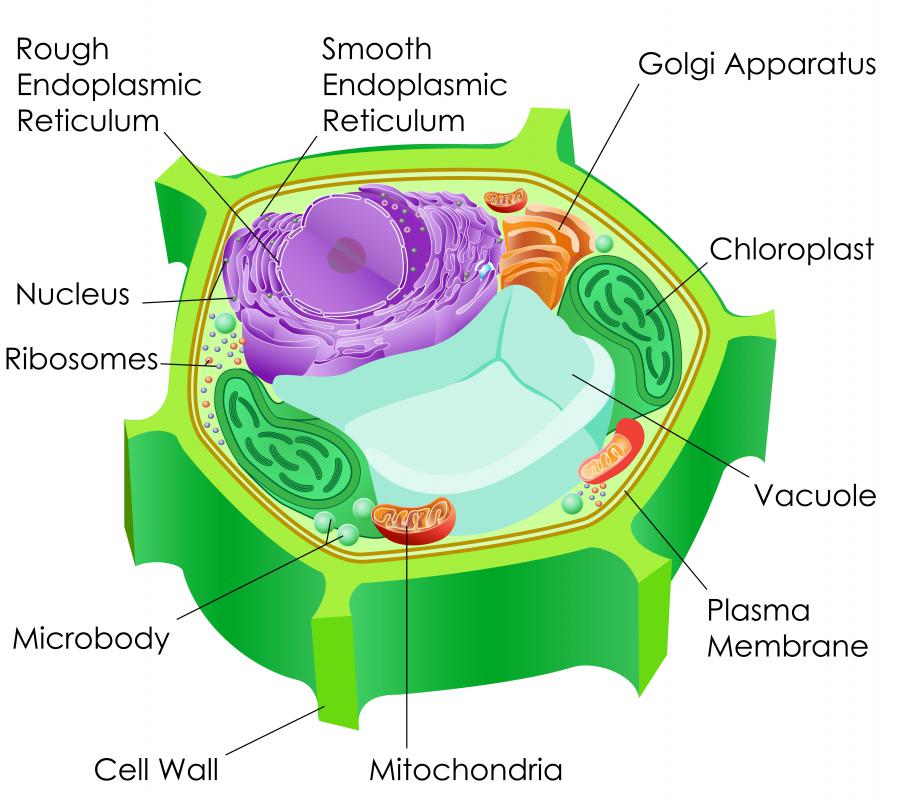
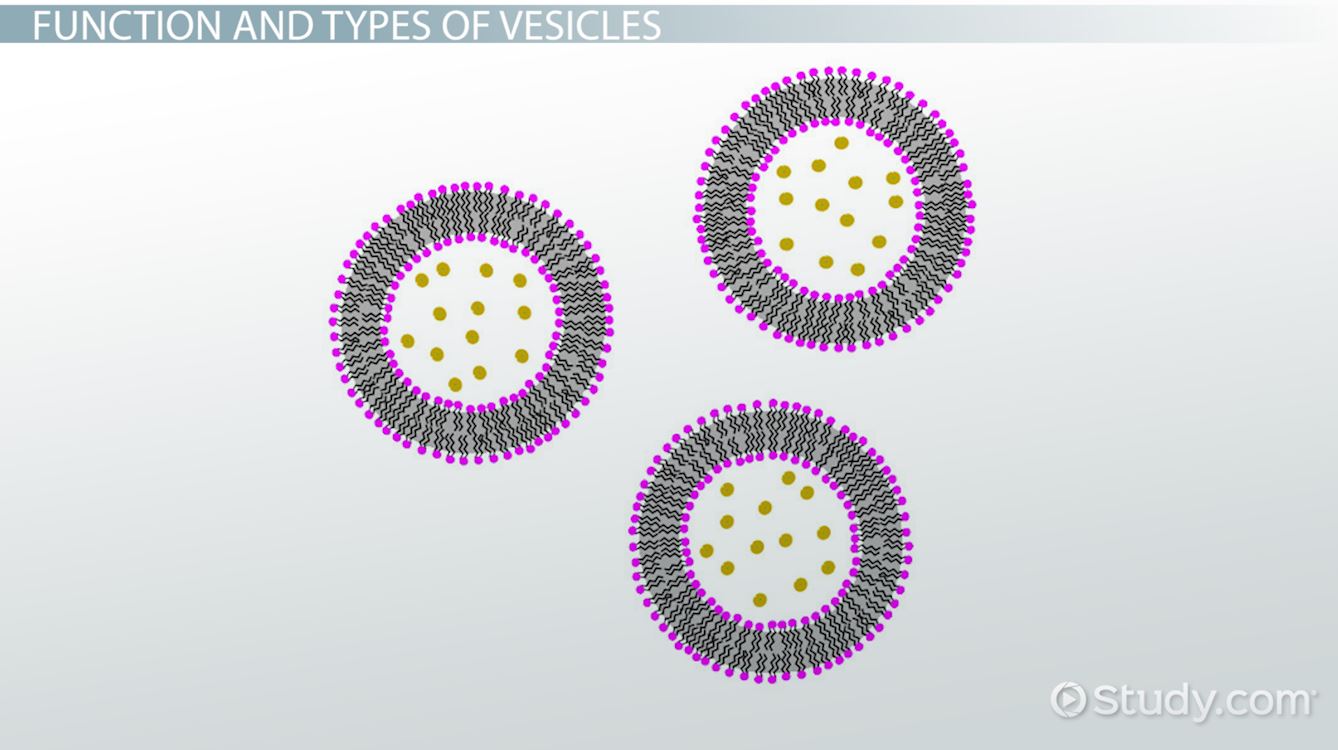
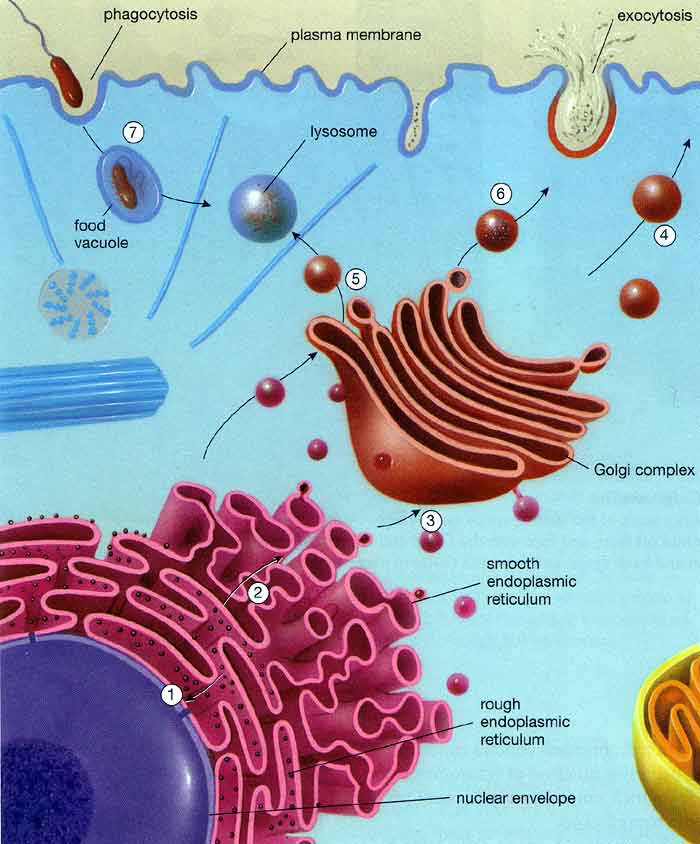
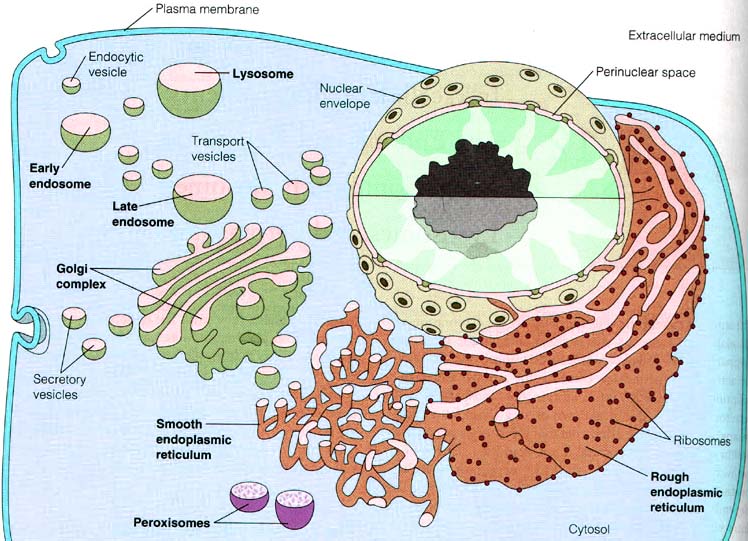
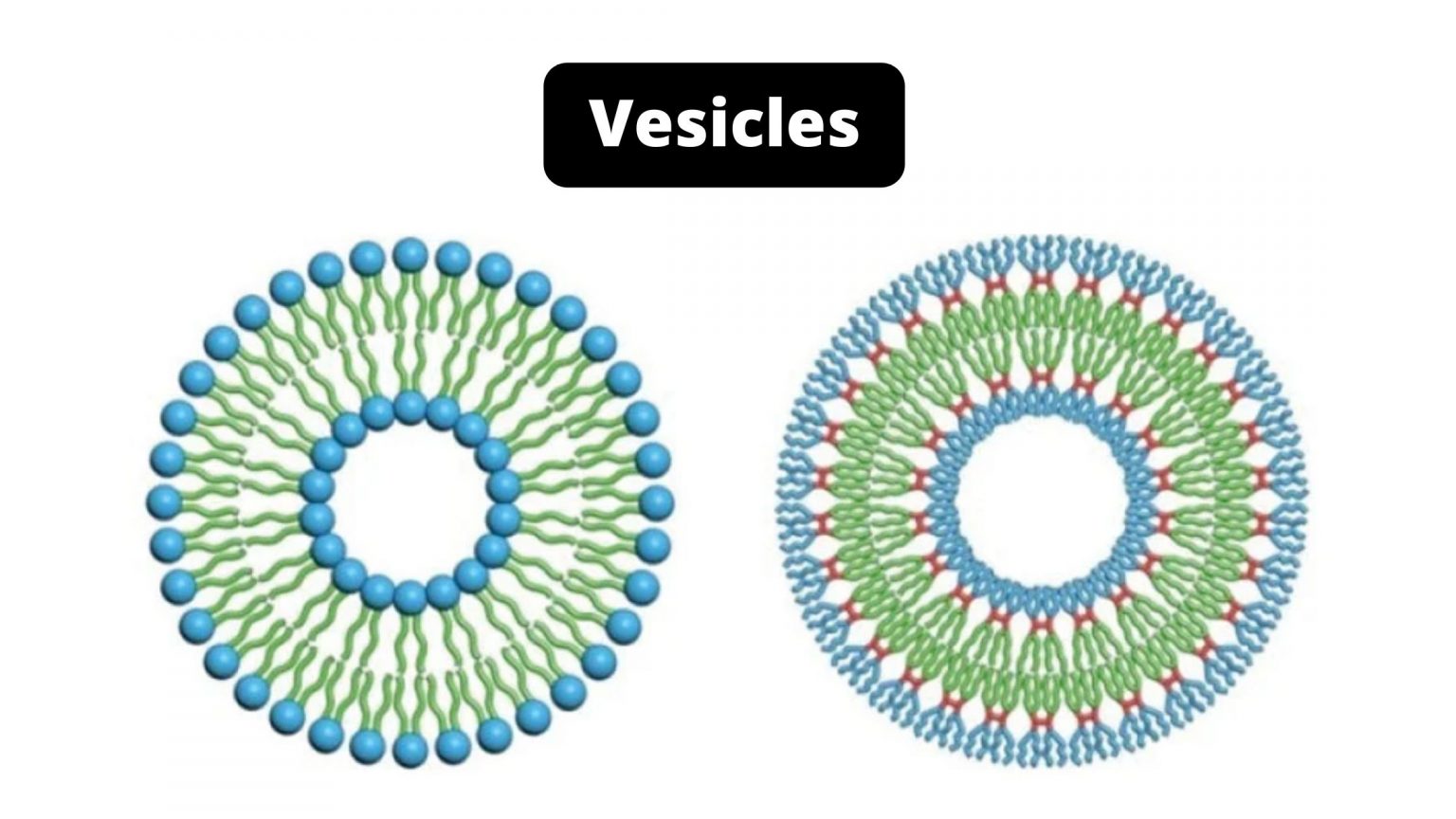
Vesicles Drawing
Vesicles Drawing - Each vesicle is coated with a protein complex, and understanding the structure and function of these complexes is a central challenge in cell biology. Web find out how vesicles function in the body and what the five main types of vesicle are. The small, spherical compartment of vesicles is separated from the cytosol by at least one lipid bilayer. A vesicle is a small structure within a cell, consisting of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Web extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi complex, and can be moved along cytoskeletal elements by motor proteins. The membrane that surrounds the vesicle also has a lamellar phase like the plasma membrane. They contain hydrolase enzymes and degrade damaged cell structures, ingested food particles and unwanted things such as bacteria. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. Click the info button at the top right corner to find more tutorials, quiz questions and an interactive drawing pad!.
They can contain either liquids or gases and have a wide range of functions in cells across the living world from regulating buoyancy to secreting hormones. Web choose from 30 vesicles drawing stock illustrations from istock. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. No covalent steps are required. Web a vesicle consists of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. We also discuss how vesicles interact with other cells and pathogens. Web secretory vesicles definition. Click the info button at the top right corner to find more tutorials, quiz questions and an interactive drawing pad!. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma membrane. Web vesicle structures primarily embody spherical capsules composed of a single or multiple bilayers, entrapping a pool of aqueous solution in their interior.
No covalent steps are required. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. Next, draw the nucleus by adding a circle inside the membrane with a smaller circle inside it. Web vesicle structures primarily embody spherical capsules composed of a single or multiple bilayers, entrapping a pool of aqueous solution in their interior. They can contain either liquids or gases and have a wide range of functions in cells across the living world from regulating buoyancy to secreting hormones. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. Web a vesicle consists of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Web a vesicle is a small structure within a cell, consisting of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (phagocytosis) and transport of materials within the cytoplasm. Then, draw a small shaded circle inside the nucleus to.
Biochemistry Glossary Transport Vesicle Draw It to Know It
Then, draw a small shaded circle inside the nucleus to. They can contain either liquids or gases and have a wide range of functions in cells across the living world from regulating buoyancy to secreting hormones. A vesicle is a small structure within a cell, consisting of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of.
In Cell Biology, what are Vesicles? (with picture)
Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. Next, draw the nucleus by adding a circle inside the membrane with a smaller circle inside it. Then, draw a small shaded circle inside the nucleus to. Web extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as.
Vesicles Definition & Function Video & Lesson Transcript
They contain hydrolase enzymes and degrade damaged cell structures, ingested food particles and unwanted things such as bacteria. Then, draw a small shaded circle inside the nucleus to. The membrane that surrounds the vesicle also has a lamellar phase like the plasma membrane. Web a vesicle can be described as a tiny part of a cell comprised of fluid that.
Vesicles Transport Information
Web choose from 30 vesicles drawing stock illustrations from istock. Web spherical bilayers that enclose an aqueous compartment are called vesicles or liposomes. Click the info button at the top right corner to find more tutorials, quiz questions and an interactive drawing pad!. Web learn how transport vesicles form and fuse with their target membranes. Web extremely important for the.
Functions of Vesicles Biology Wise
Web learn how transport vesicles form and fuse with their target membranes. Web to draw an animal cell, start by drawing an oval shape for the cell membrane. Web spherical bilayers that enclose an aqueous compartment are called vesicles or liposomes. The small, spherical compartment of vesicles is separated from the cytosol by at least one lipid bilayer. Click the.
Transport Vesicles (colored spheres) abound in cells [Illustration by
The space inside the vesicle can be. Web learn how transport vesicles form and fuse with their target membranes. Click the info button at the top right corner to find more tutorials, quiz questions and an interactive drawing pad!. They contain hydrolase enzymes and degrade damaged cell structures, ingested food particles and unwanted things such as bacteria. Alternatively, they may.
Vesicle tenderness.co
Then, draw a small shaded circle inside the nucleus to. The bilayers can be synthesised by phospholipids or other amphiphiles (surfactants, block copolymers, etc.). Web find out how vesicles function in the body and what the five main types of vesicle are. The membrane that surrounds the vesicle also has a lamellar phase like the plasma membrane. Web vesicle structures.
Vesicles Definition, Structure, Types, and Functions
Web secretory vesicles definition. Web a vesicle consists of fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer. We also discuss how vesicles interact with other cells and pathogens. Web find out how vesicles function in the body and what the five main types of vesicle are. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma.
Biology 2e, The Cell, Structure and Function of Plasma Membranes, Bulk
Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. Web in this short tutorial, learn how to draw an endosome fusing with a lysosome. The space inside the vesicle can be. Web in this short tutorial, learn how to create a vesicle. Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not.
2.4.7 Explain how vesicles are
Web extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi complex, and can be moved along cytoskeletal elements by motor proteins. Web learn how transport vesicles form and fuse with their target membranes. A vesicle is a small structure within a cell, consisting of fluid.
No Covalent Steps Are Required.
Web in this short tutorial, learn how to draw an endosome fusing with a lysosome. We also discuss how vesicles interact with other cells and pathogens. Web lysosomes are formed by budding off from golgi apparatus. Web find out how vesicles function in the body and what the five main types of vesicle are.
Web Choose From 30 Vesicles Drawing Stock Illustrations From Istock.
Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: They can contain either liquids or gases and have a wide range of functions in cells across the living world from regulating buoyancy to secreting hormones. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. The small, spherical compartment of vesicles is separated from the cytosol by at least one lipid bilayer.
Alternatively, They May Be Prepared Artificially, In Which Case They Are Called Liposomes.
Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (phagocytosis) and transport of materials within the cytoplasm. Web vesicles perform a wide range of functions within cells, such as the transport of proteins and lipids between the different parts of a cell. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (phagocytosis) and transport of materials within the cytoplasm.
Web Secretory Vesicles Definition.
Web spherical bilayers that enclose an aqueous compartment are called vesicles or liposomes. Web vesicle structures primarily embody spherical capsules composed of a single or multiple bilayers, entrapping a pool of aqueous solution in their interior. Each vesicle is coated with a protein complex, and understanding the structure and function of these complexes is a central challenge in cell biology. Web to draw an animal cell, start by drawing an oval shape for the cell membrane.