Freezing Point Drawing
Freezing Point Drawing - In this experiment, you will determine the freezing point of cyclohexane and the freezing point of a solution containing a weighed amount of unknown solute and cyclohexane. Using omni's freezing point depression calculator, you can estimate the change in the freezing point temperature of a solution compared to the pure solvent. Web freezing point depression is a colligative property observed in solutions that results from the introduction of solute molecules to a solvent. Do you know the freezing point of water? Web the freezing point depression is the difference in temperature between the freezing point of the pure solvent and that of the solution. It is a colligative property of solutions that is generally proportional to the molality of the added solute. For example, the freezing point of seawater is lower than that of pure water. The decrease in freezing point, ∆tf (freezing point depression) for a near ideal solution can be described by the equation: What is freezing point depression? Artistic practices, art history, critical thinking, and architecture.
This means that a solution must be cooled to a lowertemperature than the pure solvent in order for freezing to occur. ∆tf = kf · m eq 1. What is the concentration of ethylene glycol in a solution of water, in molality, if the freezing point dropped by \(2.64^\text{o} \text{c}\)? The freezing point of the solvent in a solution changes as the concentration of the solute in the solution changes (but it does. Fluid freezing or melting point (k) acetic acid: Web freezing point depression is a colligative property observed in solutions that results from the introduction of solute molecules to a solvent. The solution has a lower freezing point than that of the pure solvent. On the graph, the freezing point depression is represented by δtf. Molal freezing point depression constant and van't hoff factor. For example, the freezing point of seawater is lower than that of pure water.
The experiment to be performed is divided into three sections: Freezing point depression occurs when the freezing point of a liquid is lowered or depressed by adding another compound to it. This is the colligative property called freezing point depression. Web the main component in antifreeze is ethylene glycol, \(\ce{c_2h_4(oh)_2}\). Web the freezing point depression is the difference in temperature between the freezing point of the pure solvent and that of the solution. This means that a solution must be cooled to a lowertemperature than the pure solvent in order for freezing to occur. Web freezing point depression refers to the lowering of the freezing point of solvents upon the addition of solutes. Web valton tyler, freezing point, 1971, etching on paper, 23 inches x 34.5 inches, tyler museum of art. The solution has a lower freezing point than that of the pure solvent. Molar mass by freezing point depression.
What Is the Freezing Point of Water? Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin
The freezing point constant, \(k_f\), for water is \(1.86^\text{o} \text{c/m}\). Here is a look at the temperature of the freezing point, the factors that affect it, and whether it’s identical to the melting point. Do you know the freezing point of water? Web the freezing point depression is the difference in the freezing points of the solution from the pure.
What Is the Freezing Point of Water?
Here is a look at the temperature of the freezing point, the factors that affect it, and whether it’s identical to the melting point. Web freezing point depression refers to the lowering of the freezing point of solvents upon the addition of solutes. Fluid freezing or melting point (k) acetic acid: The more solute dissolved, the greater the effect. Artistic.
Melting Point, Boiling Point and Freezing Point Chemistry YouTube
Web the freezing point of water is 32 degrees fahrenheit, 0 degrees celsius, and 273.15 kelvin. Do you know the freezing point of water? You will determine the molar mass of the unknown solute based on the decrease in the freezing point. Web the van't hoff factor. The freezing point of the solution will be lower than the freezing point.
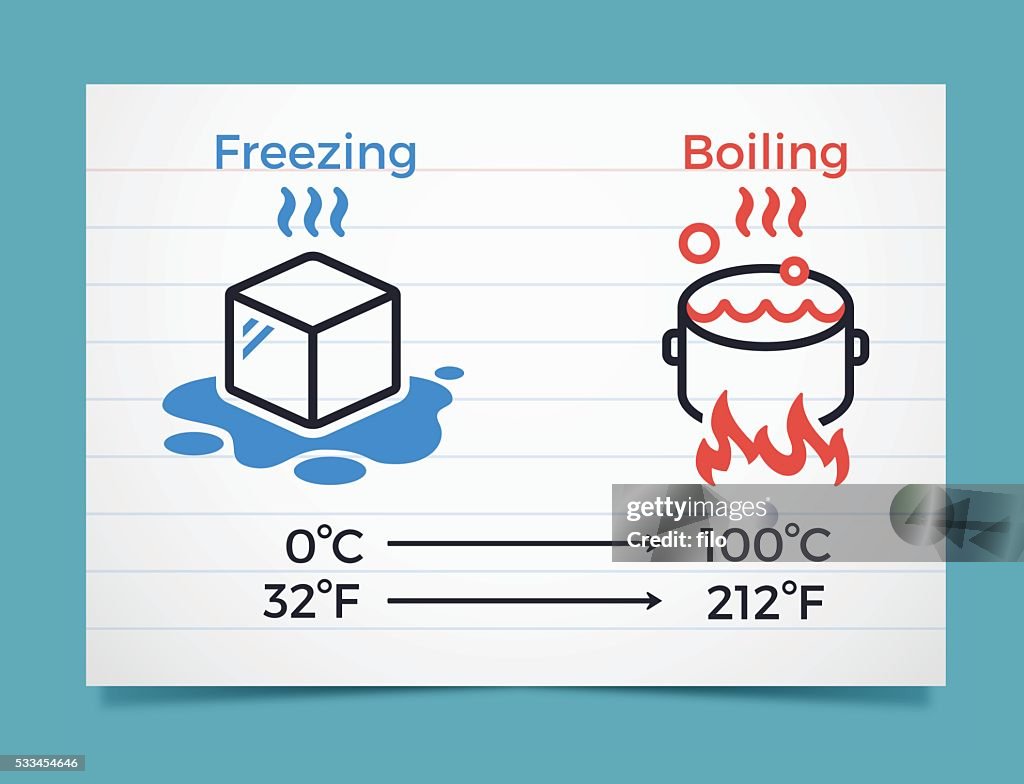
Freezing And Boiling Points In Celsius And Fahrenheit HighRes Vector
Web updated on july 07, 2019. What is the concentration of ethylene glycol in a solution of water, in molality, if the freezing point dropped by \(2.64^\text{o} \text{c}\)? Molar mass by freezing point depression. The freezing points of solutions are all lower than that of the pure solvent and is. The solution has a lower freezing point than that of.
Boiling and Evaporation, Freezing and Melting Points of Water Stock
Molar mass by freezing point depression. This is the colligative property called freezing point depression. An equation has been developed for this behavior. The freezing points of solutions are all lower than that of the pure solvent and is. The freezing point of a solution is less than the freezing point of the pure solvent.
Freezing Point On Phase Diagram
Online calculator, figures and tables with melting points of ice to water at pressures ranging from 0 to 29000 psia (0 to 2000 bara). The freezing point of the solution will be lower than the freezing point. On the graph, the freezing point depression is represented by δtf. The freezing point of a solution is less than the freezing point.
Freezing Point Depression Setup
Web the main component in antifreeze is ethylene glycol, \(\ce{c_2h_4(oh)_2}\). The vapor pressure of a solution (blue) is lower than the vapor pressure of a pure solvent (pink). The freezing point of the solution will be lower than the freezing point. Tyler museum of art’s permanent collection. Web the addition of one mole (molecular weight in grams) of any nonionic.
PPT Freezing/Melting and Boiling Points PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web the freezing point of water is 32 degrees fahrenheit, 0 degrees celsius, and 273.15 kelvin. Web the boiling point elevation (\(δt_b\)) and freezing point depression (\(δt_f\)) of a solution are defined as the differences between the boiling and freezing points, respectively, of the solution and the pure solvent. This means that a solution must be cooled to a lowertemperature.
[DIAGRAM] How To Find The Freezing Point On A Phase Diagram MYDIAGRAM
The freezing point of the solution will be lower than the freezing point. What is freezing point depression? Δt = i k f m. The experiment to be performed is divided into three sections: Web freezing point depression is a colligative property observed in solutions that results from the introduction of solute molecules to a solvent.
Water Freezing Point Definition, Factors Affecting It & Supercooled
Temperature given as °c, °f, k and °r. In this experiment you will determine the molar mass of an unknown solute by measuring the freezing point depression of a solution of this solute in a solvent. ∆tf = kf · m eq 1. An equation has been developed for this behavior. In this experiment, you will determine the freezing point.
In Part 1, The Fp Of The Pure Solvent, Cyclohexane, Is Determined By Constructing And/Or Observing A Cooling Curve.
Temperature given as °c, °f, k and °r. A sample vapor pressure diagram for a pure solvent and its solution is shown below. Web the freezing point of water is 32 degrees fahrenheit, 0 degrees celsius, and 273.15 kelvin. The decrease in freezing point, ∆tf (freezing point depression) for a near ideal solution can be described by the equation:
This Is The Colligative Property Called Freezing Point Depression.
Web a solution will solidfy (freeze) at a lower temperature than the pure solvent. What is freezing point depression? Is the freezing point the same as the melting point? 62.2 g / 92.1402 g/mol = 0.675058 mol δt = i k f m.
The Experiment To Be Performed Is Divided Into Three Sections:
The freezing point of a solution is less than the freezing point of the pure solvent. Web the van't hoff factor. Web the addition of one mole (molecular weight in grams) of any nonionic (does not form ions) solute to 1,000 grams of water lowers the freezing point of the water by 1.885 °c, and this has been used as an accurate method for determining molecular weights. Web the main component in antifreeze is ethylene glycol, \(\ce{c_2h_4(oh)_2}\).
Molal Freezing Point Depression Constant And Van't Hoff Factor.
Web the freezing point depression is the difference in the freezing points of the solution from the pure solvent. The freezing point constant, \(k_f\), for water is \(1.86^\text{o} \text{c/m}\). Using omni's freezing point depression calculator, you can estimate the change in the freezing point temperature of a solution compared to the pure solvent. Web freezing point depression is a colligative property observed in solutions that results from the introduction of solute molecules to a solvent.

/the-freezing-point-of-water-609418_FINAL-01f50f5f4f7d4a39854bebcc59df1aa4.gif)





![[DIAGRAM] How To Find The Freezing Point On A Phase Diagram MYDIAGRAM](http://image1.slideserve.com/2158502/freezing-and-boiling-point-graph-aka-phase-change-diagram-or-heating-cooling-curve-n.jpg)
